Animals
Curious Creatures: Animals That Start with C

Did you realize that there are many captivating animals that begin with the letter C? From formidable predators to aquatic-loving creatures, the animal realm constantly impresses. Whether you’re an animal lover or just interested in the world of nature, delving into the wide variety of animals that start with C will surely spark your curiosity.
Key Takeaways:
- Animals that start with C include caimans, camels, caracals, cardinals, caribou, and more.
- Caimans are powerful reptilian predators found in central and south America.
- Camels are remarkable desert-adapted animals known as the “ships of the desert.”
- Chameleons are masters of color change and camouflage.
- Cardinals are vibrant songbirds with striking plumage.
- Caribou are majestic arctic deer famous for their annual migrations.
- Explore the fascinating world of animals that start with C to discover more about their unique characteristics and natural habitats.
Caiman: A Powerful Predator of Central and South America
When it comes to formidable predators in Central and South America, few creatures can match the caiman. These semi-aquatic reptiles, closely related to alligators and crocodiles, inhabit various aquatic environments, including rivers, swamps, and coastal areas.
The caiman plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling the populations of other species. As a top predator, it helps regulate the numbers of prey animals such as fish, birds, and small mammals. By doing so, caimans contribute to the stability of their ecosystems.
One notable behavior of caimans is their burrowing activity. They create essential refuges for themselves and other animals during times of drought or environmental stress. These underground shelters help provide protection and enable various species to survive challenging conditions.
The Power and Adaptations of the Caiman
The caiman is equipped with powerful jaws lined with sharp teeth, allowing it to capture and consume a wide range of prey. Its muscular body and strong limbs enable swift movement both on land and in the water, making the caiman a highly efficient and agile hunter.
With their incredible adaptability, caimans have successfully colonized diverse habitats within Central and South America. From the murky depths of rivers to the dense vegetation of swamps, they have developed the skills to thrive in various environments.
“Caimans are formidable predators that have evolved to dominate the waters of Central and South America. Their ability to control other species’ populations and create vital refuges showcases their importance in maintaining the ecological balance of their habitats.”
To better understand the unique characteristics and significance of the caiman, let’s take a closer look at some key features in the table below:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | Caimans vary in size depending on the species, ranging from around 4 to 13 feet in length. |
| Habitat | They inhabit a range of aquatic environments, including rivers, swamps, and coastal areas. |
| Diet | Caimans are opportunistic predators and feed on fish, birds, mammals, and even smaller reptiles. |
| Behavior | They are primarily active during the night, and their nesting behavior and burrowing play important roles in maintaining ecosystem balance. |
| Conservation Status | Several species of caimans are listed as either threatened or vulnerable due to habitat loss and hunting. |
As fascinating as they are, caimans remain an integral part of Central and South American ecosystems. By understanding and appreciating these powerful reptiles, we can work towards their conservation and the preservation of their natural habitats.
Caiman Lizard: A Semi-Aquatic Reptile with Stunning Scales
The caiman lizard is a remarkable semi-aquatic reptile that calls the flooded forests and slow-moving rivers of South America its home. With its impressive scales resembling the pattern of a caiman hide, this lizard is truly a sight to behold.
Known for their size and striking appearance, caiman lizards are captivating creatures. They have bold-colored scales that immediately catch the eye. These scales not only serve as an aesthetic feature but also provide protection and insulation against their watery habitats.
What sets the caiman lizard apart is its swimming prowess. These reptiles are excellent swimmers, effortlessly gliding through their aquatic surroundings. Their strong jaws and specialized teeth are adaptations for their diet, which mainly consists of snails and clams. With their powerful jaws, they can crush through the tough shells of their prey with ease.
While many lizards tend to be solitary and territorial, caiman lizards display a remarkably calm demeanor and can tolerate the presence of other individuals. This unique social behavior sets them apart from their reptilian counterparts. They are often found basking in the sun alongside their companions, creating a serene and peaceful sight.
Impressive Characteristics of the Caiman Lizard
- Large size and stunning scales that resemble a caiman’s hide
- Excellent swimming abilities and adaptability to aquatic environments
- Strong jaws and specialized teeth for crushing prey
- Uncommon tolerance of the presence of other lizards
Discovering the caiman lizard in its natural habitat is truly an awe-inspiring experience. Their unique combination of size, impressive scales, and remarkable behaviors make them a fascinating addition to the diverse world of reptiles.
| Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Caiman crocodilus |
| Size | Reaching up to 4-5 feet in length |
| Habitat | Flooded forests and slow-moving rivers of South America |
| Diet | Primarily snails and clams |
| Behavior | Social and tolerant of other individuals |
Camel: The Desert Adapted “Ship of the Desert”
Camels, also known as “ships of the desert,” are large hoofed animals primarily found in the hot deserts of Northern Africa and the Middle East. These remarkable desert inhabitants have unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in the harshest arid conditions.
One of the most distinctive features of camels is their humps, which store fat for energy reserves. Contrary to popular belief, the humps do not contain water but provide sustenance during periods of food scarcity. These adaptable creatures can survive for days or even weeks without water, making them well-suited for the desert environment.
In addition to their humps, camels have other remarkable adaptations that help them withstand the challenges of the desert. They possess broad, tough feet that distribute their weight and prevent them from sinking into the loose sand. Camels also have long, powerful legs that allow them to traverse vast stretches of arid terrain with ease.
Another essential adaptation for camels is their ability to protect themselves from desert sandstorms. They have long eyelashes and bushy eyebrows that shield their eyes from both the glaring desert sun and the blowing sand. Additionally, camels have closable nostrils to prevent sand from entering their respiratory system, ensuring their survival in the most extreme weather conditions.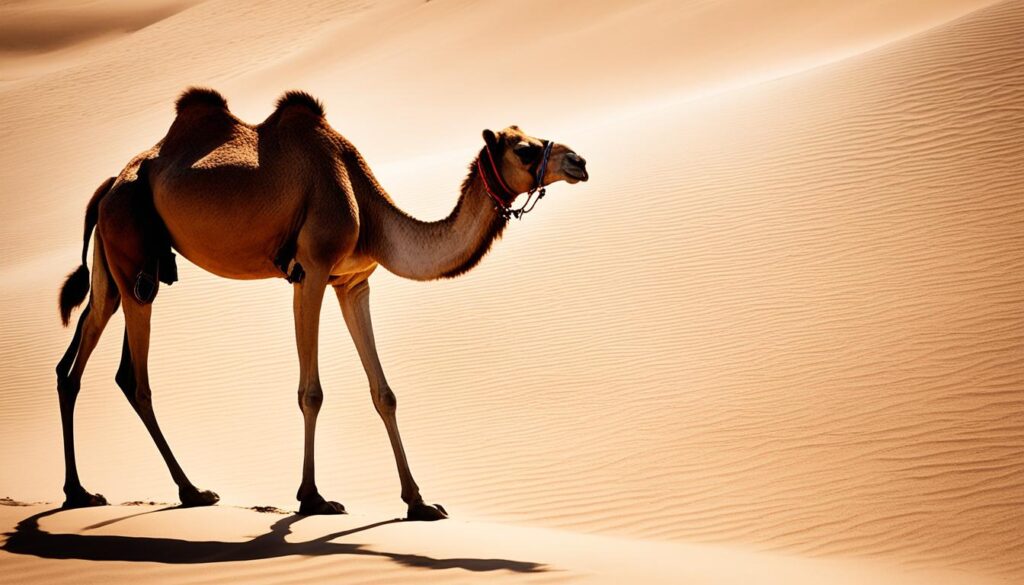
“Camels, with their remarkable adaptations, have become a symbol of resilience in the harsh desert environment. They are uniquely built to survive and thrive where other creatures struggle.”
The Strength of Camels
The strength and endurance of camels are legendary. These mighty creatures have been domesticated for thousands of years, serving as invaluable companions for trade and transport in desert regions throughout history. The ability of camels to carry heavy loads for long distances without tiring has made them instrumental in facilitating commerce and cultural exchanges across vast desert landscapes.
A Comparison of Different Camel Species
| Species | Location | Distinctive Features |
|---|---|---|
| Dromedary Camel | Northern Africa, Arabian Peninsula | Single hump, long legs, adapted to extreme heat |
| Bactrian Camel | Central Asia, Mongolia | Two humps, thick shaggy coat for insulation |
Camels are truly remarkable desert animals. Their ability to thrive in extreme conditions and transport heavy loads has earned them the nickname “ships of the desert.” Whether you encounter a dromedary camel in the sand dunes of the Sahara or a Bactrian camel in the rugged mountains of Central Asia, these magnificent creatures exemplify resilience and adaptability in the face of adversity.
Camel Spider: Arachnid with a Fearsome Reputation
When it comes to desert-dwelling creatures, the camel spider, also known as the wind scorpion or sun spider, is often met with fascination and fear. Contrary to its name, the camel spider is not actually a spider but rather an arachnid belonging to the order Solifugae. These fascinating creatures can be found in regions with dry climates, including the deserts of the Middle East, Mexico, and the southwestern United States.
The camel spider’s appearance alone is enough to instill a sense of trepidation. With their sizable jaws and long hairy legs, these arachnids can often be mistaken for venomous spiders. However, camel spiders do not possess venom glands or silk-producing capabilities like true spiders. Despite their fearsome appearance, camel spiders are not typically aggressive towards humans and will typically avoid confrontation if given the chance.
One of the camel spider’s most remarkable features is its incredible speed. These arachnids are fast-moving creatures, capable of achieving running speeds of up to 10 miles per hour to navigate their sandy desert habitats. They are primarily nocturnal, preferring to hunt and scavenge under the cover of darkness. This behavior allows them to avoid the scorching heat of the day and unfavorable daytime conditions.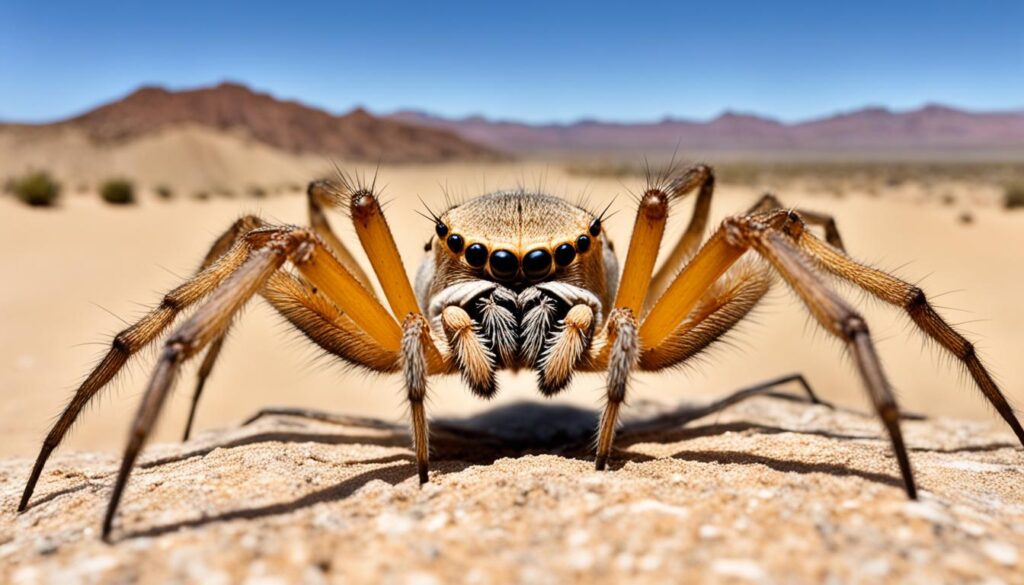
While it is true that camel spiders have been associated with certain urban legends and misconceptions, such as their ability to eat the insides of camels, it’s important to separate fact from fiction. Camel spiders are not a threat to humans or large animals, as their diet primarily consists of insects, small arthropods, and occasionally small reptiles or rodents. These arachnids play a valuable role in desert ecosystems by helping to control insect populations.
In summary, the camel spider is a fascinating and unique arachnid that has captured the imagination of many. While its appearance and reputation may be intimidating, it is essential to separate fact from myth when it comes to understanding these curious creatures. With their incredible speed and adaptation to desert environments, camel spiders continue to thrive in arid regions across the globe.
Capybara: The World’s Largest Rodent
The capybara, scientifically known as Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, holds the impressive title of being the largest rodent in the world. These fascinating creatures are native to South America and are characterized by their semi-aquatic lifestyle, making them unique among other rodents.
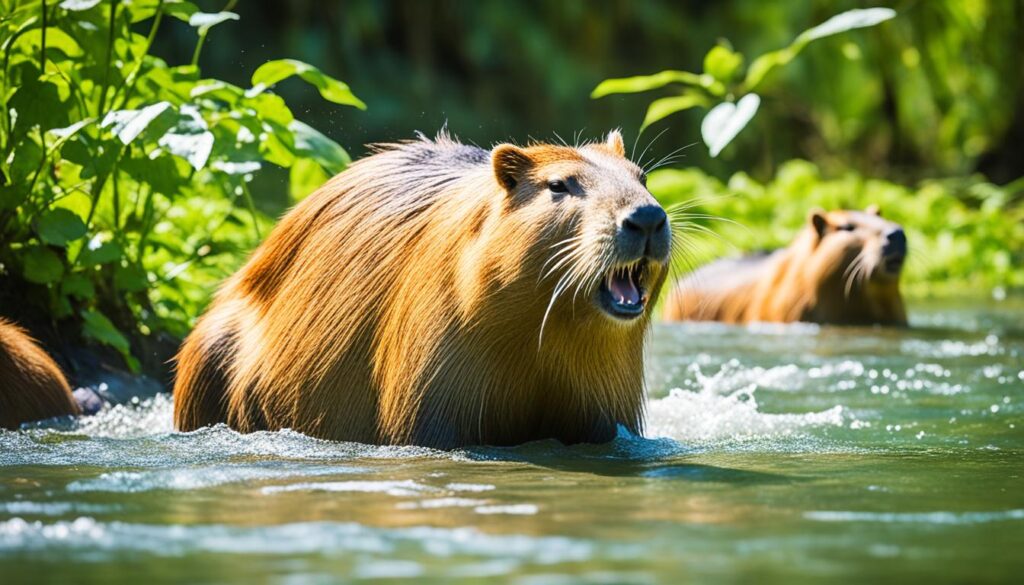

