Animals
Discover the Fascinating World of Fish: Traits, Varieties & Selections
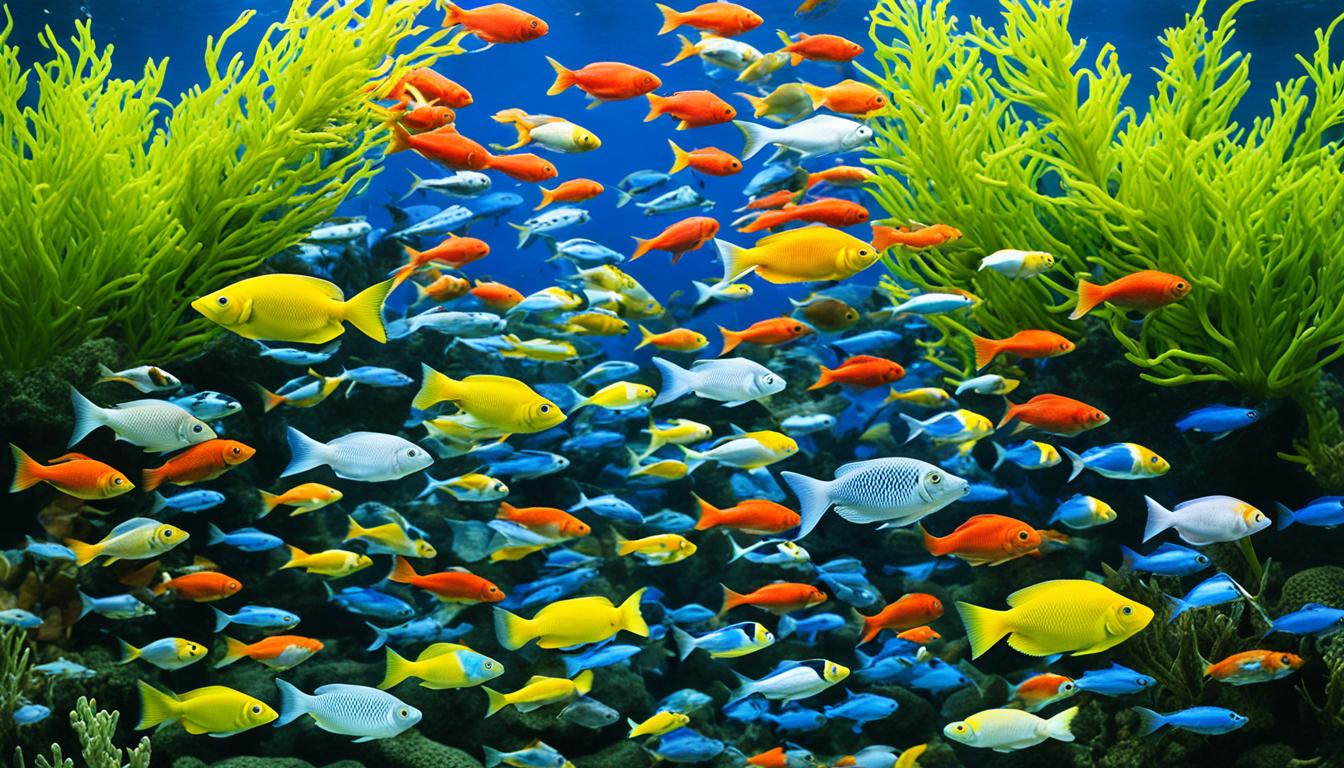

Fish are the most diverse group of vertebrates on Earth, with over 34,000 known species. From tiny transparent paedomorphic fish measuring a mere 8 millimeters to massive whale sharks spanning up to 40 feet in length, fish come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors. Their adaptability, unique traits, and captivating behaviors make them a fascinating subject to explore.
Key Takeaways:
- Fish are the most diverse group of vertebrates, with over 34,000 known species.
- They come in a wide range of sizes, from tiny transparent fish to massive whale sharks.
- Fish possess unique traits and behaviors that make them intriguing to study.
- Exploring the world of fish opens up a whole new understanding of aquatic ecosystems.
- Understanding fish traits, varieties, and selections is essential for aquarium enthusiasts and conservation efforts.
Characteristics Of Fish
Fish possess a range of unique characteristics that enable them to live successfully in water. Let’s explore some of these fascinating traits:
Aquatic Habitat
Fish are exclusively aquatic creatures, inhabiting various bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. They have evolved specific adaptations to thrive in their aquatic environments.
Streamlined Body
Fish have streamlined bodies that are perfectly shaped for efficient movement through water. Their sleek and hydrodynamic shape minimizes resistance, allowing them to swim swiftly and navigate through their surroundings with ease.
Gills for Respiration
Unlike mammals and other land-dwelling creatures, fish do not have lungs. Instead, they have gills, specialized organs that extract oxygen from the water. Gills enable fish to respire and obtain the oxygen necessary for their survival.
Cold-Blooded
One distinguishing characteristic of fish is that they are cold-blooded, which means their body temperature varies with the temperature of their surroundings. Their metabolic rate and bodily functions are influenced by the temperature of the water they inhabit.
Fins for Locomotion
Fish have fins that play a crucial role in their locomotion. These appendages help them maneuver through the water, change direction, maintain balance, and achieve propulsion. Different types of fins serve distinct purposes, allowing fish to adapt to various swimming styles and habitats.
Scales
Scales are a prominent feature of fish, serving as a protective layer for their bodies. Scales not only provide defense against external threats but also assist in maintaining their internal water balance and regulating body temperature.
Swim Bladder
Many fish possess a specialized organ called a swim bladder, which helps them control their buoyancy. By adjusting the air or gas content in the swim bladder, fish can either ascend or descend in the water column, effectively controlling their depth within the water.
Reproduction by Eggs
Fish reproduce by laying eggs, a characteristic feature of their life cycle. The reproductive strategy and behavior of fish vary greatly across species, with some laying thousands of eggs at once, while others exhibit complex courtship rituals to ensure successful fertilization.
Wide Diversity
Fish exhibit an incredible diversity in terms of species, sizes, shapes, colors, and ecological adaptations. From the smallest goby to the massive whale shark, fish have evolved to occupy a wide range of niches in aquatic ecosystems.
Eyesight
Fish possess excellent eyesight, allowing them to navigate their surroundings, find food, and detect potential threats. Some species even have specialized adaptations to see in low light conditions or perceive colors in their environment.
Ectothermic Metabolism
Fish are ectothermic animals, meaning their body temperature is regulated by the surrounding environment. As a result, their metabolic rate and overall activity levels are influenced by the temperature of the water they inhabit.
Diverse Feeding Strategies
Fish employ various feeding strategies based on their ecological niche and available food sources. They may be herbivorous, carnivorous, omnivorous, filter feeders, scavengers, or even specialized feeders with unique adaptations to capture prey.
Vertebrate
As vertebrates, fish possess a backbone or spinal column, which provides structural support and protection for their internal organs. This characteristic distinguishes them from invertebrates and is a defining feature of the phylum Chordata to which fish belong.
These are just some of the remarkable characteristics that make fish a diverse and fascinating group of creatures.
Types Of Fish
Fish are classified into three main types: jawless fish (Agnatha), cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes), and bony fish (Osteichthyes). Each type of fish has its own unique characteristics and adaptations that allow them to thrive in their respective environments.
Jawless fish (Agnatha)
Jawless fish, such as lampreys and hagfish, are characterized by their lack of jaws. They have long, cylindrical bodies and are typically found in freshwater and marine environments.
Cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes)
Cartilaginous fish, including sharks and rays, have skeletons made of cartilage instead of bone. They have streamlined bodies and powerful jaws, making them efficient hunters in the ocean. Cartilaginous fish are mostly marine species, although some can be found in freshwater habitats.
Bony fish (Osteichthyes)
Bony fish make up the majority of fish species. They have skeletons composed of bone and are the most diverse group of fish. Bony fish inhabit a wide range of habitats, including freshwater rivers, lakes, and the ocean. They exhibit a wide variety of body shapes and sizes, with adaptations that enable them to survive in different ecological niches.
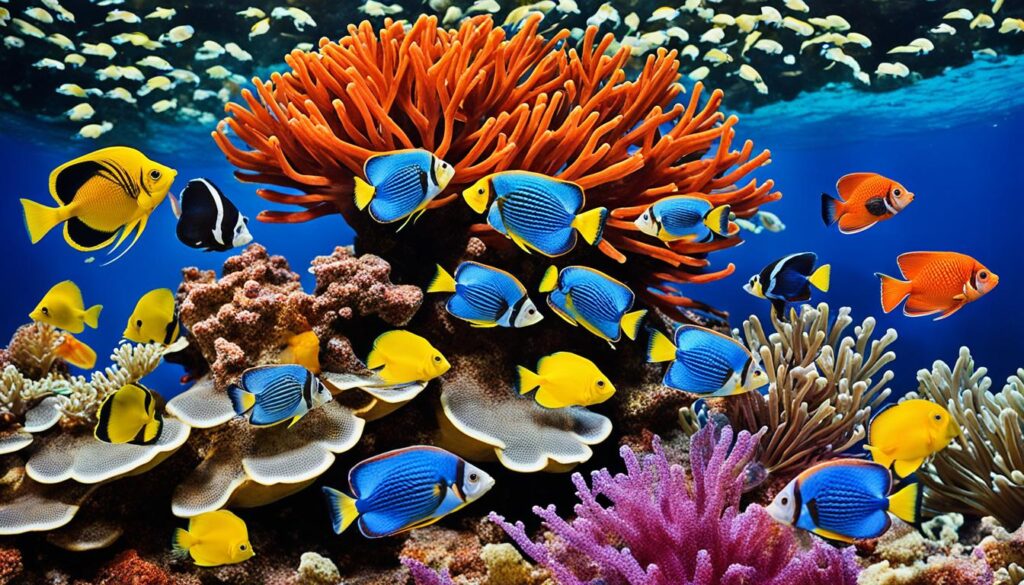

