Animals
Which Small Animal Looks Like a Chipmunk?
Are you curious about animals resembling chipmunks? Discover fascinating creatures with unique stripes and survival strategies in this insightful article.
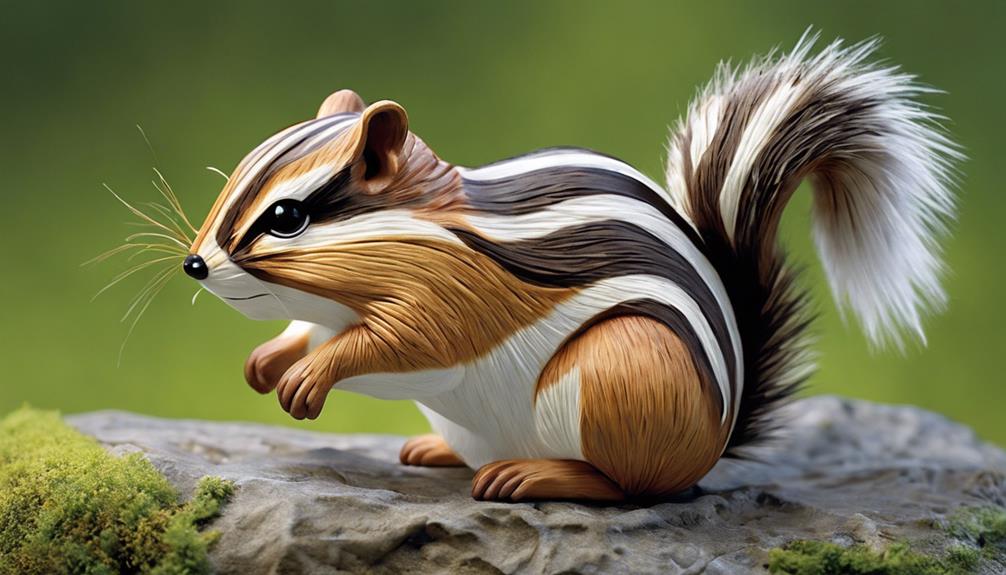

If you're wondering about animals resembling chipmunks, the Thirteen-Lined Ground Squirrel, Eastern Chipmunk, Least Chipmunk, and Colorado Chipmunk are similar. They all have unique stripes, cheek pouches, and quick movements for survival. The Thirteen-Lined Ground Squirrel thrives in grasslands, while the Eastern Chipmunk has reddish-brown fur and excellent climbing skills. The Least Chipmunk survives harsh winters through torpor, and the Colorado Chipmunk sports distinctive stripes for camouflage. Each of these creatures showcases fascinating adaptations for their habitats.
Key Takeaways
- Uinta chipmunks resemble chipmunks with black and white facial stripes.
- They have reddish-brown fur and gray undersides.
- Bushy tails aid in balance and add charm.
- Agile and dart around habitats effortlessly.
- Inhabit forests, meadows, and rocky areas, showcasing adaptability.
Thirteen-Lined Ground Squirrel
Thirteen-Lined Ground Squirrels, often mistaken for chipmunks, are small rodents known for their distinctive 13 alternating dark and light stripes on their back. These Ground Squirrels can be found in grasslands and prairies across North America, showcasing their remarkable adaptability to diverse environments. One key feature that sets them apart from chipmunks is their quick movements and burrowing behavior, allowing them to swiftly navigate their surroundings and create intricate tunnel systems underground.
Observing Ground Squirrels in their natural habitat can be an exciting experience, as they showcase agility and resourcefulness in their foraging activities. Their keen sense of awareness helps them detect potential threats, enabling quick actions to safeguard their safety. Additionally, their burrowing capabilities play an essential role in sheltering them from predators and extreme weather conditions.
Eastern Chipmunk
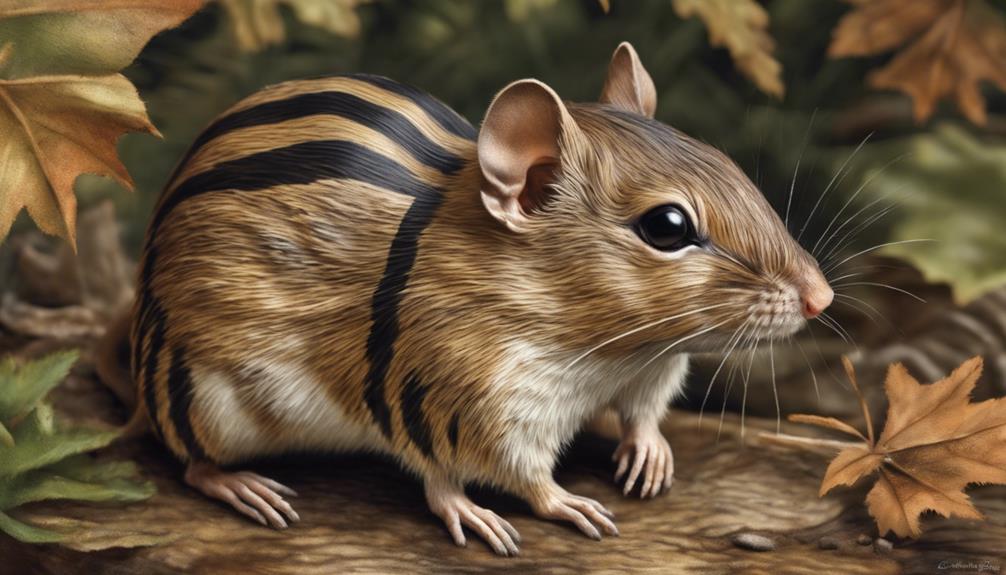