Capybaras are well-adapted to their environments, which include grasslands, forests, and wetlands. With their stocky bodies, webbed feet, and strong legs, they are efficient both on land and in water. Their webbed feet enable them to navigate through water effortlessly, while their strong legs provide them with the agility to move swiftly on land.
One of the distinguishing features of capybaras is their perpetually growing teeth. Their chisel-like incisor teeth are constantly worn down due to their herbivorous diet, which consists of tough aquatic plants, grasses, and fruits. This continuous tooth growth allows them to maintain their ability to eat their preferred vegetation.
Not only are capybaras known for their physical adaptations, but they also possess a friendly and sociable nature. They are often seen interacting harmoniously with other animals, creating interesting dynamics within their habitats. Capybaras have even gained popularity online, with numerous adorable and heartwarming videos showcasing their playful and sociable behavior.
“The capybara’s size, adaptability, and friendly disposition make it a truly captivating creature worth observing and understanding.”
Here are some key characteristics of capybaras:
- Size: Capybaras can reach an impressive weight of up to 150 pounds (68 kilograms) and measure around 3 feet (1 meter) in length.
- Habitat: They inhabit a variety of environments, including grasslands, forests, and wetlands, preferring areas near water bodies.
- Behavior: Capybaras are social animals, often living in small groups. They engage in activities such as grooming each other, huddling together for warmth, and vocalizing with a range of sounds.
- Range: Capybaras are native to South America, with their distribution covering countries such as Brazil, Argentina, Venezuela, and Colombia.
- Conservation Status: While capybaras are not currently considered endangered, their habitat loss and hunting pose threats to their populations in certain regions.
Capybaras are undoubtedly captivating creatures, combining their large size, unique adaptations, and friendly demeanor. Their semi-aquatic lifestyle and sociable nature make them intriguing subjects for wildlife enthusiasts and a true wonder of the animal kingdom.
Cardinal: A Vibrant Songbird with Striking Plumage
Cardinals are stunning songbirds known for their vibrant red plumage in males and subtler gray and reddish-orange hues in females. They are named after the red robes worn by Catholic Cardinals.
These songbirds are skilled singers and their seed-feeding courtship and duets are a common sight and sound in gardens across North America. In addition to their beautiful songs, cardinals are also known for their striking appearance, with their vibrant red feathers standing out against the green foliage.
“The male cardinal is a visual delight with its brilliant crimson plumage. It’s like a tiny flame lighting up the landscape.”
– John James Audubon
Cardinals are cherished by bird enthusiasts and are a welcome visitor to backyard feeders. Their bright colors and melodious songs bring joy and beauty to any garden. In fact, these birds are so beloved that they are the official state bird of seven U.S. states, including North Carolina, Ohio, and Virginia.
| Common Name | Cardinal |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cardinalis cardinalis |
| Family | Cardinalidae |
| Habitat | Woodlands, forests, gardens, and shrubby areas |
| Range | Eastern and central parts of North America |
| Diet | Seeds, fruits, insects |
| Size | 8.3 to 9.1 inches (21 to 23 cm) in length |
| Weight | 1.5 to 1.8 ounces (42 to 52 grams) |
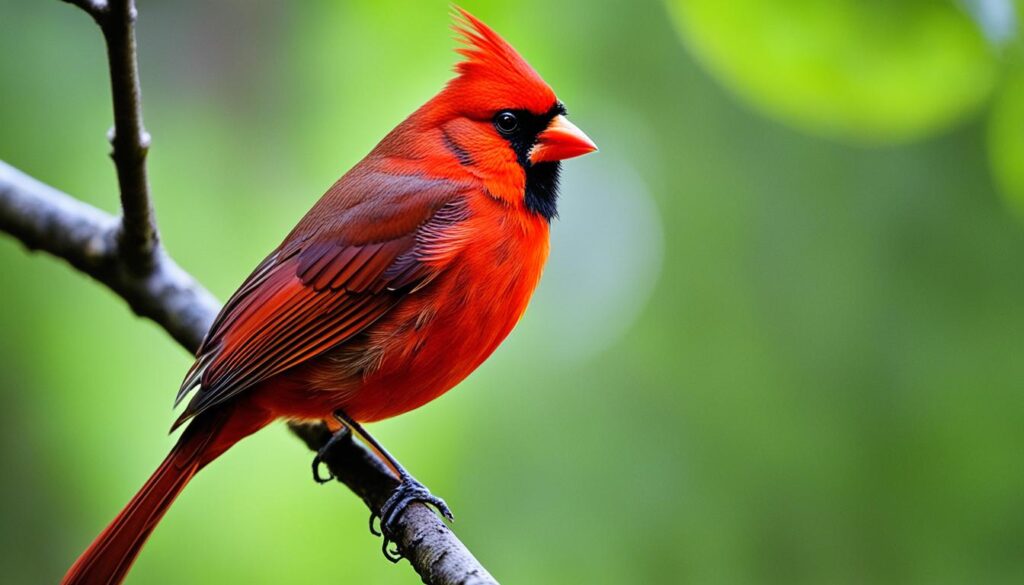

Whether perched on a branch or gracefully hopping on the ground, cardinals are a delightful sight to behold. Their vibrant plumage and melodic songs make them a beloved part of the avian world. The next time you spot a flash of red in your garden, you’ll know that the cardinal has graced you with its presence.
Caribou: Majestic Arctic Deer with Unique Adaptations
Caribou, also known as reindeer in Europe and Asia, are majestic deer species native to Arctic and Subarctic regions. These resilient creatures have evolved a range of adaptations that allow them to thrive in the harsh conditions of their icy habitats.
Camouflaged Coat for Survival
One of the most remarkable features of the caribou is its coat, which changes color with the seasons. In winter, the fur of both males and females turns a snowy white, providing excellent camouflage in the snow-covered landscape. This helps protect them from predators, such as wolves and bears, by allowing them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings. In contrast, during the summer months, their fur transitions to a reddish-brown hue, helping them blend with the tundra vegetation.
Nasal Passages for Cold Weather Adaptation
Caribou have specialized nasal passages that warm the cold air they breathe in. These intricate structures help minimize heat loss and ensure that the caribou’s lungs receive warm oxygen, even in frigid temperatures. By pre-warming the air before it reaches their lungs, caribou can conserve precious energy and maintain their core body temperature.
Impressive Migration Patterns
Caribou are well-known for their extensive migration across vast distances. They undertake epic journeys, covering thousands of miles annually in search of food and breeding grounds. This migration is an incredible testament to their adaptability and survival instincts. Caribou rely on their sharp senses, long legs, and impressive stamina to traverse treacherous landscapes, crossing rivers, navigating through snowstorms, and enduring harsh weather conditions.
During their migration, caribou form large herds, sometimes consisting of thousands of individuals. These herds provide protection against predators and facilitate the sharing of resources. The caribou’s ability to migrate allows them to access areas with abundant vegetation during the summer months and find suitable mating grounds during the breeding season.