Different Types Of Fish:
The world of fish is incredibly diverse, with numerous species that inhabit various ecosystems. Each type of fish has its own fascinating characteristics and qualities. Let’s dive into some of the most interesting types:
Anglerfish: The Deep-sea Lurkers
Anglerfish are known for their unique method of hunting. They have a bioluminescent lure that attracts prey in the dark depths of the ocean. These mysterious creatures have adapted to survive in extreme conditions and are fascinating to observe.
Betta Fish: The Colorful Fighters
Betta fish, also known as Siamese fighting fish, are popular for their vibrant colors and elaborate fins. They are known for their aggressive behavior and are best kept alone or in carefully selected community tanks.
Clownfish: The Reef Dwellers
Clownfish are famous for their symbiotic relationship with anemones. They live among the tentacles of these marine creatures, finding protection from predators while providing food and cleaning services in return.
Catfish: The Bottom Dwellers
Catfish are bottom-dwelling scavengers that play an essential role in maintaining the cleanliness of aquatic ecosystems. They have specialized barbels and are skilled at finding food in the substrate.
Carp: The Hardy Swimmers
Carp are hardy fish species that are adaptable to various environments. They are cherished by anglers for their strength and fighting spirit. Carp are also commonly bred in aquaculture due to their fast growth and ability to thrive in different conditions.
Goldfish: The Classic Tank Dwellers
Goldfish are classic aquarium fish that have been kept for centuries. They come in various colors and wondrous tail shapes. Known for their beauty and longevity, goldfish are a popular choice for both beginners and experienced aquarists.
Guppy: The Vibrant Community Fish
Guppies are small, colorful fish often kept in community tanks. They are known for their lively behavior and striking patterns. Guppies are relatively easy to care for, making them a favorite among hobbyists.
Tuna: The Swift Ocean Wanderers
Tuna are highly migratory fish that inhabit the open ocean. Renowned for their speed and endurance, tuna undertake long-distance journeys in search of food. These agile swimmers are prized for their commercial and recreational value.
Salmon: The Upstream Navigators
Salmon are anadromous fish, meaning they migrate from the ocean to freshwater rivers to spawn. They possess incredible navigational skills, returning to their birthplace against all odds. Salmon are crucial to the ecosystems they inhabit and are valued for their meat.
Pufferfish: The Inflatable Defenders
Pufferfish have a remarkable ability to inflate themselves when threatened, deterring potential predators. They have a spiky appearance and toxic flesh, making them unappealing to most predators. Pufferfish are fascinating to observe but require specialized care due to their unique needs.
Swordfish: The Oceanic Gladiators
Swordfish are large, predatory fish with long, bill-like snouts. Their distinctive shape and powerful swimming abilities make them formidable hunters in the open ocean. Swordfish are known for their speed and agility, often leaping out of the water in pursuit of prey.
Marlin: The High-speed Hunters
Marlin are some of the fastest fish in the ocean, capable of reaching incredible speeds. They are known for their iconic bill and stunning colors. Marlin are prized targets for sport fishing enthusiasts due to their strength and acrobatic displays.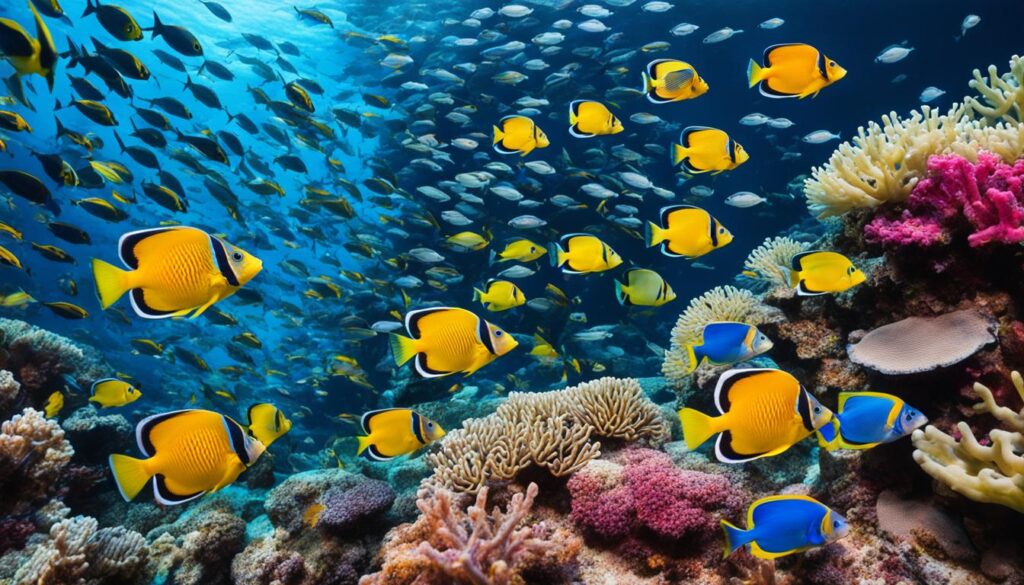
Stingray: The Graceful Ocean Skaters
Stingrays are graceful creatures that glide through the ocean, using their pectoral fins to propel themselves. They have a unique flattened body shape and can often be found resting on the sandy ocean floor. Stingrays are mesmerizing to watch and are a popular attraction in aquariums.
Lionfish: The Striking Predators
Lionfish are known for their striking appearance, with colorful stripes and venomous spines. They are predatory fish that feed on smaller fish and invertebrates. Lionfish have become invasive species in some regions, causing concern for native marine life.
Moorish Idol: The Exotic Beauties
Moorish idols are stunning reef fish often admired for their vibrant colors and elaborate fin patterns. They are delicate and require specific water conditions to thrive. Moorish idols are highly sought after by reef aquarium enthusiasts.
Piranha: The Feisty Hunters
Piranhas are notorious for their sharp teeth and aggressive feeding behavior. They are ferocious hunters that can strip prey down to the bone in a matter of minutes. Piranhas inhabit freshwater rivers and are a subject of fascination for many.
Trout: The Stream Champions
Trout are freshwater fish that thrive in streams and rivers. They are known for their excellent swimming abilities and are a popular target for anglers. Trout species vary in size, habitat preferences, and stunning coloration.
Sunfish (Mola): The Gentle Giants
Sunfish, also known as Mola, are the largest bony fish in the world. They have a unique appearance, with a tall dorsal fin and a flattened body. Sunfish are gentle creatures that feed on jellyfish and are often seen basking at the ocean surface.
Eel: The Sly Ambushers
Eels are secretive and nocturnal fish that prefer to hide in crevices and ambush their prey. They have a slimy body and can dart quickly through small openings. Eels are fascinating to observe but require specific care due to their specialized needs.
Bass: The Agile Ambushers
Bass are predatory fish known for their aggressive nature and impressive speed. They are skilled ambush hunters, lying in wait for their prey. Bass are popular targets for both recreational and competitive fishing due to their fighting abilities.
Threats And Conservation Of Fish
Fish face numerous threats to their survival, many of which are caused by human activities. Overfishing, where the fish population is harvested at a rate faster than it can reproduce, is a significant threat to fish species and leads to declines in populations. Habitat destruction, such as the destruction of coral reefs and deforestation of riverbanks, can disrupt fish habitats and reduce their available resources. Pollution, from sources such as agricultural runoff and industrial waste, can have detrimental effects on fish populations and the overall health of aquatic ecosystems. Climate change, including rising temperatures and ocean acidification, can impact fish physiology and their ability to survive. Invasive species, when introduced into new environments, can outcompete native species and disrupt ecological balance.
Conservation efforts aim to mitigate these threats and protect fish populations and their habitats. Sustainable fishing practices, habitat restoration, and pollution reduction are some of the strategies employed to conserve fish species and ensure their long-term survival.
| Threats to Fish | Conservation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Overfishing | Sustainable fishing practices, such as implementing catch limits and fishing quotas, to prevent the depletion of fish populations. |
| Habitat destruction | Habitat restoration projects, such as reef rehabilitation and reforestation of riverbanks, to restore fish habitats and improve their resilience. |
| Pollution | Efforts to reduce pollution sources, such as implementing better waste management systems and promoting eco-friendly agricultural practices, to minimize the impact on fish populations and aquatic ecosystems. |
| Climate change | Adaptation and mitigation measures, such as creating marine protected areas and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, to address the effects of climate change on fish habitats and populations. |
| Invasive species | Prevention and control programs, including strict biosecurity measures and monitoring systems, to prevent the introduction and spread of invasive species that can harm native fish populations. |
What Are the Common Traits of Fish?
Fish possess a range of common traits that are crucial for their survival and ecological role. Understanding fish anatomy, from their fins to gills, helps us comprehend their unique adaptations and behaviors. Fish exhibit a tremendous diversity of species, ranging from bony fish, which make up the majority, to cartilaginous fish like sharks and rays. This diversity is essential for maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems, as fish play vital roles in nutrient cycling, predation, and maintaining ecological balance.
Understanding Fish Anatomy: From Fins to Gills
Fish anatomy is adapted to their life in water. Let’s explore some of the key anatomical features of fish:
- Fins: Fish have various types of fins, such as the dorsal, caudal, pectoral, and pelvic fins. These fins enable fish to swim, change direction, and maintain balance in the water.
- Gills: Gills are specialized organs that fish use to extract oxygen from the water and remove carbon dioxide. Through a process called respiration, the gills allow fish to breathe and obtain the oxygen they need to survive.

Diversity in Fish Species: From Bony to Cartilaginous Fish
The world of fish is incredibly diverse, with a wide range of species. Here are two major groups of fish:
- Bony fish: Bony fish, also known as osteichthyans, have skeletons made of bone. They are the most common type of fish and include familiar species like salmon, trout, and goldfish.
- Cartilaginous fish: Cartilaginous fish, such as sharks and rays, have skeletons made of cartilage. They are known for their unique adaptations and predatory nature.
The Importance of Fish in Aquatic Ecosystems
Fish play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of aquatic ecosystems. Here are some of the reasons why fish are important:
- Nutrient cycling: Fish help recycle nutrients in the water by consuming organic matter and excreting waste, which nourishes other organisms.
- Predation: Fish serve as predators, controlling populations of other organisms and maintaining ecological balance.
- Ecological balance: Fish interactions with other species, such as their role as prey or competitors, help maintain the stability and diversity of aquatic ecosystems.
Therefore, fish are not only fascinating creatures but also key players in the intricate web of life in our oceans, rivers, and lakes.
How Can You Select the Right Fish for Your Aquarium?
When it comes to selecting fish for your aquarium, making the right choices is essential for the well-being and compatibility of the fish. There are several factors to consider that can help you create a harmonious and thriving aquatic environment.
First, think about the size of your fish tank. Different fish species have varying space requirements, so it’s important to choose fish that will comfortably fit in your aquarium. Overcrowding can lead to stress, aggression, and poor water quality, so ensure you select fish that can coexist peacefully.
Next, research the specific requirements of the fish species you’re interested in. Fish have diverse needs when it comes to water temperature, pH levels, and filtration. Understanding these requirements will enable you to provide an environment that promotes their health and well-being.
Consider the compatibility of different fish species. Some fish may have aggressive tendencies or specific territorial needs, while others are more peaceful and sociable. It’s essential to select fish that can cohabitate without causing harm to one another.
Lastly, pay attention to the size and dietary needs of the fish you’re considering. Fish vary in size, and some species can outgrow smaller aquariums. Additionally, different fish have specific feeding requirements, so make sure you choose fish that can be easily fed with the available food options.
By taking into account factors such as fish tank size, species requirements, compatibility, and feeding needs, you can select the right fish for your aquarium. Creating a suitable environment with proper water parameters and filtration will contribute to the long-term health and happiness of your fish.FAQ
What unique traits do fish possess that allow them to live successfully in water?
How are fish classified?
What are some notable species of fish?
What are the threats to fish and how are they conserved?
What are the common traits of fish?
How can you select the right fish for your aquarium?
As our Editor-in-Chief, James plays a pivotal role in ensuring the quality and integrity of our content. With a keen eye for detail and a passion for storytelling, James oversees the editorial process here at A Place for Animals. With years of experience in content editing, James ensures that every piece of content meets our high standards of accuracy and clarity. Under James’ guidance, you can rest assured that the content you read is informative and impeccably crafted.
Animals
3 Animals Similar to Squirrels
Curious about animals resembling squirrels? Meet chipmunks, marmots, and flying squirrels, each with unique traits that set them apart.

Chipmunks, marmots, and flying squirrels are similar to squirrels. Chipmunks have striped backs and communicate vocally. Marmots are ground-dwellers with bushy tails and hibernate for 8 months. Flying squirrels glide at night with large eyes and a unique membrane. These animals share traits with squirrels, such as agility and adaptability.
Key Takeaways
- Chipmunks share traits with squirrels like agility and varied diet.
- Flying squirrels resemble squirrels in agility and diverse diet.
- Marmots, though different, are diurnal rodents with essential roles in ecosystems.
- All three animals communicate vocally like squirrels for survival.
- Observing these animals in the wild provides insights into behaviors and ecosystem dynamics.
Chipmunks: Small Rodents With Striped Backs
Chipmunks, closely related to squirrels, are small rodents distinguished by the stripes running along their backs. As members of the rodent family, chipmunks exhibit fascinating behaviors that set them apart. These omnivores are active during the daytime, making them a crucial sight in many habitats. Their exceptional climbing abilities allow them to scurry up trees and bushes in search of food, which includes nuts, seeds, fruits, insects, and even small animals.
Communication among chipmunks is crucial for their survival. Through various vocalizations, these small rodents convey messages about potential dangers, food availability, and territorial boundaries. Understanding their intricate language enhances our appreciation for these remarkable creatures.
Next time you spot a chipmunk darting around, take a moment to observe their behaviors and listen to their unique sounds. Chipmunks truly exemplify the beauty of nature's diversity in the animal kingdom.
Marmots: Ground-Dwelling Rodents With Bushy Tails

Marmots, distinguished by their bushy tails, are ground-dwelling rodents that play an essential role in their ecosystems. Belonging to the Sciuridae family, these diurnal creatures are active during the day, using their burrows to live in family groups.
With a weight of up to 11 pounds, marmots have brown fur with white-tipped hair, adapting well to higher altitudes. They hibernate for about 8 months, emerging in spring to forage and reproduce.
In their habitats, marmots influence vegetation dynamics and serve as prey for various predators, contributing significantly to the ecosystem's balance. Observing marmots in the wild can provide insights into their behaviors and interactions with other species, showcasing the importance of these ground-dwelling rodents with their striking bushy tails.
They're fascinating creatures to study due to their unique adaptations and crucial roles within their environments.
Flying Squirrels: Nocturnal Gliding Mammals