Caribou Migration Facts
| Migration Facts | Details |
|---|---|
| Distance Covered | Thousands of miles annually |
| Group Size | Herds of varying sizes, sometimes thousands of individuals |
| Migration Purpose | Find food and breeding grounds |
| Challenges Faced | River crossings, snowstorms, harsh weather conditions |
As the seasons change, so do the landscapes that caribou call home. Their remarkable adaptations and migration patterns showcase their resilience and ability to adapt to the harshest environments.
Chameleon: Masters of Color Change and Camouflage
Chameleons are the true magicians of the animal kingdom, captivating us with their remarkable ability to change colors in a matter of seconds. These incredible reptiles possess specialized cells called chromatophores that contain pigments which, when triggered by different factors, can alter their skin’s hues and patterns.
One of the primary reasons chameleons change colors is for communication. They use their vibrant displays to attract mates, signal aggression, or convey their mood. However, their color-changing skills go beyond mere showmanship. Chameleons are also masters of camouflage, blending seamlessly into their surroundings to evade predators and silently stalk their prey.

Chameleons have a range of colors at their disposal, including greens, browns, blues, and even yellows. They can shift their appearance based on various factors such as temperature, lighting conditions, emotions, and even social interactions. This incredible ability allows them to adapt to different environments, whether it be the lush rainforests or the arid deserts.
The Science Behind Chameleon Color Change
To better understand the science behind this remarkable phenomenon, let’s take a closer look at how chameleons achieve their mesmerizing color change:
- Chromatophores: These specialized cells in the chameleon’s skin contain pigments that give them their distinct colors. By expanding or contracting these cells or adjusting the dispersion of pigments, chameleons can alter their skin’s color and intensity.
- Environmental Factors: Chameleons are highly responsive to their environment. Changes in light, temperature, humidity, and even the colors of nearby objects can influence their appearance. Their color change acts as an adaptation mechanism to help them blend in and protect themselves.
- Emotional Response: Chameleons’ color change is not limited to their surroundings; it is also influenced by their emotions. When they feel threatened or anxious, they may display darker and more intense colors. Conversely, when they are calm or content, they may exhibit lighter or more vibrant shades.
- Social Signaling: Chameleon color change plays a crucial role in communication among individuals. It helps establish hierarchies, signal reproductive status, and convey territorial boundaries. By changing their colors, chameleons can send clear messages to their peers.
Chameleons’ ability to change colors and blend into their environment is truly extraordinary. It showcases the complexity of nature and the remarkable adaptations that animals have developed to survive and thrive.
“The chameleon’s transformative ability to change colors is a testament to the beauty and diversity of the natural world.” – John Mendez, Wildlife Biologist.
| Chameleon Facts | |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Chamaeleonidae |
| Habitat | Rainforests, deserts, mountains, and even some coastal areas |
| Native Regions | Africa, Madagascar, southern Europe, and parts of Asia |
| Size | Chameleons vary in size, ranging from a few inches to almost 2 feet in length |
| Diet | Primarily insects, such as crickets, grasshoppers, and spiders |
| Lifespan | Can live anywhere from 2 to 10 years, depending on the species |
Chesapeake Bay Retriever: A Water-Loving Sporting Dog
The Chesapeake Bay Retriever is a remarkable breed of sporting dog that excels in retrieving waterfowl. With their water-loving nature and impressive skills, they have become valued companions for outdoor enthusiasts and hunters. These intelligent and loyal dogs possess a unique set of qualities that make them the perfect fit for those who enjoy water activities and sporting endeavors.
The Water-Loving Breed
Chesapeake Bay Retrievers are known for their love of water, which stems from their history as working dogs in the Chesapeake Bay area. They have a distinctive water-resistant double coat that keeps them warm and buoyant while swimming. This remarkable coat enables them to brave cold waters and challenging weather conditions, making them excellent partners for all kinds of water-related activities.
Furthermore, Chesapeake Bay Retrievers have webbed feet that enhance their swimming ability and strong muscular bodies that allow them to navigate rough waters with ease. These physical attributes, combined with their natural instinct for retrieving, make them outstanding water companions.
Athleticism and Intelligence
Beyond their water-loving nature, Chesapeake Bay Retrievers are highly athletic dogs with immense physical endurance. They possess the strength and agility required to perform demanding retrieves in challenging terrain. Whether it’s long-distance swimming in open water or maneuvering through dense vegetation, these dogs are built to excel in any situation.
Moreover, Chesapeake Bay Retrievers are known for their remarkable intelligence and problem-solving abilities. They are quick learners and have a strong desire to please their owners, making them highly trainable. These traits, combined with their natural athleticism, make them versatile sporting dogs that can adapt to various environments and tasks.
Loyalty and Friendly Nature
Chesapeake Bay Retrievers are cherished for their unwavering loyalty and friendly nature. They form strong bonds with their families and are excellent companions for both adults and children. These dogs thrive on human interaction and excel in family settings where they can be fully integrated into daily activities.
Despite their strong work ethic, Chesapeake Bay Retrievers also have a playful and gentle side. They are known for their friendly demeanor and love for socializing with other dogs and animals. Their friendly nature and adaptability make them well-suited for multi-pet households and families with an active lifestyle.
The Perfect Water Companion
In conclusion, the Chesapeake Bay Retriever is a water-loving breed that combines athleticism, intelligence, loyalty, and a friendly nature. These dogs thrive in water-related activities and excel in retrieving waterfowl. Whether it’s accompanying hunters on a challenging hunt or joining outdoor enthusiasts on water adventures, the Chesapeake Bay Retriever is the ideal sporting companion for those who treasure the bond between humans and dogs.

| Traits | Description |
|---|---|
| Water-Loving Nature | Chesapeake Bay Retrievers possess a strong affinity for water activities due to their unique water-resistant coat and webbed feet. |
| Athleticism | These dogs showcase impressive physical endurance, strength, and agility, making them capable of performing demanding retrieves in various terrains. |
| Intelligence | Chesapeake Bay Retrievers are highly intelligent and quick learners, allowing them to adapt to different environments and tasks. |
| Loyalty and Friendly Nature | These dogs form strong bonds with their families and are known for their friendly and gentle nature, making them excellent companions for all family members. |
Caiman: Reptiles That Rule the Waters of Central and South America
Caimans, belonging to the Alligatoridae family, are a group of semi-aquatic reptiles native to Central and South America. These powerful creatures share a close kinship with alligators and crocodiles, making them formidable hunters in their respective habitats. With their extraordinary adaptability to aquatic environments, they shape their ecosystems by regulating the populations of other species and creating vital sanctuaries during periods of drought.
Characterized by their muscular bodies, caimans possess sharp teeth that enable them to successfully capture and devour their prey. Their hunting abilities are finely honed, allowing them to strike with precision in the water or on land. Caimans have a significant impact on maintaining the balance of their ecosystems, ensuring the sustainability of the diverse species that coexist with them.
“Caimans play a vital role in their ecosystems by controlling the populations of other species and creating refuges during dry periods.” – Wildlife Expert
Central and South America: A Natural Playground for Caimans
The rich biodiversity of the Central and South American regions provides the ideal habitat for caimans to thrive. These reptiles can be found in various aquatic environments, such as rivers, swamps, and coastal areas, where they serve as apex predators in the intricate food chains. Their ability to adapt to both freshwater and brackish water habitats further expands their ecological influence.
In Central and South America, caimans coexist with a diverse array of species, forming complex ecological relationships. They not only shape the populations of their prey but also indirectly impact the vegetation and the overall health of the ecosystems they inhabit. As both predators and prey, caimans contribute to the intricate ecological balance of the region.
Caiman Species in Central and South America
| Caiman Species | Scientific Name | Habitat | Size | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yacare Caiman | Caiman yacare | Marshes and rivers in South America | Up to 3.5 meters (11.5 feet) | Near Threatened |
| Black Caiman | Melanosuchus niger | Rivers and lakes in the Amazon basin | Up to 5 meters (16.4 feet) | Least Concern |
| Spectacled Caiman | Caiman crocodilus | Various freshwater habitats in Central and South America | Up to 2.5 meters (8.2 feet) | Least Concern |
Despite their formidable presence, caimans are not a threat to humans when left undisturbed. These remarkable reptiles are a testament to the incredible diversity of wildlife found in Central and South America, creating awe-inspiring and enriching experiences for both locals and visitors alike.
Caiman Lizard: Large Lizards with a Love for Water
Originating in South America, caiman lizards are among the largest lizard species and are known for their love of water. Often referred to as water tegus, these semiaquatic reptiles possess strong swimming skills and can be found in rivers and other aquatic habitats.
Despite their large size, caiman lizards are considerably smaller than their reptilian cousins, the caimans. But what they lack in size, they make up for with unique scales that resemble the skin of caimans, adding to their distinct appearance.
“Caiman lizards have evolved to thrive in their semiaquatic habitats. Their love for water is not only a source of survival but also a defining characteristic that sets them apart from other lizard species,” says Dr. Maria Rodriguez, a reptile expert.
These large lizards have adapted to their semiaquatic lifestyle by developing strong limbs and robust tails, ensuring efficient movement both on land and in the water. Their powerful jaws and specialized teeth are designed for crushing prey, particularly snails and clams.
“Caiman lizards’ specialized diet of snails and clams is essential to maintaining the ecological balance in their habitats,” explains Dr. Rodriguez. “By controlling the populations of these organisms, caiman lizards play a vital role in the overall health of their ecosystems.”
Adapting to Life in the Water
With their impressive swimming skills and ability to thrive in aquatic environments, caiman lizards have attracted the attention of researchers and wildlife enthusiasts alike. Their calm demeanor and tolerance for sharing their habitat with other individuals make them fascinating subjects of study.
According to a recent study conducted by Dr. Anna Thompson, a herpetologist, caiman lizards exhibit highly developed social behaviors, often forming small groups during the breeding season. This behavior is unique among large lizard species and provides valuable insights into their social dynamics.
Caiman lizards continue to captivate the interest of experts and nature enthusiasts, drawing attention to the delicate balance of ecosystems and the remarkable adaptations that allow these large lizards to thrive in their semiaquatic habitats.

A Comparison Between Caimans and Caiman Lizards
| Attribute | Caimans | Caiman Lizards |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Large | Considerably smaller than caimans |
| Habitat | Rivers, swamps, coastal areas | Rivers, other aquatic habitats |
| Diet | Wide range of prey | Snails, clams |
| Behavior | Territorial, aggressive | Calm, tolerant |
Camel: Resilient Desert Adapted Animals with Impressive Abilities
Camels are well-known desert animals recognized for their remarkable resilience and ability to survive in harsh desert conditions. These desert dwellers have developed numerous adaptations that enable them to thrive in environments with extreme heat and limited water availability.
One of the most iconic adaptations of camels is their distinctive humps. Contrary to popular belief, these humps do not store water. Instead, they store fat, which serves as an energy reserve during times of scarcity. When food and water are scarce, camels can rely on the fat stored in their humps to sustain them for weeks.
Camels have also evolved specialized features to protect themselves from the harsh desert environment. Their long eyelashes shield their eyes from blowing sand and dust, while their hairy ears act as filters to keep out debris.
Another remarkable adaptation of camels is their closable nostrils. This adaptation allows them to prevent sand particles from entering their respiratory system during sandstorms, ensuring they can continue breathing freely even in the midst of a desert tempest.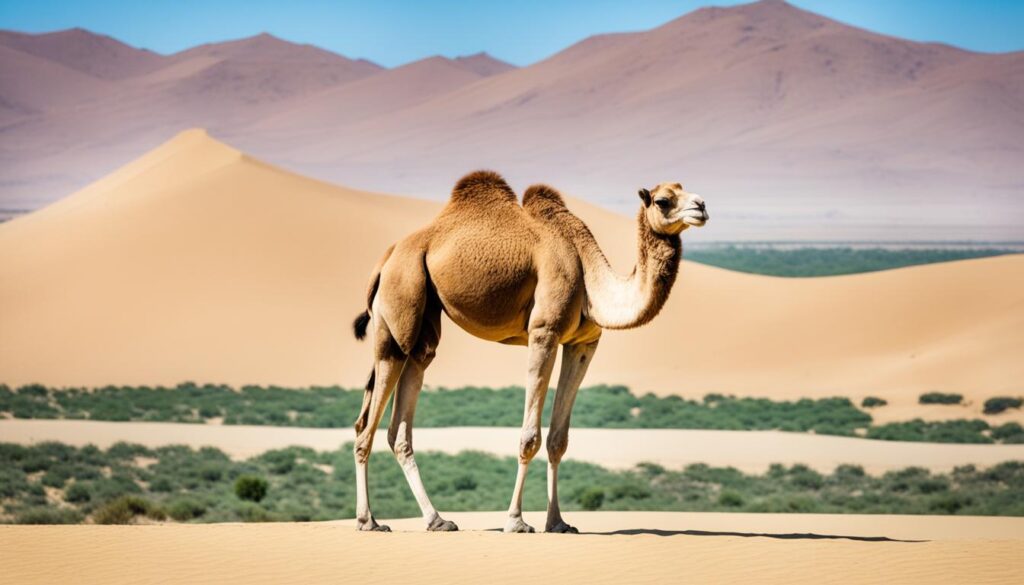
Camels have been instrumental in the trade and transportation of goods in desert regions throughout history. Their ability to carry heavy loads for long distances makes them invaluable companions for desert nomads and traders. Moreover, their endurance and agility make them well-suited for traversing the treacherous terrain of the desert.
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Humps | Store fat for energy reserves during times of scarcity |
| Long Eyelashes | Shield eyes from blowing sand and dust |
| Hairy Ears | Filter out debris from entering the ear canal |
| Closable Nostrils | Protect respiratory system from sand particles during sandstorms |
Did You Know?
“Camels have been domesticated for at least 4,000 years, and they continue to play a crucial role in the lives of people living in desert regions.”
The resilience and adaptability of camels have allowed these magnificent creatures to thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth. Their unique features and abilities make them a symbol of survival and endurance in the desert. Whether trekking across the rolling dunes or providing reliable transportation, camels are truly remarkable creatures that exemplify the power of resilient adaptation.
Camel Spider: Leaping into the Limelight with Misconceptions
Camel spiders, also known as wind scorpions or sun spiders, are arachnids found in desert regions worldwide. Despite their name, they are not true spiders and lack venom and silk glands. Camel spiders are known for their impressive running speed and can move up to 10 miles per hour to avoid overheating in hot desert climates. They are primarily active at night and prefer to hunt in cooler temperatures. Contrary to popular myth, camel spiders do not eat the insides of camels or cause harm to humans.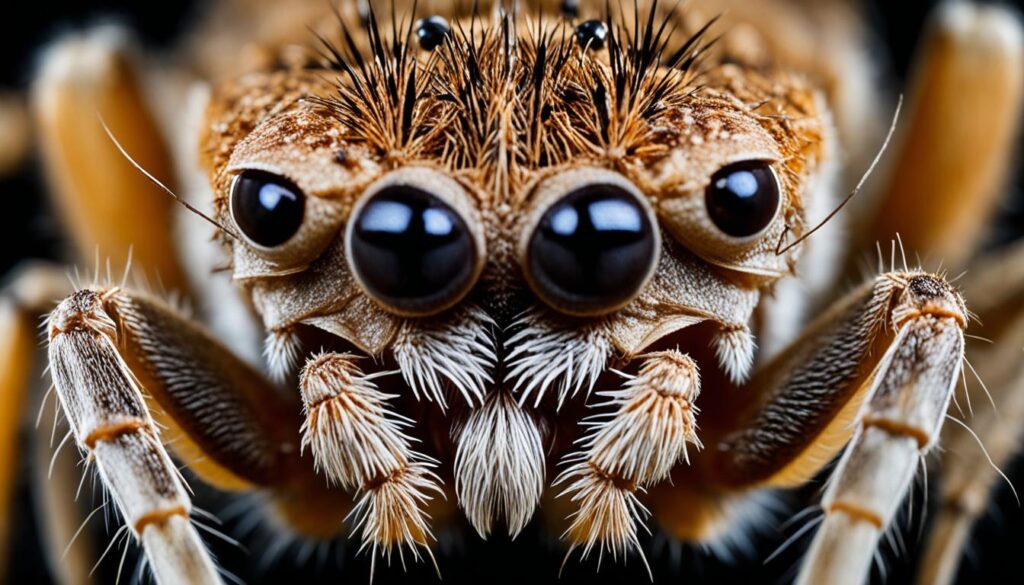
These fascinating arachnids have been subjected to numerous misconceptions throughout history. Their unique appearance and behavior have contributed to various myths and urban legends. One common myth suggests that camel spiders are the size of camels and can run as fast as a car. While they are indeed fast runners, they are relatively small creatures, averaging around 6 inches in length, including their legs.
“Despite their fearsome reputation, camel spiders are more likely to flee from humans than attack. They are harmless to people and play an important role in desert ecosystems.”
Moreover, camel spiders are often misunderstood due to their unusual appearance. With long, segmented bodies, powerful jaws, and robust legs, they can seem intimidating to those unfamiliar with these arachnids. However, it is essential to distinguish between perception and reality. Camel spiders are not venomous, and their bites, while rare, are generally harmless to humans.
Dispelling the Myths
Understanding the truth about camel spiders can help dispel the misconceptions surrounding these fascinating creatures.
- They are not spiders: Despite their name, camel spiders are not true spiders. They belong to the class Arachnida, along with spiders and scorpions, but are not classified as spiders.
- No venom or silk glands: Camel spiders lack venom glands, meaning they cannot inject venom into prey or humans. Additionally, they do not produce silk for web-spinning purposes.
- No harm to humans: While their appearance may be intimidating, camel spiders are not aggressive toward humans and do not actively seek out human interaction. They are more likely to flee when encountered.
It is crucial to approach camel spiders with an open mind and dispel the myths and misconceptions that surround them. Recognizing their important ecological role and unique adaptations can foster a greater appreciation for these intriguing desert-dwelling arachnids.
Conclusion
In this captivating wildlife exploration, we have delved into the enchanting world of animals that start with C. From the powerful caimans of Central and South America to the resilient camels of the desert and the mesmerizing color-changing chameleons, we have encountered a diverse array of curious creatures.
Each animal possesses unique adaptations and traits that enable them to thrive in their respective habitats. The caimans’ formidable bodies and hunting prowess make them rulers of the waters, while camels’ exceptional resilience and desert adaptations have earned them the title of the “ship of the desert.” The chameleons’ remarkable ability to change colors and blend into their surroundings showcases their unparalleled camouflaging skills.
By delving into the lives of these fascinating animals, we gain an appreciation for the wondrous variety and intricacy of the natural world. From the depths of the jingling footsteps of the caribou during its epic migration, to the vibrant plumage of the cardinals as they serenade with their melodious songs, the exploration of animals that start with C has only scratched the surface of nature’s captivating creations.FAQ
What are some animals that start with the letter C?
What is a caiman?
What is a caiman lizard?
Where are camels found?
What are camel spiders?
What is a capybara?
What is special about a cardinal bird?
What are some unique characteristics of caribou?
How do chameleons change colors?
What is unique about the Chesapeake Bay Retriever breed?
What are caimans?
What makes caiman lizards unique?
How do camels survive in the desert?
Do camel spiders pose harm to humans?
What are some interesting facts about capybaras?
What sets cardinals apart from other birds?
How do caribou adapt to life in the Arctic?
How do chameleons change their colors?
What makes the Chesapeake Bay Retriever breed special?
Laura is a versatile writer and editor whose passion for animals shines through in her work. With a keen understanding of language and a love for storytelling, Laura crafts compelling narratives that captivate our audience and inspire action regarding animal welfare. Whether she’s delving into the latest research or sharing heartwarming stories of animal companionship, Laura’s work will leave a lasting impression on all who read it.
Animals
3 Animals Similar to Squirrels
Curious about animals resembling squirrels? Meet chipmunks, marmots, and flying squirrels, each with unique traits that set them apart.