Gliding effortlessly through the night, flying squirrels showcase their remarkable ability to navigate the darkness using their unique gliding membrane. These nocturnal mammals are known for their extraordinary gliding skills, allowing them to move gracefully through the air.
With their large, dark eyes providing excellent night vision, flying squirrels can easily maneuver through dimly lit environments like forests where they reside. These omnivorous creatures have a diverse diet, including nuts, seeds, insects, and occasionally bird eggs.
Despite their name, flying squirrels don't truly fly but rather glide by extending their limbs and using the membrane to catch the air, enabling them to travel between trees effortlessly. Their gliding ability sets them apart from other squirrel species, making them fascinating creatures to observe in their natural habitat.
With their adaptation to the night and unique way of moving, flying squirrels offer a glimpse into the innovative ways animals have evolved to thrive in their environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Animal Is Similar to Squirrel?
When considering animals similar to squirrels, one might think of the agile chipmunk. This ground-dwelling rodent, like squirrels, boasts bushy tails and climbing prowess. Chipmunks play an essential role in seed dispersal and ecosystem balance, mirroring squirrels' impact.
What Is the Closest Pet to a Squirrel?
The closest pet to a squirrel is a chipmunk. These adorable rodents require care similar to squirrels. Providing a spacious enclosure with climbing opportunities and a diet of nuts, seeds, fruits, and insects guarantees a fulfilling experience.
What Are Squirrels Most Closely Related To?
Squirrels are most closely related to chipmunks, marmots, and prairie dogs. These species within the Sciuridae family share common traits like bushy tails and diurnal habits. Exploring these relationships sheds light on their evolution and adaptations.
What Animals Are in the Same Family as Squirrels?
In the same family as squirrels are chipmunks, prairie dogs, and other fascinating creatures. This diverse Sciuridae family showcases various species with shared evolutionary history. Their roles in ecosystems worldwide highlight their importance for biodiversity and habitat health.
Are There Any Animals Similar to Squirrels That Resemble Possums?
Yes, there are some fascinating species of possum lookalikes that bear a striking resemblance to squirrels. The sugar glider, for example, is a small arboreal possum that shares many physical characteristics with squirrels, such as their bushy tails and similar feeding habits.
Conclusion
Just like the diverse array of animals in the forest, there are many creatures similar to squirrels that share similar characteristics and behaviors.
Chipmunks scurry around with their striped backs, marmots dig into the ground with their bushy tails, and flying squirrels glide through the night sky.
These creatures may be different in appearance, but they all share a common bond with their squirrel cousins in the intricate tapestry of the animal kingdom.
Dana is our Lead Content Writer, bringing a wealth of knowledge and expertise to our team. With a background deeply rooted in animal studies and a profound love for all creatures, Dana is dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that resonates with our audience. With Dana at the helm, you can trust that our content is accurate and engaging, catering to the diverse interests of animal enthusiasts everywhere.
Chickens
Can Chickens Eat Rhubarb? Safe Feeding Tips
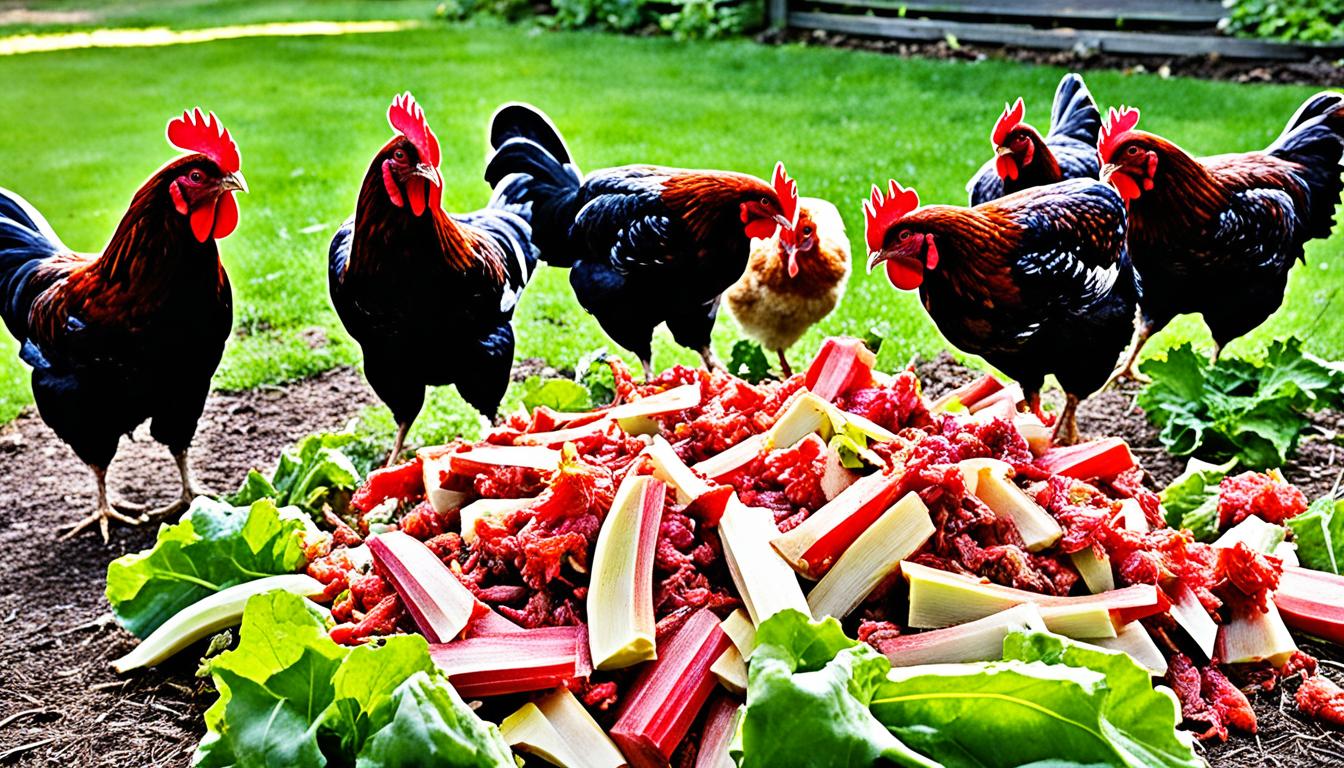

Did you know that chickens are able to consume rhubarb stalks, but they should not eat the leaves?
Chickens are known to enjoy a wide variety of foods, but when it comes to rhubarb, there are some important considerations to keep in mind. While the stalks of rhubarb can provide chickens with valuable vitamins and minerals, the leaves contain oxalic acid, which can be harmful to their health. In this article, we will explore the safe ways to feed chickens rhubarb and the potential risks it may pose.
Key Takeaways:
- Chickens can eat rhubarb stalks in moderation, but the leaves should be avoided due to their oxalic acid content.
- Feeding chickens rhubarb in small amounts can provide them with essential vitamins and minerals.
- Too much sugar in rhubarb, such as in pies or crumbles, can be harmful to chickens.
- It’s crucial to be cautious and only feed chickens rhubarb stalks in tiny amounts fed occasionally.
- Follow the 90/10 feeding rule to ensure a balanced diet for chickens, with rhubarb treats in small quantities.
Can Chickens Eat Rhubarb Stalks?
Chickens can enjoy the deliciousness of rhubarb stalks, but it’s important to feed them in moderation. Rhubarb stalks are a safe and healthy snack for chickens, providing them with essential vitamins and minerals like Vitamin A and Vitamin C, as well as dietary fiber.
To make it easier for your feathered friends to enjoy this treat, cut the rhubarb stalks into bite-size pieces. You can scatter the pieces around their feeding area or mix them in with their regular feed for added variety. Just remember, small amounts are the key to ensuring their well-being.
Rhubarb stalks offer a refreshing crunch and tangy flavor that chickens find irresistible. However, it’s essential to remember that while the stalks are safe for consumption, other parts of the rhubarb plant, such as the leaves, flowers, and seeds, contain oxalic acid and should be strictly avoided as they can be toxic to your chickens.
Providing your chickens with rhubarb stalks as an occasional treat can add nutritional variety to their diet, keeping them happy and healthy. Just be sure to practice moderation and always prioritize their safety.
Health Benefits of Rhubarb Stalks for Chickens
Rhubarb stalks are packed with essential nutrients that can contribute to your chickens’ overall well-being. Here’s a quick rundown of the vitamins and minerals they can gain from enjoying this tasty treat:
| Nutrients | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Supports healthy vision, immune function, and cellular growth |
| Vitamin C | Acts as an antioxidant, promotes growth, and boosts the immune system |
| Dietary Fiber | Aids in digestion and promotes a healthy digestive system |
Why Can’t Chickens Eat Rhubarb Leaves?
Chickens cannot eat rhubarb leaves due to the high content of oxalic acid. Oxalic acid is a naturally occurring compound found in many plants, including rhubarb leaves. While rhubarb stalks can be safely consumed by chickens in small amounts, the leaves contain a concentrated amount of oxalic acid, which can be toxic to them.
Oxalic acid can lead to kidney failure and can be fatal for chickens if ingested in large quantities. The oxalic acid in rhubarb leaves binds with calcium in the chicken’s body, forming crystals that can cause damage to their kidneys.
It’s crucial to avoid feeding chickens rhubarb leaves, as well as other parts of the rhubarb plant like flowers and seeds, which also contain oxalic acid. Feeding these parts to chickens can put their health at risk.
Effects of Oxalic Acid on Chickens
“The presence of oxalic acid in rhubarb leaves can have severe consequences for chickens’ health. It’s important to be aware of the potential dangers and take necessary precautions.”
The ingestion of oxalic acid in rhubarb leaves can result in symptoms such as weakness, difficulty breathing, trembling, and decreased appetite in chickens. Over time, the crystals formed by the oxalic acid can lead to kidney damage, which may cause kidney failure and other complications.
Chickens should never have access to rhubarb leaves, and it’s crucial to prevent them from consuming these potentially harmful plant parts.
Comparison of Oxalic Acid Content
| Rhubarb Part | Oxalic Acid Content |
|---|---|
| Rhubarb Stalks | Low |
| Rhubarb Leaves | High |
| Rhubarb Flowers | High |
| Rhubarb Seeds | High |
Comparison of oxalic acid content in different parts of the rhubarb plant.
As shown in the table above, rhubarb leaves, flowers, and seeds contain a significantly higher concentration of oxalic acid compared to rhubarb stalks. It’s important to be cautious and ensure that chickens do not have access to these parts of the rhubarb plant.