Chipmunks, marmots, and flying squirrels are similar to squirrels. Chipmunks have striped backs and communicate vocally. Marmots are ground-dwellers with bushy tails and hibernate for 8 months. Flying squirrels glide at night with large eyes and a unique membrane. These animals share traits with squirrels, such as agility and adaptability.
Key Takeaways
- Chipmunks share traits with squirrels like agility and varied diet.
- Flying squirrels resemble squirrels in agility and diverse diet.
- Marmots, though different, are diurnal rodents with essential roles in ecosystems.
- All three animals communicate vocally like squirrels for survival.
- Observing these animals in the wild provides insights into behaviors and ecosystem dynamics.
Chipmunks: Small Rodents With Striped Backs
Chipmunks, closely related to squirrels, are small rodents distinguished by the stripes running along their backs. As members of the rodent family, chipmunks exhibit fascinating behaviors that set them apart. These omnivores are active during the daytime, making them a crucial sight in many habitats. Their exceptional climbing abilities allow them to scurry up trees and bushes in search of food, which includes nuts, seeds, fruits, insects, and even small animals.
Communication among chipmunks is crucial for their survival. Through various vocalizations, these small rodents convey messages about potential dangers, food availability, and territorial boundaries. Understanding their intricate language enhances our appreciation for these remarkable creatures.
Next time you spot a chipmunk darting around, take a moment to observe their behaviors and listen to their unique sounds. Chipmunks truly exemplify the beauty of nature's diversity in the animal kingdom.
Marmots: Ground-Dwelling Rodents With Bushy Tails

Marmots, distinguished by their bushy tails, are ground-dwelling rodents that play an essential role in their ecosystems. Belonging to the Sciuridae family, these diurnal creatures are active during the day, using their burrows to live in family groups.
With a weight of up to 11 pounds, marmots have brown fur with white-tipped hair, adapting well to higher altitudes. They hibernate for about 8 months, emerging in spring to forage and reproduce.
In their habitats, marmots influence vegetation dynamics and serve as prey for various predators, contributing significantly to the ecosystem's balance. Observing marmots in the wild can provide insights into their behaviors and interactions with other species, showcasing the importance of these ground-dwelling rodents with their striking bushy tails.
They're fascinating creatures to study due to their unique adaptations and crucial roles within their environments.
Flying Squirrels: Nocturnal Gliding Mammals

Gliding effortlessly through the night, flying squirrels showcase their remarkable ability to navigate the darkness using their unique gliding membrane. These nocturnal mammals are known for their extraordinary gliding skills, allowing them to move gracefully through the air.
With their large, dark eyes providing excellent night vision, flying squirrels can easily maneuver through dimly lit environments like forests where they reside. These omnivorous creatures have a diverse diet, including nuts, seeds, insects, and occasionally bird eggs.
Despite their name, flying squirrels don't truly fly but rather glide by extending their limbs and using the membrane to catch the air, enabling them to travel between trees effortlessly. Their gliding ability sets them apart from other squirrel species, making them fascinating creatures to observe in their natural habitat.
With their adaptation to the night and unique way of moving, flying squirrels offer a glimpse into the innovative ways animals have evolved to thrive in their environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Animal Is Similar to Squirrel?
When considering animals similar to squirrels, one might think of the agile chipmunk. This ground-dwelling rodent, like squirrels, boasts bushy tails and climbing prowess. Chipmunks play an essential role in seed dispersal and ecosystem balance, mirroring squirrels' impact.
What Is the Closest Pet to a Squirrel?
The closest pet to a squirrel is a chipmunk. These adorable rodents require care similar to squirrels. Providing a spacious enclosure with climbing opportunities and a diet of nuts, seeds, fruits, and insects guarantees a fulfilling experience.
What Are Squirrels Most Closely Related To?
Squirrels are most closely related to chipmunks, marmots, and prairie dogs. These species within the Sciuridae family share common traits like bushy tails and diurnal habits. Exploring these relationships sheds light on their evolution and adaptations.
What Animals Are in the Same Family as Squirrels?
In the same family as squirrels are chipmunks, prairie dogs, and other fascinating creatures. This diverse Sciuridae family showcases various species with shared evolutionary history. Their roles in ecosystems worldwide highlight their importance for biodiversity and habitat health.
Are There Any Animals Similar to Squirrels That Resemble Possums?
Yes, there are some fascinating species of possum lookalikes that bear a striking resemblance to squirrels. The sugar glider, for example, is a small arboreal possum that shares many physical characteristics with squirrels, such as their bushy tails and similar feeding habits.
Conclusion
Just like the diverse array of animals in the forest, there are many creatures similar to squirrels that share similar characteristics and behaviors.
Chipmunks scurry around with their striped backs, marmots dig into the ground with their bushy tails, and flying squirrels glide through the night sky.
These creatures may be different in appearance, but they all share a common bond with their squirrel cousins in the intricate tapestry of the animal kingdom.
Dana is our Lead Content Writer, bringing a wealth of knowledge and expertise to our team. With a background deeply rooted in animal studies and a profound love for all creatures, Dana is dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that resonates with our audience. With Dana at the helm, you can trust that our content is accurate and engaging, catering to the diverse interests of animal enthusiasts everywhere.
Chickens
Can Chickens Eat Rhubarb? Safe Feeding Tips

Did you know that chickens are able to consume rhubarb stalks, but they should not eat the leaves?
Chickens are known to enjoy a wide variety of foods, but when it comes to rhubarb, there are some important considerations to keep in mind. While the stalks of rhubarb can provide chickens with valuable vitamins and minerals, the leaves contain oxalic acid, which can be harmful to their health. In this article, we will explore the safe ways to feed chickens rhubarb and the potential risks it may pose.
Key Takeaways:
- Chickens can eat rhubarb stalks in moderation, but the leaves should be avoided due to their oxalic acid content.
- Feeding chickens rhubarb in small amounts can provide them with essential vitamins and minerals.
- Too much sugar in rhubarb, such as in pies or crumbles, can be harmful to chickens.
- It’s crucial to be cautious and only feed chickens rhubarb stalks in tiny amounts fed occasionally.
- Follow the 90/10 feeding rule to ensure a balanced diet for chickens, with rhubarb treats in small quantities.
Can Chickens Eat Rhubarb Stalks?
Chickens can enjoy the deliciousness of rhubarb stalks, but it’s important to feed them in moderation. Rhubarb stalks are a safe and healthy snack for chickens, providing them with essential vitamins and minerals like Vitamin A and Vitamin C, as well as dietary fiber.
To make it easier for your feathered friends to enjoy this treat, cut the rhubarb stalks into bite-size pieces. You can scatter the pieces around their feeding area or mix them in with their regular feed for added variety. Just remember, small amounts are the key to ensuring their well-being.
Rhubarb stalks offer a refreshing crunch and tangy flavor that chickens find irresistible. However, it’s essential to remember that while the stalks are safe for consumption, other parts of the rhubarb plant, such as the leaves, flowers, and seeds, contain oxalic acid and should be strictly avoided as they can be toxic to your chickens.
Providing your chickens with rhubarb stalks as an occasional treat can add nutritional variety to their diet, keeping them happy and healthy. Just be sure to practice moderation and always prioritize their safety.
Health Benefits of Rhubarb Stalks for Chickens
Rhubarb stalks are packed with essential nutrients that can contribute to your chickens’ overall well-being. Here’s a quick rundown of the vitamins and minerals they can gain from enjoying this tasty treat:
| Nutrients | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Supports healthy vision, immune function, and cellular growth |
| Vitamin C | Acts as an antioxidant, promotes growth, and boosts the immune system |
| Dietary Fiber | Aids in digestion and promotes a healthy digestive system |
Why Can’t Chickens Eat Rhubarb Leaves?
Chickens cannot eat rhubarb leaves due to the high content of oxalic acid. Oxalic acid is a naturally occurring compound found in many plants, including rhubarb leaves. While rhubarb stalks can be safely consumed by chickens in small amounts, the leaves contain a concentrated amount of oxalic acid, which can be toxic to them.
Oxalic acid can lead to kidney failure and can be fatal for chickens if ingested in large quantities. The oxalic acid in rhubarb leaves binds with calcium in the chicken’s body, forming crystals that can cause damage to their kidneys.
It’s crucial to avoid feeding chickens rhubarb leaves, as well as other parts of the rhubarb plant like flowers and seeds, which also contain oxalic acid. Feeding these parts to chickens can put their health at risk.
Effects of Oxalic Acid on Chickens
“The presence of oxalic acid in rhubarb leaves can have severe consequences for chickens’ health. It’s important to be aware of the potential dangers and take necessary precautions.”
The ingestion of oxalic acid in rhubarb leaves can result in symptoms such as weakness, difficulty breathing, trembling, and decreased appetite in chickens. Over time, the crystals formed by the oxalic acid can lead to kidney damage, which may cause kidney failure and other complications.
Chickens should never have access to rhubarb leaves, and it’s crucial to prevent them from consuming these potentially harmful plant parts.
Comparison of Oxalic Acid Content
| Rhubarb Part | Oxalic Acid Content |
|---|---|
| Rhubarb Stalks | Low |
| Rhubarb Leaves | High |
| Rhubarb Flowers | High |
| Rhubarb Seeds | High |
Comparison of oxalic acid content in different parts of the rhubarb plant.
As shown in the table above, rhubarb leaves, flowers, and seeds contain a significantly higher concentration of oxalic acid compared to rhubarb stalks. It’s important to be cautious and ensure that chickens do not have access to these parts of the rhubarb plant.