What Happens if Chickens Eat Rhubarb?
When chickens consume rhubarb, it can have detrimental effects on their health. The consequences of chickens eating rhubarb can include:
- Diarrhea: Chickens may experience loose stools or increased bowel movements after consuming rhubarb.
- Abdominal Pain: The oxalic acid present in rhubarb can irritate the digestive system, leading to discomfort and abdominal pain in chickens.
- Lethargy: Chickens may become lethargic, displaying decreased activity levels and reduced energy after ingesting rhubarb.
- Abnormal Behaviors: Eating rhubarb can cause chickens to exhibit abnormal behaviors such as decreased appetite, depression, or reduced vocalization.
It is vital to recognize the signs of rhubarb poisoning in chickens and take immediate action to prevent severe illness or even death. If you suspect your chickens have consumed rhubarb and are displaying any of these symptoms, it is best to seek veterinary care as soon as possible.
“Feeding rhubarb to chickens can lead to diarrhea, abdominal pain, lethargy, and abnormal behaviors.”
It is advisable to avoid feeding rhubarb to chickens altogether as a precautionary measure, considering its potential adverse effects. Instead, focus on offering them a balanced diet that consists of safe and nutritionally appropriate foods.
In the table below, you will find a summary of the potential consequences of chickens eating rhubarb:
| Consequences | Description |
|---|---|
| Diarrhea | Loose stools or increased bowel movements |
| Abdominal Pain | Discomfort and pain in the abdominal region |
| Lethargy | Decreased activity levels and reduced energy |
| Abnormal Behaviors | Decreased appetite, depression, or reduced vocalization |
It is crucial to prioritize the well-being of your chickens and make sure to provide them with a diet that is safe and suitable for their nutritional needs. Understanding the potential consequences of feeding rhubarb to chickens can help you make informed decisions and ensure their health and happiness.
How to Treat Rhubarb Poisoning in Chickens?
If your chickens have eaten rhubarb and show signs of poisoning, there are a few home remedies you can try to help alleviate their symptoms and aid in their recovery. Administering a flush can help flush out the toxins from their body and promote healing. Two popular home remedies for rhubarb poisoning in chickens are the Epsom salt flush and the molasses flush.
Epsom Salt Flush
Epsom salt is known for its laxative properties, which can aid in the removal of toxins from the chicken’s system. Here’s how to administer the Epsom salt flush:
- Dissolve 1 tablespoon of Epsom salt in 1 cup of warm water.
- Using a syringe or dropper, gently administer the mixture into the back of the chicken’s throat.
- Ensure the chicken swallows the mixture.
- Repeat the process every 4 to 6 hours, as needed.
Molasses Flush
Molasses acts as a natural laxative and can help flush out toxins from the chicken’s digestive system. Here’s how to administer the molasses flush:
- Mix 1 tablespoon of molasses with 1 cup of warm water.
- Using a syringe or dropper, gently administer the mixture into the back of the chicken’s throat.
- Ensure the chicken swallows the mixture.
- Repeat the process every 4 to 6 hours, as needed.
These home remedies can be effective in treating mild cases of rhubarb poisoning in chickens. However, if the symptoms worsen or persist, it’s important to consult a veterinarian for further guidance and treatment.
It is worth noting that prevention is better than cure when it comes to rhubarb poisoning. It is essential to keep chickens away from rhubarb plants and ensure they have access to a safe and balanced diet. Regularly monitoring their feeding habits and providing appropriate nutrition can help minimize the risk of rhubarb poisoning in chickens.
Nutritional Analysis of Rhubarb for Chickens
When it comes to the nutritional value of rhubarb for chickens, it’s important to understand what this vibrant stalk vegetable provides. Rhubarb stalks contain a variety of essential nutrients that can contribute to the overall health of your chickens. Let’s take a closer look at the vitamins and minerals found in rhubarb that can benefit your feathered friends.
Vitamins in Rhubarb for Chickens
Rhubarb is a good source of several vitamins that are vital for the well-being of chickens. One of the key vitamins found in rhubarb is Vitamin C. This vitamin plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system and promoting overall health. Chickens, just like humans, require Vitamin C to maintain optimal health and combat diseases.
In addition to Vitamin C, rhubarb also contains Vitamin A. This vitamin is essential for maintaining healthy vision, promoting growth and development, and supporting the reproductive system. Vitamin A is crucial for chickens’ overall well-being and can contribute to their overall vitality.
Minerals in Rhubarb for Chickens
Rhubarb is not just a source of vitamins but also provides vital minerals that can benefit chickens. One of these minerals is calcium. Calcium is essential for maintaining strong bones and eggshell production in hens. Including rhubarb in your chickens’ diet can help fulfill their calcium requirements and contribute to their overall skeletal health.
Another important mineral found in rhubarb is iron. Iron is necessary for the production of healthy red blood cells, which help transport oxygen throughout the body. By incorporating rhubarb into their diet, you can help ensure your chickens receive adequate iron levels to support their overall well-being.
Furthermore, rhubarb contains potassium, a mineral that plays a vital role in regulating fluid balance, muscle function, and nerve signals. Including rhubarb as a part of your chickens’ diet can help maintain these essential functions and support their overall health and vitality.
It’s important to note that while rhubarb can provide certain vitamins and minerals beneficial to chickens, it should be fed in moderation. Rhubarb stalks also contain a relatively high sugar content, which can be harmful if consumed in excess. Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure that rhubarb is offered as a treat rather than a staple part of their diet.
Overall, rhubarb can be a nutritious addition to your chickens’ diet when fed responsibly and in appropriate amounts. Its vitamin and mineral content, including Vitamin C, Vitamin A, calcium, iron, and potassium, can contribute to their overall health and well-being. Remember to always provide rhubarb in moderation and prioritize a balanced diet for your feathered friends.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g of Raw Rhubarb Stalks |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 13.8 mg |
| Vitamin A | 102 IU |
| Calcium | 86 mg |
| Iron | 0.22 mg |
| Potassium | 288 mg |

- USDA FoodData Central: Rhubarb, raw. (2021, May 31).
- Raising Happy Chickens: Understanding and Caring for Chickens’ Nutritional Needs.
Best Plants to Feed Chickens
Chickens love to explore and peck at a variety of plants. While their main diet should consist of complete feeds, offering them safe plants as treats can be enjoyable for them. Here are some plants that chickens can eat:
- Lettuce
- Beets
- Broccoli
- Carrots
- Kale
- Mint
- Parsley
These plants provide additional nutrients and flavors to their diet. Chickens can enjoy small quantities of these plants as an occasional snack. However, it’s important to note that while these plants are safe, they should still be offered in moderation. Too much of any plant can upset their digestive system.
It’s crucial to avoid feeding chickens toxic plants that can harm their health. Some plants to avoid feeding chickens include:
- Onions
- Raw beans
These plants can be toxic to chickens and should be kept away from their reach. Always prioritize their safety and well-being when offering plants as treats.
Note: Keep in mind that the plant suggestions provided here are not an exhaustive list. It’s always important to do thorough research and consult with poultry experts to ensure the plants you offer to your chickens are safe and appropriate for their consumption.
Worst Plants to Avoid Feeding Chickens
When it comes to feeding chickens, it’s important to be aware of the plants that can be toxic and dangerous to them. Certain plants can cause various health issues and even be fatal if consumed by chickens. Here are some of the worst plants that you should avoid feeding your chickens:
- Onions: Onions contain compounds that can lead to anemia and liver problems in chickens. It’s best to keep onions away from their diet to ensure their well-being.
- Raw beans: Raw beans contain a compound called hemagglutinin, which can be harmful to chickens. It can interfere with digestion and nutrient absorption, causing digestive issues and other health problems.
- Avocados (except for the flesh): While avocados themselves are not toxic to chickens, the leaves, bark, and pit contain a substance called persin, which can be harmful. It’s important to only offer chickens the flesh of avocados and avoid feeding them any other parts of the plant.
- Moldy or rotten foods: Moldy or rotten foods can contain harmful molds and bacteria that can cause digestive issues and other health problems in chickens. It’s important to ensure that the food you offer your chickens is fresh and free from any signs of spoilage.
- Very salty foods: Excessive salt can be detrimental to a chicken’s health, leading to electrolyte imbalances and dehydration. It’s best to avoid feeding them very salty foods to maintain their well-being.
By being aware of these plants and avoiding them in your chickens’ diet, you can help keep them safe and healthy. It’s always a good idea to research and consult with experts to ensure that you are providing the best diet for your feathered friends.
| Plants | Potential Health Issues |
|---|---|
| Onions | Anemia, liver problems |
| Raw beans | Digestive issues, nutrient absorption problems |
| Avocados (except for the flesh) | Persin toxicity |
| Moldy or rotten foods | Digestive issues, bacterial infections |
| Very salty foods | Electrolyte imbalances, dehydration |
How to Keep Chickens Safe from Rhubarb Plants
To protect your chickens from rhubarb plants, it’s important to take certain precautions and create a safe environment. Follow these tips to ensure the well-being of your feathered friends:
1. Gate off Areas with Rhubarb Plants
Start by securing the areas where rhubarb plants are growing. Install sturdy fencing or use chicken wire to create a barrier around the plants. This will prevent chickens from accessing the rhubarb and potentially ingesting the harmful parts.
2. Restrict Access to Gardens
In addition to gating off the rhubarb plants, restrict your chickens’ access to gardens where rhubarb may be present. Utilize fences, netting, or other forms of physical barriers to keep them out of these areas. This will prevent accidental ingestion or nibbling on rhubarb stalks.
3. Separate or Remove Toxic Plants
Along with rhubarb, there may be other toxic plants in your garden that can harm chickens. Take the time to identify and remove or separate these plants from the areas where your chickens roam. This precaution will further minimize the risk of exposure to harmful vegetation.
4. Create a Chicken-Friendly Garden
Consider creating a dedicated chicken-friendly garden where your chickens can freely explore and forage. Plant safe and nutritious vegetation, such as lettuces, beets, kale, and herbs like mint and parsley. This provides an alternative and safe environment for your chickens to enjoy without the risk of encountering harmful plants.
5. Avoid Planting Rhubarb
If you have chickens or other pets and animals, it’s best to avoid planting rhubarb altogether. By eliminating rhubarb from your garden, you eliminate the potential danger it poses to your chickens. Instead, focus on cultivating plants that are safe and beneficial for your feathered companions.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure the safety of your chickens and protect them from the potential hazards of rhubarb plants. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to keeping your chickens healthy and happy!
| Harmful Plants | Safe Plants |
|---|---|
| Rhubarb leaves | Lettuce |
| Onions | Beets |
| Raw beans | Kale |
| Avocado (except for flesh) | Mint |
| Moldy or rotten foods | Parsley |
| Very salty foods |
90/10 Feeding Rule for Chickens
When it comes to feeding chickens, maintaining a balanced diet is essential for their health and well-being. The 90/10 feeding rule provides a guideline on how to achieve this balance. According to this rule, 90% of a chicken’s diet should consist of complete feed, while the remaining 10% can be treats and other food sources.
Complete feeds are specially formulated to provide chickens with all the necessary nutrients they need to thrive. These feeds typically contain a balanced combination of grains, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, ensuring that your feathered friends receive a well-rounded diet. By offering complete feed as the main component of their diet, you are providing a solid foundation for their nutritional needs.
On the other hand, the remaining 10% of a chicken’s diet can be allocated to treats and supplementary food sources. Treats can come in the form of kitchen scraps, vegetables, fruits, or even insects that your chickens can forage for. However, it’s important to note that treats should be given in moderation to avoid overfeeding and upsetting the balance of their diet.
Following the 90/10 rule ensures that chickens receive the necessary nutrients from their complete feed while still enjoying the occasional treat. It’s important to resist the temptation to go overboard with treats, as excessive indulgence can lead to dietary imbalances and unbalanced growth in chickens.
Remember, a balanced diet is vital for a chicken’s overall health, ensuring they receive the right nutrients to support their immune system, feather quality, and egg production.
By adhering to the 90/10 feeding rule, you can be confident that your chickens are receiving a nutritionally balanced diet. Not only does this promote their well-being, but it also contributes to their optimal growth and development.
The Benefits of the 90/10 Feeding Rule:
- Provides a balanced diet with essential nutrients
- Promotes healthy growth and development
- Reduces the risk of dietary imbalances
- Maintains optimal egg production and feather quality
- Prevents overfeeding and obesity
Foods That Increase Chicken’s Appetite
If your chickens are experiencing a decreased appetite, it’s important to find ways to stimulate their appetite and encourage them to eat. By offering certain foods known to increase a chicken’s appetite, you can help them regain their strength and ensure they are getting the necessary nutrition. Here are some appetite-stimulating foods for chickens:
- Hard-boiled eggs: Eggs are a rich source of protein and can be a highly enticing treat for chickens. Chop the eggs into small pieces and offer them as a snack.
- Cooked vegetables: Vegetables like carrots, peas, sweet potatoes, and green beans can be cooked and mashed or chopped to create a soft and easy-to-eat meal for chickens.
- Cooked meat: Leftover cooked meat, such as chicken or turkey, can be shredded and added to their regular feed or offered as a separate treat. Make sure to remove any bones before feeding.
- Herbs: Fresh herbs like parsley, basil, and oregano can help enhance the flavor of their feed and entice chickens to eat. Chop the herbs finely and sprinkle them over their food.
- Electrolytes: Electrolyte solutions designed for chickens can help replenish lost nutrients and stimulate their appetite. Follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer.
- Supplements: There are specific supplements available in the market that can boost a chicken’s appetite. Consult with a veterinarian or poultry specialist to determine the best supplement for your chickens.
Remember, it’s important to introduce these appetite-stimulating foods gradually and in moderation. Observe your chickens’ response and adjust the quantities accordingly. Offering a varied and balanced diet with these appetite-boosting foods can help improve your chickens’ appetite and overall well-being.
Nutritional Analysis of Appetite-Stimulating Foods
Here is a nutritional analysis of the appetite-stimulating foods mentioned above:
| Food | Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Hard-boiled eggs | Protein, vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin B12 |
| Cooked vegetables | Fiber, vitamins (A, C, K), potassium |
| Cooked meat | Protein, iron, zinc, vitamin B12 |
| Herbs | Antioxidants, vitamins, minerals |
| Electrolytes | Essential minerals (sodium, potassium, magnesium) |
| Supplements | Varies depending on the supplement |
Offering these foods to your chickens can provide nutritional benefits and help increase their appetite. However, it’s important to remember that a balanced diet is crucial for their overall health. Consult with a veterinarian or poultry nutritionist to ensure you are providing a well-rounded diet that meets their nutritional needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is safe for chickens to eat rhubarb stalks in moderation. However, they should avoid consuming the leaves, flowers, and seeds of the rhubarb plant due to their high oxalic acid content. While rhubarb stalks can provide chickens with beneficial vitamins and minerals, it is important to feed them in small amounts as part of a balanced diet.
Adhering to the 90/10 feeding rule is crucial for maintaining the health of chickens. This rule suggests that 90% of their diet should consist of complete feeds, while the remaining 10% can include treats and supplemental foods like rhubarb stalks. By following this rule, chicken owners can ensure that their feathered friends receive adequate nutrition without overindulging in potentially harmful treats.
Furthermore, it is essential to prioritize the safety of chickens by preventing access to toxic plants like rhubarb. This can be achieved by gating off areas where rhubarb grows and planting chicken-friendly gardens with safe plant options. By creating a secure environment, chicken owners can minimize the risk of accidental consumption of harmful plants and keep their chickens healthy and thriving.FAQ
Can chickens eat rhubarb stalks?
Why can’t chickens eat rhubarb leaves?
What happens if chickens eat rhubarb?
How to treat rhubarb poisoning in chickens?
What is the nutritional analysis of rhubarb for chickens?
What are the best plants to feed chickens?
What are the worst plants to avoid feeding chickens?
How to keep chickens safe from rhubarb plants?
What is the 90/10 feeding rule for chickens?
What are some foods that increase a chicken’s appetite?
Laura is a versatile writer and editor whose passion for animals shines through in her work. With a keen understanding of language and a love for storytelling, Laura crafts compelling narratives that captivate our audience and inspire action regarding animal welfare. Whether she’s delving into the latest research or sharing heartwarming stories of animal companionship, Laura’s work will leave a lasting impression on all who read it.
Chickens
Can Chickens Eat Persimmons? Safe Feeding Tips
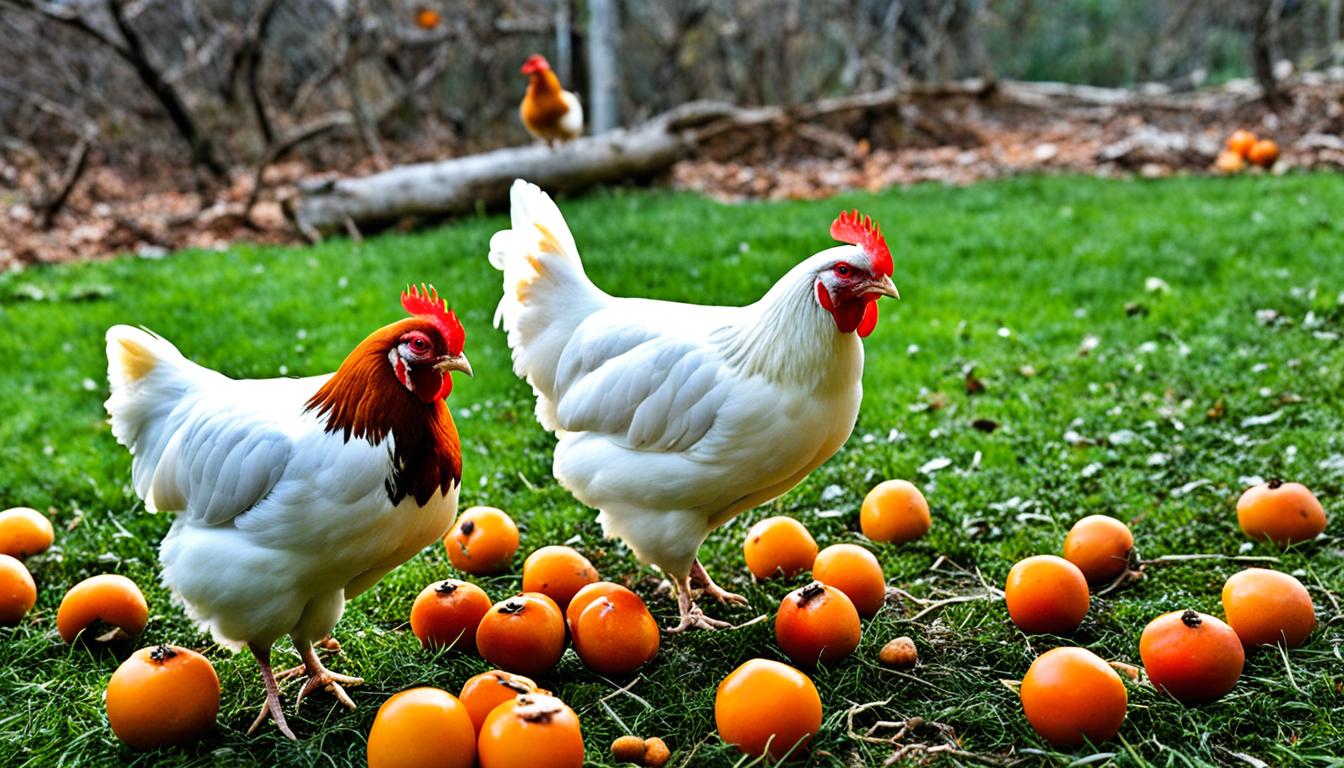