What Happens if Chickens Eat Rhubarb?
When chickens consume rhubarb, it can have detrimental effects on their health. The consequences of chickens eating rhubarb can include:
- Diarrhea: Chickens may experience loose stools or increased bowel movements after consuming rhubarb.
- Abdominal Pain: The oxalic acid present in rhubarb can irritate the digestive system, leading to discomfort and abdominal pain in chickens.
- Lethargy: Chickens may become lethargic, displaying decreased activity levels and reduced energy after ingesting rhubarb.
- Abnormal Behaviors: Eating rhubarb can cause chickens to exhibit abnormal behaviors such as decreased appetite, depression, or reduced vocalization.
It is vital to recognize the signs of rhubarb poisoning in chickens and take immediate action to prevent severe illness or even death. If you suspect your chickens have consumed rhubarb and are displaying any of these symptoms, it is best to seek veterinary care as soon as possible.
“Feeding rhubarb to chickens can lead to diarrhea, abdominal pain, lethargy, and abnormal behaviors.”
It is advisable to avoid feeding rhubarb to chickens altogether as a precautionary measure, considering its potential adverse effects. Instead, focus on offering them a balanced diet that consists of safe and nutritionally appropriate foods.
In the table below, you will find a summary of the potential consequences of chickens eating rhubarb:
| Consequences | Description |
|---|---|
| Diarrhea | Loose stools or increased bowel movements |
| Abdominal Pain | Discomfort and pain in the abdominal region |
| Lethargy | Decreased activity levels and reduced energy |
| Abnormal Behaviors | Decreased appetite, depression, or reduced vocalization |
It is crucial to prioritize the well-being of your chickens and make sure to provide them with a diet that is safe and suitable for their nutritional needs. Understanding the potential consequences of feeding rhubarb to chickens can help you make informed decisions and ensure their health and happiness.
How to Treat Rhubarb Poisoning in Chickens?
If your chickens have eaten rhubarb and show signs of poisoning, there are a few home remedies you can try to help alleviate their symptoms and aid in their recovery. Administering a flush can help flush out the toxins from their body and promote healing. Two popular home remedies for rhubarb poisoning in chickens are the Epsom salt flush and the molasses flush.
Epsom Salt Flush
Epsom salt is known for its laxative properties, which can aid in the removal of toxins from the chicken’s system. Here’s how to administer the Epsom salt flush:
- Dissolve 1 tablespoon of Epsom salt in 1 cup of warm water.
- Using a syringe or dropper, gently administer the mixture into the back of the chicken’s throat.
- Ensure the chicken swallows the mixture.
- Repeat the process every 4 to 6 hours, as needed.
Molasses Flush
Molasses acts as a natural laxative and can help flush out toxins from the chicken’s digestive system. Here’s how to administer the molasses flush:
- Mix 1 tablespoon of molasses with 1 cup of warm water.
- Using a syringe or dropper, gently administer the mixture into the back of the chicken’s throat.
- Ensure the chicken swallows the mixture.
- Repeat the process every 4 to 6 hours, as needed.
These home remedies can be effective in treating mild cases of rhubarb poisoning in chickens. However, if the symptoms worsen or persist, it’s important to consult a veterinarian for further guidance and treatment.
It is worth noting that prevention is better than cure when it comes to rhubarb poisoning. It is essential to keep chickens away from rhubarb plants and ensure they have access to a safe and balanced diet. Regularly monitoring their feeding habits and providing appropriate nutrition can help minimize the risk of rhubarb poisoning in chickens.
Nutritional Analysis of Rhubarb for Chickens
When it comes to the nutritional value of rhubarb for chickens, it’s important to understand what this vibrant stalk vegetable provides. Rhubarb stalks contain a variety of essential nutrients that can contribute to the overall health of your chickens. Let’s take a closer look at the vitamins and minerals found in rhubarb that can benefit your feathered friends.
Vitamins in Rhubarb for Chickens
Rhubarb is a good source of several vitamins that are vital for the well-being of chickens. One of the key vitamins found in rhubarb is Vitamin C. This vitamin plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system and promoting overall health. Chickens, just like humans, require Vitamin C to maintain optimal health and combat diseases.
In addition to Vitamin C, rhubarb also contains Vitamin A. This vitamin is essential for maintaining healthy vision, promoting growth and development, and supporting the reproductive system. Vitamin A is crucial for chickens’ overall well-being and can contribute to their overall vitality.
Minerals in Rhubarb for Chickens
Rhubarb is not just a source of vitamins but also provides vital minerals that can benefit chickens. One of these minerals is calcium. Calcium is essential for maintaining strong bones and eggshell production in hens. Including rhubarb in your chickens’ diet can help fulfill their calcium requirements and contribute to their overall skeletal health.
Another important mineral found in rhubarb is iron. Iron is necessary for the production of healthy red blood cells, which help transport oxygen throughout the body. By incorporating rhubarb into their diet, you can help ensure your chickens receive adequate iron levels to support their overall well-being.
Furthermore, rhubarb contains potassium, a mineral that plays a vital role in regulating fluid balance, muscle function, and nerve signals. Including rhubarb as a part of your chickens’ diet can help maintain these essential functions and support their overall health and vitality.
It’s important to note that while rhubarb can provide certain vitamins and minerals beneficial to chickens, it should be fed in moderation. Rhubarb stalks also contain a relatively high sugar content, which can be harmful if consumed in excess. Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure that rhubarb is offered as a treat rather than a staple part of their diet.
Overall, rhubarb can be a nutritious addition to your chickens’ diet when fed responsibly and in appropriate amounts. Its vitamin and mineral content, including Vitamin C, Vitamin A, calcium, iron, and potassium, can contribute to their overall health and well-being. Remember to always provide rhubarb in moderation and prioritize a balanced diet for your feathered friends.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g of Raw Rhubarb Stalks |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 13.8 mg |
| Vitamin A | 102 IU |
| Calcium | 86 mg |
| Iron | 0.22 mg |
| Potassium | 288 mg |

- USDA FoodData Central: Rhubarb, raw. (2021, May 31).
- Raising Happy Chickens: Understanding and Caring for Chickens’ Nutritional Needs.
Best Plants to Feed Chickens
Chickens love to explore and peck at a variety of plants. While their main diet should consist of complete feeds, offering them safe plants as treats can be enjoyable for them. Here are some plants that chickens can eat:
- Lettuce
- Beets
- Broccoli
- Carrots
- Kale
- Mint
- Parsley
These plants provide additional nutrients and flavors to their diet. Chickens can enjoy small quantities of these plants as an occasional snack. However, it’s important to note that while these plants are safe, they should still be offered in moderation. Too much of any plant can upset their digestive system.
It’s crucial to avoid feeding chickens toxic plants that can harm their health. Some plants to avoid feeding chickens include:
- Onions
- Raw beans
These plants can be toxic to chickens and should be kept away from their reach. Always prioritize their safety and well-being when offering plants as treats.
Note: Keep in mind that the plant suggestions provided here are not an exhaustive list. It’s always important to do thorough research and consult with poultry experts to ensure the plants you offer to your chickens are safe and appropriate for their consumption.
Worst Plants to Avoid Feeding Chickens
When it comes to feeding chickens, it’s important to be aware of the plants that can be toxic and dangerous to them. Certain plants can cause various health issues and even be fatal if consumed by chickens. Here are some of the worst plants that you should avoid feeding your chickens:
- Onions: Onions contain compounds that can lead to anemia and liver problems in chickens. It’s best to keep onions away from their diet to ensure their well-being.
- Raw beans: Raw beans contain a compound called hemagglutinin, which can be harmful to chickens. It can interfere with digestion and nutrient absorption, causing digestive issues and other health problems.
- Avocados (except for the flesh): While avocados themselves are not toxic to chickens, the leaves, bark, and pit contain a substance called persin, which can be harmful. It’s important to only offer chickens the flesh of avocados and avoid feeding them any other parts of the plant.
- Moldy or rotten foods: Moldy or rotten foods can contain harmful molds and bacteria that can cause digestive issues and other health problems in chickens. It’s important to ensure that the food you offer your chickens is fresh and free from any signs of spoilage.
- Very salty foods: Excessive salt can be detrimental to a chicken’s health, leading to electrolyte imbalances and dehydration. It’s best to avoid feeding them very salty foods to maintain their well-being.
By being aware of these plants and avoiding them in your chickens’ diet, you can help keep them safe and healthy. It’s always a good idea to research and consult with experts to ensure that you are providing the best diet for your feathered friends.
| Plants | Potential Health Issues |
|---|---|
| Onions | Anemia, liver problems |
| Raw beans | Digestive issues, nutrient absorption problems |
| Avocados (except for the flesh) | Persin toxicity |
| Moldy or rotten foods | Digestive issues, bacterial infections |
| Very salty foods | Electrolyte imbalances, dehydration |
How to Keep Chickens Safe from Rhubarb Plants
To protect your chickens from rhubarb plants, it’s important to take certain precautions and create a safe environment. Follow these tips to ensure the well-being of your feathered friends:
1. Gate off Areas with Rhubarb Plants
Start by securing the areas where rhubarb plants are growing. Install sturdy fencing or use chicken wire to create a barrier around the plants. This will prevent chickens from accessing the rhubarb and potentially ingesting the harmful parts.
2. Restrict Access to Gardens
In addition to gating off the rhubarb plants, restrict your chickens’ access to gardens where rhubarb may be present. Utilize fences, netting, or other forms of physical barriers to keep them out of these areas. This will prevent accidental ingestion or nibbling on rhubarb stalks.
3. Separate or Remove Toxic Plants
Along with rhubarb, there may be other toxic plants in your garden that can harm chickens. Take the time to identify and remove or separate these plants from the areas where your chickens roam. This precaution will further minimize the risk of exposure to harmful vegetation.
4. Create a Chicken-Friendly Garden
Consider creating a dedicated chicken-friendly garden where your chickens can freely explore and forage. Plant safe and nutritious vegetation, such as lettuces, beets, kale, and herbs like mint and parsley. This provides an alternative and safe environment for your chickens to enjoy without the risk of encountering harmful plants.
5. Avoid Planting Rhubarb
If you have chickens or other pets and animals, it’s best to avoid planting rhubarb altogether. By eliminating rhubarb from your garden, you eliminate the potential danger it poses to your chickens. Instead, focus on cultivating plants that are safe and beneficial for your feathered companions.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure the safety of your chickens and protect them from the potential hazards of rhubarb plants. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to keeping your chickens healthy and happy!
| Harmful Plants | Safe Plants |
|---|---|
| Rhubarb leaves | Lettuce |
| Onions | Beets |
| Raw beans | Kale |
| Avocado (except for flesh) | Mint |
| Moldy or rotten foods | Parsley |
| Very salty foods |
90/10 Feeding Rule for Chickens
When it comes to feeding chickens, maintaining a balanced diet is essential for their health and well-being. The 90/10 feeding rule provides a guideline on how to achieve this balance. According to this rule, 90% of a chicken’s diet should consist of complete feed, while the remaining 10% can be treats and other food sources.
Complete feeds are specially formulated to provide chickens with all the necessary nutrients they need to thrive. These feeds typically contain a balanced combination of grains, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, ensuring that your feathered friends receive a well-rounded diet. By offering complete feed as the main component of their diet, you are providing a solid foundation for their nutritional needs.
On the other hand, the remaining 10% of a chicken’s diet can be allocated to treats and supplementary food sources. Treats can come in the form of kitchen scraps, vegetables, fruits, or even insects that your chickens can forage for. However, it’s important to note that treats should be given in moderation to avoid overfeeding and upsetting the balance of their diet.
Following the 90/10 rule ensures that chickens receive the necessary nutrients from their complete feed while still enjoying the occasional treat. It’s important to resist the temptation to go overboard with treats, as excessive indulgence can lead to dietary imbalances and unbalanced growth in chickens.
Remember, a balanced diet is vital for a chicken’s overall health, ensuring they receive the right nutrients to support their immune system, feather quality, and egg production.
By adhering to the 90/10 feeding rule, you can be confident that your chickens are receiving a nutritionally balanced diet. Not only does this promote their well-being, but it also contributes to their optimal growth and development.
The Benefits of the 90/10 Feeding Rule:
- Provides a balanced diet with essential nutrients
- Promotes healthy growth and development
- Reduces the risk of dietary imbalances
- Maintains optimal egg production and feather quality
- Prevents overfeeding and obesity
Foods That Increase Chicken’s Appetite
If your chickens are experiencing a decreased appetite, it’s important to find ways to stimulate their appetite and encourage them to eat. By offering certain foods known to increase a chicken’s appetite, you can help them regain their strength and ensure they are getting the necessary nutrition. Here are some appetite-stimulating foods for chickens:
- Hard-boiled eggs: Eggs are a rich source of protein and can be a highly enticing treat for chickens. Chop the eggs into small pieces and offer them as a snack.
- Cooked vegetables: Vegetables like carrots, peas, sweet potatoes, and green beans can be cooked and mashed or chopped to create a soft and easy-to-eat meal for chickens.
- Cooked meat: Leftover cooked meat, such as chicken or turkey, can be shredded and added to their regular feed or offered as a separate treat. Make sure to remove any bones before feeding.
- Herbs: Fresh herbs like parsley, basil, and oregano can help enhance the flavor of their feed and entice chickens to eat. Chop the herbs finely and sprinkle them over their food.
- Electrolytes: Electrolyte solutions designed for chickens can help replenish lost nutrients and stimulate their appetite. Follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer.
- Supplements: There are specific supplements available in the market that can boost a chicken’s appetite. Consult with a veterinarian or poultry specialist to determine the best supplement for your chickens.
Remember, it’s important to introduce these appetite-stimulating foods gradually and in moderation. Observe your chickens’ response and adjust the quantities accordingly. Offering a varied and balanced diet with these appetite-boosting foods can help improve your chickens’ appetite and overall well-being.
Nutritional Analysis of Appetite-Stimulating Foods
Here is a nutritional analysis of the appetite-stimulating foods mentioned above:
| Food | Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Hard-boiled eggs | Protein, vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin B12 |
| Cooked vegetables | Fiber, vitamins (A, C, K), potassium |
| Cooked meat | Protein, iron, zinc, vitamin B12 |
| Herbs | Antioxidants, vitamins, minerals |
| Electrolytes | Essential minerals (sodium, potassium, magnesium) |
| Supplements | Varies depending on the supplement |
Offering these foods to your chickens can provide nutritional benefits and help increase their appetite. However, it’s important to remember that a balanced diet is crucial for their overall health. Consult with a veterinarian or poultry nutritionist to ensure you are providing a well-rounded diet that meets their nutritional needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is safe for chickens to eat rhubarb stalks in moderation. However, they should avoid consuming the leaves, flowers, and seeds of the rhubarb plant due to their high oxalic acid content. While rhubarb stalks can provide chickens with beneficial vitamins and minerals, it is important to feed them in small amounts as part of a balanced diet.
Adhering to the 90/10 feeding rule is crucial for maintaining the health of chickens. This rule suggests that 90% of their diet should consist of complete feeds, while the remaining 10% can include treats and supplemental foods like rhubarb stalks. By following this rule, chicken owners can ensure that their feathered friends receive adequate nutrition without overindulging in potentially harmful treats.
Furthermore, it is essential to prioritize the safety of chickens by preventing access to toxic plants like rhubarb. This can be achieved by gating off areas where rhubarb grows and planting chicken-friendly gardens with safe plant options. By creating a secure environment, chicken owners can minimize the risk of accidental consumption of harmful plants and keep their chickens healthy and thriving.FAQ
Can chickens eat rhubarb stalks?
Why can’t chickens eat rhubarb leaves?
What happens if chickens eat rhubarb?
How to treat rhubarb poisoning in chickens?
What is the nutritional analysis of rhubarb for chickens?
What are the best plants to feed chickens?
What are the worst plants to avoid feeding chickens?
How to keep chickens safe from rhubarb plants?
What is the 90/10 feeding rule for chickens?
What are some foods that increase a chicken’s appetite?
Laura is a versatile writer and editor whose passion for animals shines through in her work. With a keen understanding of language and a love for storytelling, Laura crafts compelling narratives that captivate our audience and inspire action regarding animal welfare. Whether she’s delving into the latest research or sharing heartwarming stories of animal companionship, Laura’s work will leave a lasting impression on all who read it.
Chickens
Can Chickens Eat Persimmons? Safe Feeding Tips