Did you know that chickens can indulge in a diverse range of fruits? Surprisingly, chickens can also enjoy persimmons! These tasty fruits not only give your feathered friends a delicious snack but also provide important nutrients to keep them healthy. However, before you start giving persimmons to your flock, it’s important to learn the proper feeding guidelines to keep them safe and well.
Key Takeaways:
- Chickens can safely eat persimmons in moderation.
- Persimmons provide a vitamin boost, especially during the cold winter months.
- It’s important to limit persimmon intake due to their high sugar content.
- Introduce persimmons gradually to chickens and observe their reactions.
- Consult with a veterinarian for personalized advice on feeding persimmons to your flock.
Persimmons: A Berry for Chickens
When it comes to feeding chickens, the options can sometimes seem limited. However, one fruit that can provide a tasty and nutritious addition to their diet is the persimmon. Whether it’s the Fuyu, Hachiya, or American variety, persimmons are considered a type of berry that chickens can safely enjoy.
Persimmons come in different sizes and colors, ranging from yellow to dark red or orange. This vibrant range adds visual appeal to the chickens’ diet while providing a delectable treat. Chickens are likely to enjoy the sweet and succulent taste of persimmons, making it a popular choice among poultry enthusiasts.
However, it’s important to exercise moderation when feeding persimmons to chickens. Just like other fruits with a high sugar content, persimmons should be given in limited amounts to avoid overindulgence. While chickens can benefit from the vitamins and nutrients found in persimmons, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet and not rely solely on this fruity delicacy.
Nutritional Benefits of Persimmons for Chickens
Persimmons offer several nutritional benefits for chickens. They are rich in vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin B6. These vitamins support the immune system, promote healthy skin, and boost metabolism. Persimmons also contain folate, thiamin, riboflavin, manganese, and other essential minerals that are vital for the overall health and well-being of chickens.
When chickens consume persimmons, they receive a nutritious and delicious treat that can supplement their regular feed. These vibrant fruits provide a natural source of vitamins and minerals, which are crucial for their growth, development, and overall vitality.
Vitamins in Persimmons
Persimmons are particularly rich in vitamins that offer a range of health benefits for chickens. Let’s take a closer look at the key vitamins found in persimmons and their roles in supporting chickens’ health:
1. Vitamin A
Vitamin A plays a crucial role in maintaining a strong immune system, enhancing vision, and promoting healthy skin and feathers in chickens. It also supports their reproductive health and improves their overall resistance to diseases.
2. Vitamin C
Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting chickens’ cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also plays a vital role in collagen synthesis, which is essential for healthy skin, bones, and connective tissues.
3. Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is involved in various metabolic processes in chickens, including protein synthesis and red blood cell production. It also supports their nervous and immune systems, contributing to their overall health and vitality.
In addition to these key vitamins, persimmons contain other essential nutrients, including folate, thiamin, riboflavin, and manganese. These nutrients play important roles in various bodily functions, such as energy production, DNA synthesis, and bone health in chickens.
However, it’s important to feed persimmons in moderation to avoid oversupplying these nutrients and disrupting the chickens’ balanced diet. Too much of a good thing can be harmful, so it’s crucial to maintain a proper balance between persimmons and their regular feed.
To ensure chickens receive the nutritional benefits of persimmons without overindulging, it’s recommended to offer them small quantities of persimmons as occasional treats. This way, chickens can enjoy the delicious flavor and reap the rewards of the vitamins and minerals found in these delightful fruits.
| Vitamin | Function |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Enhances immune system, promotes healthy skin and feathers |
| Vitamin C | Acts as an antioxidant, improves skin health, and supports collagen synthesis |
| Vitamin B6 | Aids in metabolism, protein synthesis, and immune system function |
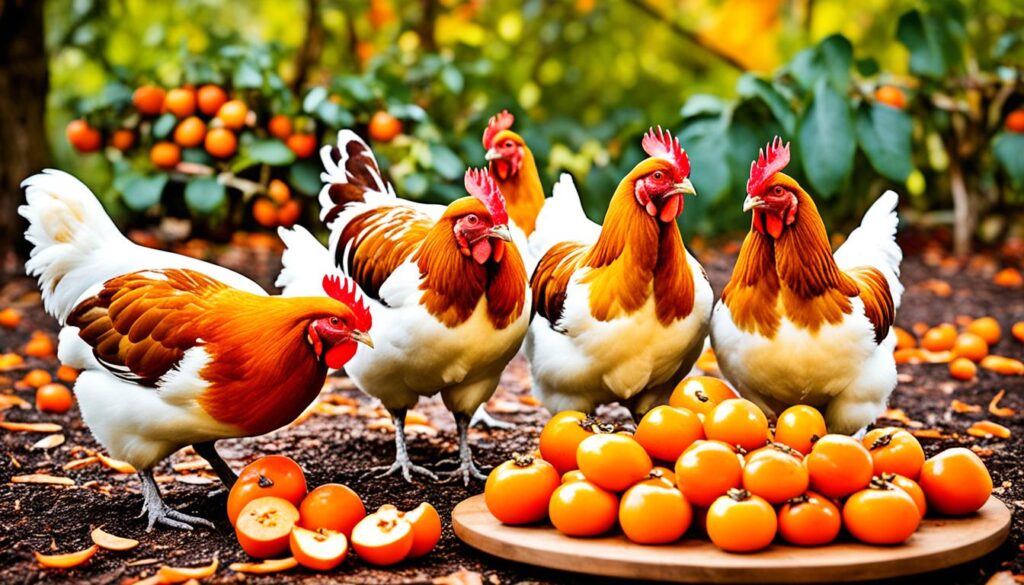

By including persimmons as part of a varied and balanced diet, chickens can enjoy the nutritional benefits of these vibrant fruits while leading healthy and active lives.
Feeding Persimmons to Chickens
To introduce persimmons to chickens, it’s important to start slowly and observe their reaction. Chickens may be hesitant to try new foods, so gradual introduction is key. One effective method is to hang a piece of persimmon in the chicken coop, allowing them to examine it before giving it a try. The soft skin and flesh of persimmons make them easy for chickens to consume, so there’s no need to cut them into small pieces or remove the skin.
Feeding Tips:
- Start by offering small pieces of persimmon.
- Observe the chickens’ reaction and appetite.
- Gradually increase the quantity of persimmons over time.
- Ensure persimmons are ripe and fresh for the best taste.
Once your chickens are accustomed to persimmons, you can make the feeding experience more enjoyable by cutting the fruit into different shapes or even hiding pieces for them to find. This adds a fun and stimulating element to their diet.
Remember, while persimmons are a healthy treat, they should be given in moderation to maintain a balanced diet for the chickens.
Potential Drawbacks of Persimmons for Chickens
While persimmons are generally safe for chickens to consume, there are a few potential drawbacks and risks associated with feeding persimmons to them. It’s essential for chicken owners to be aware of these considerations to ensure the well-being and health of their flock.
High Sugar Content: One concern when it comes to feeding persimmons to chickens is their high sugar content. Persimmons are naturally sweet fruits, and excessive consumption of high-sugar foods can lead to various health issues for chickens. It is crucial to moderate the quantity of persimmons and avoid feeding them in large quantities to prevent blood sugar imbalances and weight gain.
Health Conditions: Chickens with certain health conditions, such as diabetes or obesity, should be cautious when consuming persimmons. The high sugar content in persimmons can exacerbate these conditions and potentially lead to further health complications. It is advisable to consult with a veterinarian for specific dietary guidelines if your chickens have pre-existing health conditions.
Potential Intestinal Blockages: Another risk associated with persimmons for chickens is the presence of seeds. Persimmon seeds contain tannins, which can clump together and potentially lead to intestinal blockages if chickens consume them excessively. It’s crucial to monitor chickens’ intake and ensure that they don’t overindulge in persimmon seeds, reducing the risk of digestive problems and blockages.
Did You Know? Chickens have a gizzard, which helps them grind and digest their food. However, the seeds of fruits like persimmons can be challenging for a chicken’s digestive system to break down, increasing the risk of blockages.
| Drawbacks of Persimmons for Chickens | Risks of Feeding Persimmons to Chickens |
|---|---|
| High sugar content | Potential blood sugar imbalances |
| Health conditions (diabetes, obesity) | Potential exacerbation of existing health conditions |
| Presence of tannin in seeds | Potential intestinal blockages |
By being cautious and monitoring the quantity and frequency of persimmon feedings, chicken owners can minimize the drawbacks and risks associated with feeding persimmons to their flock. It is always recommended to provide a balanced and varied diet for chickens, consulting with a veterinarian if necessary, to ensure their overall health and well-being.