Did you know that chickens can indulge in a diverse range of fruits? Surprisingly, chickens can also enjoy persimmons! These tasty fruits not only give your feathered friends a delicious snack but also provide important nutrients to keep them healthy. However, before you start giving persimmons to your flock, it’s important to learn the proper feeding guidelines to keep them safe and well.
Key Takeaways:
- Chickens can safely eat persimmons in moderation.
- Persimmons provide a vitamin boost, especially during the cold winter months.
- It’s important to limit persimmon intake due to their high sugar content.
- Introduce persimmons gradually to chickens and observe their reactions.
- Consult with a veterinarian for personalized advice on feeding persimmons to your flock.
Persimmons: A Berry for Chickens
When it comes to feeding chickens, the options can sometimes seem limited. However, one fruit that can provide a tasty and nutritious addition to their diet is the persimmon. Whether it’s the Fuyu, Hachiya, or American variety, persimmons are considered a type of berry that chickens can safely enjoy.
Persimmons come in different sizes and colors, ranging from yellow to dark red or orange. This vibrant range adds visual appeal to the chickens’ diet while providing a delectable treat. Chickens are likely to enjoy the sweet and succulent taste of persimmons, making it a popular choice among poultry enthusiasts.
However, it’s important to exercise moderation when feeding persimmons to chickens. Just like other fruits with a high sugar content, persimmons should be given in limited amounts to avoid overindulgence. While chickens can benefit from the vitamins and nutrients found in persimmons, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet and not rely solely on this fruity delicacy.
Nutritional Benefits of Persimmons for Chickens
Persimmons offer several nutritional benefits for chickens. They are rich in vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin B6. These vitamins support the immune system, promote healthy skin, and boost metabolism. Persimmons also contain folate, thiamin, riboflavin, manganese, and other essential minerals that are vital for the overall health and well-being of chickens.
When chickens consume persimmons, they receive a nutritious and delicious treat that can supplement their regular feed. These vibrant fruits provide a natural source of vitamins and minerals, which are crucial for their growth, development, and overall vitality.
Vitamins in Persimmons
Persimmons are particularly rich in vitamins that offer a range of health benefits for chickens. Let’s take a closer look at the key vitamins found in persimmons and their roles in supporting chickens’ health:
1. Vitamin A
Vitamin A plays a crucial role in maintaining a strong immune system, enhancing vision, and promoting healthy skin and feathers in chickens. It also supports their reproductive health and improves their overall resistance to diseases.
2. Vitamin C
Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting chickens’ cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also plays a vital role in collagen synthesis, which is essential for healthy skin, bones, and connective tissues.
3. Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is involved in various metabolic processes in chickens, including protein synthesis and red blood cell production. It also supports their nervous and immune systems, contributing to their overall health and vitality.
In addition to these key vitamins, persimmons contain other essential nutrients, including folate, thiamin, riboflavin, and manganese. These nutrients play important roles in various bodily functions, such as energy production, DNA synthesis, and bone health in chickens.
However, it’s important to feed persimmons in moderation to avoid oversupplying these nutrients and disrupting the chickens’ balanced diet. Too much of a good thing can be harmful, so it’s crucial to maintain a proper balance between persimmons and their regular feed.
To ensure chickens receive the nutritional benefits of persimmons without overindulging, it’s recommended to offer them small quantities of persimmons as occasional treats. This way, chickens can enjoy the delicious flavor and reap the rewards of the vitamins and minerals found in these delightful fruits.
| Vitamin | Function |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Enhances immune system, promotes healthy skin and feathers |
| Vitamin C | Acts as an antioxidant, improves skin health, and supports collagen synthesis |
| Vitamin B6 | Aids in metabolism, protein synthesis, and immune system function |

By including persimmons as part of a varied and balanced diet, chickens can enjoy the nutritional benefits of these vibrant fruits while leading healthy and active lives.
Feeding Persimmons to Chickens
To introduce persimmons to chickens, it’s important to start slowly and observe their reaction. Chickens may be hesitant to try new foods, so gradual introduction is key. One effective method is to hang a piece of persimmon in the chicken coop, allowing them to examine it before giving it a try. The soft skin and flesh of persimmons make them easy for chickens to consume, so there’s no need to cut them into small pieces or remove the skin.
Feeding Tips:
- Start by offering small pieces of persimmon.
- Observe the chickens’ reaction and appetite.
- Gradually increase the quantity of persimmons over time.
- Ensure persimmons are ripe and fresh for the best taste.
Once your chickens are accustomed to persimmons, you can make the feeding experience more enjoyable by cutting the fruit into different shapes or even hiding pieces for them to find. This adds a fun and stimulating element to their diet.
Remember, while persimmons are a healthy treat, they should be given in moderation to maintain a balanced diet for the chickens.
Potential Drawbacks of Persimmons for Chickens
While persimmons are generally safe for chickens to consume, there are a few potential drawbacks and risks associated with feeding persimmons to them. It’s essential for chicken owners to be aware of these considerations to ensure the well-being and health of their flock.
High Sugar Content: One concern when it comes to feeding persimmons to chickens is their high sugar content. Persimmons are naturally sweet fruits, and excessive consumption of high-sugar foods can lead to various health issues for chickens. It is crucial to moderate the quantity of persimmons and avoid feeding them in large quantities to prevent blood sugar imbalances and weight gain.
Health Conditions: Chickens with certain health conditions, such as diabetes or obesity, should be cautious when consuming persimmons. The high sugar content in persimmons can exacerbate these conditions and potentially lead to further health complications. It is advisable to consult with a veterinarian for specific dietary guidelines if your chickens have pre-existing health conditions.
Potential Intestinal Blockages: Another risk associated with persimmons for chickens is the presence of seeds. Persimmon seeds contain tannins, which can clump together and potentially lead to intestinal blockages if chickens consume them excessively. It’s crucial to monitor chickens’ intake and ensure that they don’t overindulge in persimmon seeds, reducing the risk of digestive problems and blockages.
Did You Know? Chickens have a gizzard, which helps them grind and digest their food. However, the seeds of fruits like persimmons can be challenging for a chicken’s digestive system to break down, increasing the risk of blockages.
| Drawbacks of Persimmons for Chickens | Risks of Feeding Persimmons to Chickens |
|---|---|
| High sugar content | Potential blood sugar imbalances |
| Health conditions (diabetes, obesity) | Potential exacerbation of existing health conditions |
| Presence of tannin in seeds | Potential intestinal blockages |
By being cautious and monitoring the quantity and frequency of persimmon feedings, chicken owners can minimize the drawbacks and risks associated with feeding persimmons to their flock. It is always recommended to provide a balanced and varied diet for chickens, consulting with a veterinarian if necessary, to ensure their overall health and well-being.

Feeding Persimmon Leaves to Chickens
Chickens can enjoy the benefits of persimmon leaves as part of their diet, but it’s important to offer them in moderation. Persimmon leaves provide fiber and other nutrients that can contribute to the overall digestion and well-being of your chickens.
Before giving persimmon leaves to your chickens, make sure to wash them thoroughly to remove any potential contaminants. Wilted or spoiled leaves should be avoided since they may contain toxins that could be harmful to your chickens.
When introducing persimmon leaves to your chickens for the first time, start with a small quantity and observe their reaction. Some chickens may have preferences, while others may take time to adjust to this new treat. Gradually increase the amount based on their response.
Feeding persimmon leaves to your chickens can be an excellent way to add variety to their diet, allowing them to enjoy the benefits of different nutrients. While persimmon leaves are generally safe for chickens, it’s always essential to monitor their diet and consult with a veterinarian for personalized advice.
Benefits of Persimmon Leaves for Chickens
Persimmon leaves offer several advantages for chickens. They are a rich source of fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes a healthy gut. Additionally, these leaves contain essential minerals and vitamins, such as potassium, manganese, and vitamin C, which contribute to the overall well-being and immune system of your chickens.
The fiber in persimmon leaves can help regulate bowel movements and prevent digestive issues in chickens. It assists in maintaining a healthy and balanced digestive system, allowing your chickens to better absorb nutrients from their food.
The table below highlights some of the key nutritional values of persimmon leaves:
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Fiber | 6g |
| Potassium | 214mg |
| Calcium | 81mg |
| Manganese | 1.5mg |
| Vitamin C | 43mg |
Remember, while persimmon leaves are beneficial for chickens, it’s important to offer them as part of a diverse diet that includes other healthy food options. Providing a balanced diet is key to maintaining the overall health and happiness of your flock.
Remember to always introduce new foods gradually and keep a close eye on your chickens’ reaction. By offering persimmon leaves in moderation, you can provide your chickens with a nutritious and enjoyable addition to their diet.
Foods to Avoid Giving Chickens
While chickens can enjoy a variety of foods, it’s important to be aware of the foods that are toxic or harmful to them. By avoiding these foods, you can ensure the health and well-being of your chickens. Some of the foods that should be kept away from chickens include:
- Chocolate: Chocolate contains theobromine, which is toxic to chickens and can lead to symptoms like increased heart rate and tremors.
- Avocado: Avocado contains persin, a toxin that can be lethal to chickens if ingested in large quantities. It’s best to completely avoid feeding avocados to chickens.
- Lemons and oranges: Citrus fruits like lemons and oranges are highly acidic, which can upset the digestive system of chickens. While small amounts can be given as an occasional treat, it’s best to limit their intake.
- Processed foods: Foods that are high in salt, sugar, or artificial additives should be avoided. These can be harmful to chickens and can lead to various health issues.
Instead of these toxic or unhealthy foods, focus on offering safe and nutritious options for your chickens. Here are some examples:
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, carrots, peas, and cucumbers are all excellent choices for chickens. These vegetables provide essential vitamins and minerals.
- Fruits: Safe fruits for chickens include apples, berries, and watermelon. These fruits offer natural sweetness and hydration.
- Grains: Whole grains like oats and rice can be given to chickens in small amounts for added nutrition.
- Protein-rich options: Eggs or mealworms are great sources of protein for chickens. These can be offered as treats to supplement their diet.
By avoiding toxic foods and focusing on safe and nutritious options, you can ensure that your chickens stay healthy and happy.
| Toxic Foods for Chickens | Safe and Nutritious Alternatives |
|---|---|
| Chocolate | Vegetables: leafy greens, carrots, peas |
| Avocado | Fruits: apples, berries, watermelon |
| Lemons and oranges | Grains: oats, rice |
| Processed foods | Protein-rich options: eggs, mealworms |

Can Chickens Eat Persimmons Skin?
Chickens can safely enjoy persimmon skins as part of their diet, as long as the skin is clean and free from pesticides. Persimmon skins contain additional nutrients and fiber, which can be beneficial to the chickens’ health. However, it’s important to offer the skin in moderation to avoid digestive issues, as it can be high in sugar. Introducing new foods gradually to chickens and monitoring their reactions is recommended to ensure their well-being. If any discomfort or digestive problems arise, it’s advisable to reduce or eliminate persimmon skin from their diet.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Value | Persimmon skins are rich in nutrients such as vitamins and fiber, which can contribute to the overall health of the chickens. |
| Moderation | Offering persimmon skins in moderation can help prevent excessive sugar intake and potential digestive issues. |
| Introduction | Gradually introducing new foods like persimmon skins allows for proper adjustment and observation of any adverse reactions. |
Feeding persimmon skins to chickens provides them with additional nutrients while enticing their taste buds. However, it’s essential to remember that persimmon skins should not replace their main diet, which should primarily consist of balanced commercial chicken feed.
List of Other Safe Fruits for Chickens
- Apples
- Bananas
- Berries
- Cantaloupe
- Grapes
- Kiwi
- Mango
- Peaches
- Pumpkins
- Watermelon
Remember to prioritize their regular feed and consult with a veterinarian for personalized advice.

Including a variety of fruits in a chicken’s diet can provide essential vitamins, minerals, and hydration. However, it’s crucial to offer fruits as occasional treats rather than a substantial part of their daily nutrition. By maintaining a balanced and varied diet, chickens can enjoy persimmon skins and other safe fruits as part of a healthy lifestyle.
What Fruits Should I Give to My Chickens?
Chickens can enjoy a variety of fruits as occasional treats. Incorporating safe fruits into their diet provides essential vitamins, minerals, and hydration. However, it’s important to remember that fruits should only make up a small portion of their overall diet, with the main focus on a balanced commercial chicken feed.
Here are some safe fruits that you can give to your chickens:
- Apples
- Bananas
- Berries
- Cantaloupe
- Grapes
- Kiwi
- Mango
- Peaches
- Pumpkins
- Watermelon
These fruits not only provide a tasty treat but also offer a range of nutritional benefits. For example, bananas are a great source of potassium, while berries are packed with antioxidants. Watermelon and cantaloupe help keep chickens hydrated, especially during hot summer months.
It’s important to introduce these fruits in moderation to prevent overindulgence and ensure a balanced diet. Too much fruit can be disruptive to their digestive system or lead to obesity. Monitor their intake and observe any changes in behavior or health to ensure their well-being.
Benefits of Safe Fruits for Chickens
| Fruit | Nutritional Benefits |
|---|---|
| Apples | High in fiber and contain vitamins A, C, and E |
| Bananas | Rich in potassium and vitamin B6 |
| Berries | Packed with antioxidants and vitamin C |
| Cantaloupe | Hydrating and a good source of vitamins A and C |
| Grapes | Contain antioxidants and vitamins C and K |
| Kiwi | Rich in vitamin C, fiber, and folate |
| Mango | High in vitamins A and C |
| Peaches | Provide vitamins A and C |
| Pumpkins | Rich in beta-carotene and a good source of fiber |
| Watermelon | Hydrating and contains vitamins A and C |
Remember to always wash fruits thoroughly, remove any pits or seeds, and serve them in appropriate sizes for chickens. By offering a variety of safe fruits as occasional treats, you can keep your chickens happy, healthy, and entertained.
Conclusion
In conclusion, persimmons can be safely incorporated into a chicken’s diet as part of a balanced feeding routine. These delicious fruits offer a range of nutritional benefits, including essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to the overall well-being of chickens.
However, it’s important to feed persimmons to chickens in moderation. While persimmons are a natural source of sweetness, their high sugar content can cause issues if consumed excessively. Therefore, it’s crucial to monitor the quantity of persimmons and ensure they are not overindulging.
Additionally, it’s essential to consider potential drawbacks when feeding persimmons to chickens. Chickens with specific health conditions, such as diabetes or obesity, should have their persimmon intake limited. Moreover, care should be taken to prevent intestinal blockages that may occur if chickens consume an excessive amount of persimmon seeds.
To safely introduce persimmons into a chicken’s diet, it’s recommended to start gradually and observe their response. By offering a varied selection of treats alongside persimmons, chickens can enjoy a diverse diet while receiving the necessary nutrients. Prioritizing their regular feed is also vital to maintain a balanced nutritional intake.
FAQ
Can chickens eat persimmons?
Do persimmons provide any nutritional benefits to chickens?
How should I introduce persimmons to my chickens?
Are there any potential risks or drawbacks to feeding persimmons to chickens?
Can chickens eat persimmon leaves?
Are there any foods that I should avoid giving to chickens?
Can chickens eat persimmon skin?
What other fruits can I give to my chickens?
Is it safe to feed persimmons to chickens?
Paul’s love for animals knows no bounds. As a dedicated writer and animal lover, Paul brings a unique perspective to our team. His firsthand experiences with various animals enrich our content and provide valuable insights into their behavior and needs. Whether he’s sharing tips for pet care or shedding light on pressing conservation issues, Paul’s passion for animals shines through in everything he does.
-

 Vetted1 month ago
Vetted1 month ago15 Best Dog Food Brands Recommended by Vets for Healthy and Happy Pups
-

 Vetted1 month ago
Vetted1 month ago14 Best Homemade Dog Food Recipes Your Pup Will Love – Vet Approved & Nutritious
-

 Vetted1 month ago
Vetted1 month ago15 Best Cat Foods for Managing Hyperthyroidism – Vet Approved and Feline Friendly
-

 Vetted3 weeks ago
Vetted3 weeks ago15 Best Dog Foods for Kidney Disease – Expert Recommendations for Your Pet's Health
-

 Vetted2 weeks ago
Vetted2 weeks ago15 Best Affordable Cat Foods That Won't Break the Bank
-

 Deers1 month ago
Deers1 month agoCaring for Baby Deer: Tips for Healthy Fawns
-
 Cats6 days ago
Cats6 days agoCat Weight Chart by Age: Kitten to Senior in Lbs
-

 Vetted1 month ago
Vetted1 month ago15 Best Kibble Dog Foods for a Healthy and Happy Pup





