Feeding Persimmon Leaves to Chickens
Chickens can enjoy the benefits of persimmon leaves as part of their diet, but it’s important to offer them in moderation. Persimmon leaves provide fiber and other nutrients that can contribute to the overall digestion and well-being of your chickens.
Before giving persimmon leaves to your chickens, make sure to wash them thoroughly to remove any potential contaminants. Wilted or spoiled leaves should be avoided since they may contain toxins that could be harmful to your chickens.
When introducing persimmon leaves to your chickens for the first time, start with a small quantity and observe their reaction. Some chickens may have preferences, while others may take time to adjust to this new treat. Gradually increase the amount based on their response.
Feeding persimmon leaves to your chickens can be an excellent way to add variety to their diet, allowing them to enjoy the benefits of different nutrients. While persimmon leaves are generally safe for chickens, it’s always essential to monitor their diet and consult with a veterinarian for personalized advice.
Benefits of Persimmon Leaves for Chickens
Persimmon leaves offer several advantages for chickens. They are a rich source of fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes a healthy gut. Additionally, these leaves contain essential minerals and vitamins, such as potassium, manganese, and vitamin C, which contribute to the overall well-being and immune system of your chickens.
The fiber in persimmon leaves can help regulate bowel movements and prevent digestive issues in chickens. It assists in maintaining a healthy and balanced digestive system, allowing your chickens to better absorb nutrients from their food.
The table below highlights some of the key nutritional values of persimmon leaves:
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Fiber | 6g |
| Potassium | 214mg |
| Calcium | 81mg |
| Manganese | 1.5mg |
| Vitamin C | 43mg |
Remember, while persimmon leaves are beneficial for chickens, it’s important to offer them as part of a diverse diet that includes other healthy food options. Providing a balanced diet is key to maintaining the overall health and happiness of your flock.
Remember to always introduce new foods gradually and keep a close eye on your chickens’ reaction. By offering persimmon leaves in moderation, you can provide your chickens with a nutritious and enjoyable addition to their diet.
Foods to Avoid Giving Chickens
While chickens can enjoy a variety of foods, it’s important to be aware of the foods that are toxic or harmful to them. By avoiding these foods, you can ensure the health and well-being of your chickens. Some of the foods that should be kept away from chickens include:
- Chocolate: Chocolate contains theobromine, which is toxic to chickens and can lead to symptoms like increased heart rate and tremors.
- Avocado: Avocado contains persin, a toxin that can be lethal to chickens if ingested in large quantities. It’s best to completely avoid feeding avocados to chickens.
- Lemons and oranges: Citrus fruits like lemons and oranges are highly acidic, which can upset the digestive system of chickens. While small amounts can be given as an occasional treat, it’s best to limit their intake.
- Processed foods: Foods that are high in salt, sugar, or artificial additives should be avoided. These can be harmful to chickens and can lead to various health issues.
Instead of these toxic or unhealthy foods, focus on offering safe and nutritious options for your chickens. Here are some examples:
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, carrots, peas, and cucumbers are all excellent choices for chickens. These vegetables provide essential vitamins and minerals.
- Fruits: Safe fruits for chickens include apples, berries, and watermelon. These fruits offer natural sweetness and hydration.
- Grains: Whole grains like oats and rice can be given to chickens in small amounts for added nutrition.
- Protein-rich options: Eggs or mealworms are great sources of protein for chickens. These can be offered as treats to supplement their diet.
By avoiding toxic foods and focusing on safe and nutritious options, you can ensure that your chickens stay healthy and happy.
| Toxic Foods for Chickens | Safe and Nutritious Alternatives |
|---|---|
| Chocolate | Vegetables: leafy greens, carrots, peas |
| Avocado | Fruits: apples, berries, watermelon |
| Lemons and oranges | Grains: oats, rice |
| Processed foods | Protein-rich options: eggs, mealworms |

Can Chickens Eat Persimmons Skin?
Chickens can safely enjoy persimmon skins as part of their diet, as long as the skin is clean and free from pesticides. Persimmon skins contain additional nutrients and fiber, which can be beneficial to the chickens’ health. However, it’s important to offer the skin in moderation to avoid digestive issues, as it can be high in sugar. Introducing new foods gradually to chickens and monitoring their reactions is recommended to ensure their well-being. If any discomfort or digestive problems arise, it’s advisable to reduce or eliminate persimmon skin from their diet.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Value | Persimmon skins are rich in nutrients such as vitamins and fiber, which can contribute to the overall health of the chickens. |
| Moderation | Offering persimmon skins in moderation can help prevent excessive sugar intake and potential digestive issues. |
| Introduction | Gradually introducing new foods like persimmon skins allows for proper adjustment and observation of any adverse reactions. |
Feeding persimmon skins to chickens provides them with additional nutrients while enticing their taste buds. However, it’s essential to remember that persimmon skins should not replace their main diet, which should primarily consist of balanced commercial chicken feed.
List of Other Safe Fruits for Chickens
- Apples
- Bananas
- Berries
- Cantaloupe
- Grapes
- Kiwi
- Mango
- Peaches
- Pumpkins
- Watermelon
Remember to prioritize their regular feed and consult with a veterinarian for personalized advice.

Including a variety of fruits in a chicken’s diet can provide essential vitamins, minerals, and hydration. However, it’s crucial to offer fruits as occasional treats rather than a substantial part of their daily nutrition. By maintaining a balanced and varied diet, chickens can enjoy persimmon skins and other safe fruits as part of a healthy lifestyle.
What Fruits Should I Give to My Chickens?
Chickens can enjoy a variety of fruits as occasional treats. Incorporating safe fruits into their diet provides essential vitamins, minerals, and hydration. However, it’s important to remember that fruits should only make up a small portion of their overall diet, with the main focus on a balanced commercial chicken feed.
Here are some safe fruits that you can give to your chickens:
- Apples
- Bananas
- Berries
- Cantaloupe
- Grapes
- Kiwi
- Mango
- Peaches
- Pumpkins
- Watermelon
These fruits not only provide a tasty treat but also offer a range of nutritional benefits. For example, bananas are a great source of potassium, while berries are packed with antioxidants. Watermelon and cantaloupe help keep chickens hydrated, especially during hot summer months.
It’s important to introduce these fruits in moderation to prevent overindulgence and ensure a balanced diet. Too much fruit can be disruptive to their digestive system or lead to obesity. Monitor their intake and observe any changes in behavior or health to ensure their well-being.
Benefits of Safe Fruits for Chickens
| Fruit | Nutritional Benefits |
|---|---|
| Apples | High in fiber and contain vitamins A, C, and E |
| Bananas | Rich in potassium and vitamin B6 |
| Berries | Packed with antioxidants and vitamin C |
| Cantaloupe | Hydrating and a good source of vitamins A and C |
| Grapes | Contain antioxidants and vitamins C and K |
| Kiwi | Rich in vitamin C, fiber, and folate |
| Mango | High in vitamins A and C |
| Peaches | Provide vitamins A and C |
| Pumpkins | Rich in beta-carotene and a good source of fiber |
| Watermelon | Hydrating and contains vitamins A and C |
Remember to always wash fruits thoroughly, remove any pits or seeds, and serve them in appropriate sizes for chickens. By offering a variety of safe fruits as occasional treats, you can keep your chickens happy, healthy, and entertained.
Conclusion
In conclusion, persimmons can be safely incorporated into a chicken’s diet as part of a balanced feeding routine. These delicious fruits offer a range of nutritional benefits, including essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to the overall well-being of chickens.
However, it’s important to feed persimmons to chickens in moderation. While persimmons are a natural source of sweetness, their high sugar content can cause issues if consumed excessively. Therefore, it’s crucial to monitor the quantity of persimmons and ensure they are not overindulging.
Additionally, it’s essential to consider potential drawbacks when feeding persimmons to chickens. Chickens with specific health conditions, such as diabetes or obesity, should have their persimmon intake limited. Moreover, care should be taken to prevent intestinal blockages that may occur if chickens consume an excessive amount of persimmon seeds.
To safely introduce persimmons into a chicken’s diet, it’s recommended to start gradually and observe their response. By offering a varied selection of treats alongside persimmons, chickens can enjoy a diverse diet while receiving the necessary nutrients. Prioritizing their regular feed is also vital to maintain a balanced nutritional intake.
FAQ
Can chickens eat persimmons?
Do persimmons provide any nutritional benefits to chickens?
How should I introduce persimmons to my chickens?
Are there any potential risks or drawbacks to feeding persimmons to chickens?
Can chickens eat persimmon leaves?
Are there any foods that I should avoid giving to chickens?
Can chickens eat persimmon skin?
What other fruits can I give to my chickens?
Is it safe to feed persimmons to chickens?
Paul’s love for animals knows no bounds. As a dedicated writer and animal lover, Paul brings a unique perspective to our team. His firsthand experiences with various animals enrich our content and provide valuable insights into their behavior and needs. Whether he’s sharing tips for pet care or shedding light on pressing conservation issues, Paul’s passion for animals shines through in everything he does.
-

 Vetted1 month ago
Vetted1 month ago15 Best Dog Food Brands Recommended by Vets for Healthy and Happy Pups
-

 Vetted1 month ago
Vetted1 month ago14 Best Homemade Dog Food Recipes Your Pup Will Love – Vet Approved & Nutritious
-

 Vetted1 month ago
Vetted1 month ago15 Best Cat Foods for Managing Hyperthyroidism – Vet Approved and Feline Friendly
-

 Vetted3 weeks ago
Vetted3 weeks ago15 Best Dog Foods for Kidney Disease – Expert Recommendations for Your Pet's Health
-

 Vetted2 weeks ago
Vetted2 weeks ago15 Best Affordable Cat Foods That Won't Break the Bank
-

 Deers1 month ago
Deers1 month agoCaring for Baby Deer: Tips for Healthy Fawns
-
 Cats6 days ago
Cats6 days agoCat Weight Chart by Age: Kitten to Senior in Lbs
-

 Vetted1 month ago
Vetted1 month ago15 Best Kibble Dog Foods for a Healthy and Happy Pup






