The Eastern Chipmunk, also known as Tamias striatus, is a small rodent with distinct black and white stripes on its back and face.
Their reddish-brown fur adds to their unique appearance in wooded areas.
These chipmunks are active during the day, foraging for nuts, seeds, berries, and insects, showcasing their excellent climbing abilities.
Physical Characteristics
With their petite size and distinctive striped fur, Eastern chipmunks are easily recognizable in their natural habitat. These small creatures typically measure around 5-6 inches in length, sporting reddish-brown fur with black and white stripes on their face, body, and tail.
One key feature of Eastern chipmunks is their large cheek pouches, which they use for storing food. Their quick movements and agility help them navigate their environment with ease.
While Eastern chipmunks share some physical characteristics with Least chipmunks, such as their size and striped fur, they can be distinguished by subtle differences in coloration and markings.
Habitat and Behavior
In their natural habitats, Eastern Chipmunks showcase remarkable climbing skills and territorial behaviors, making them intriguing creatures to observe. These small animals are native to North America, inhabiting forests, woodlands, and even suburban areas. With their excellent climbing abilities, Eastern Chipmunks use trees and shrubs as pathways and lookout points.
They're diurnal creatures, actively foraging for nuts, seeds, fruits, and insects to store in their underground burrows. Eastern Chipmunks are also territorial beings, marking their territories with scent glands and vocalizations to communicate with other chipmunks. During winter, they enter a state of torpor, reducing their metabolic rate to conserve energy and survive the cold season.
Least Chipmunk
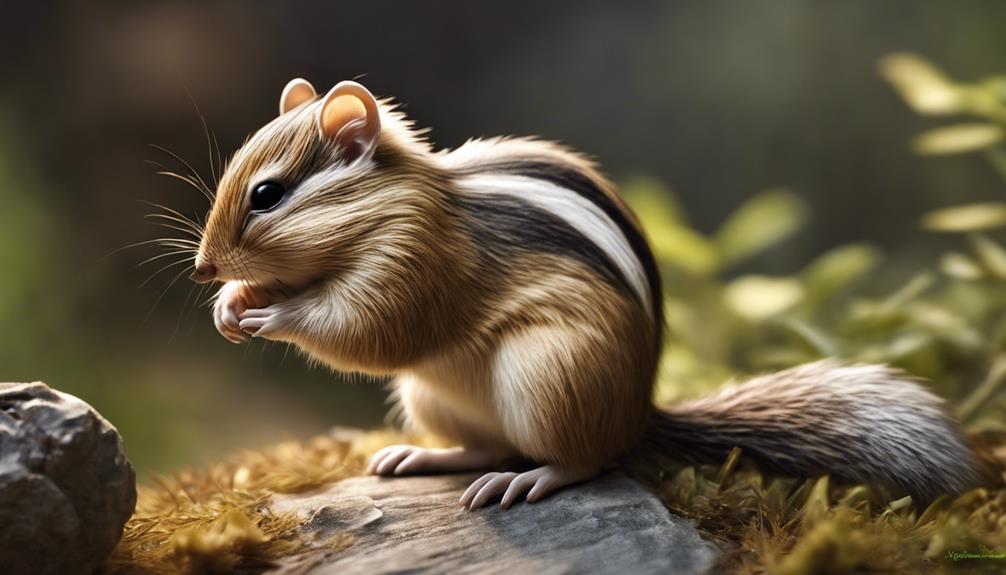

Nestled among the vibrant habitats of Colorado, roams a pint-sized chipmunk known as the Least Chipmunk. This little critter stands out with its distinctive stripes that run from its nose all the way to its tail. These stripes are like nature's signature on this tiny creature, making it easily recognizable amidst its surroundings. Despite its small size, the Least Chipmunk is a resilient species, capable of surviving harsh winters by entering a state of torpor. This adaptation allows them to conserve energy and endure the cold conditions until better times arrive.
You can spot these unique chipmunks in various habitats across Colorado, where they scurry around, foraging for food and scampering up trees with impressive agility. Their striping pattern serves as a natural camouflage, helping them blend into their environment while also adding a touch of beauty to the landscape. The Least Chipmunk is truly a fascinating creature that adds charm to the Colorado wilderness.
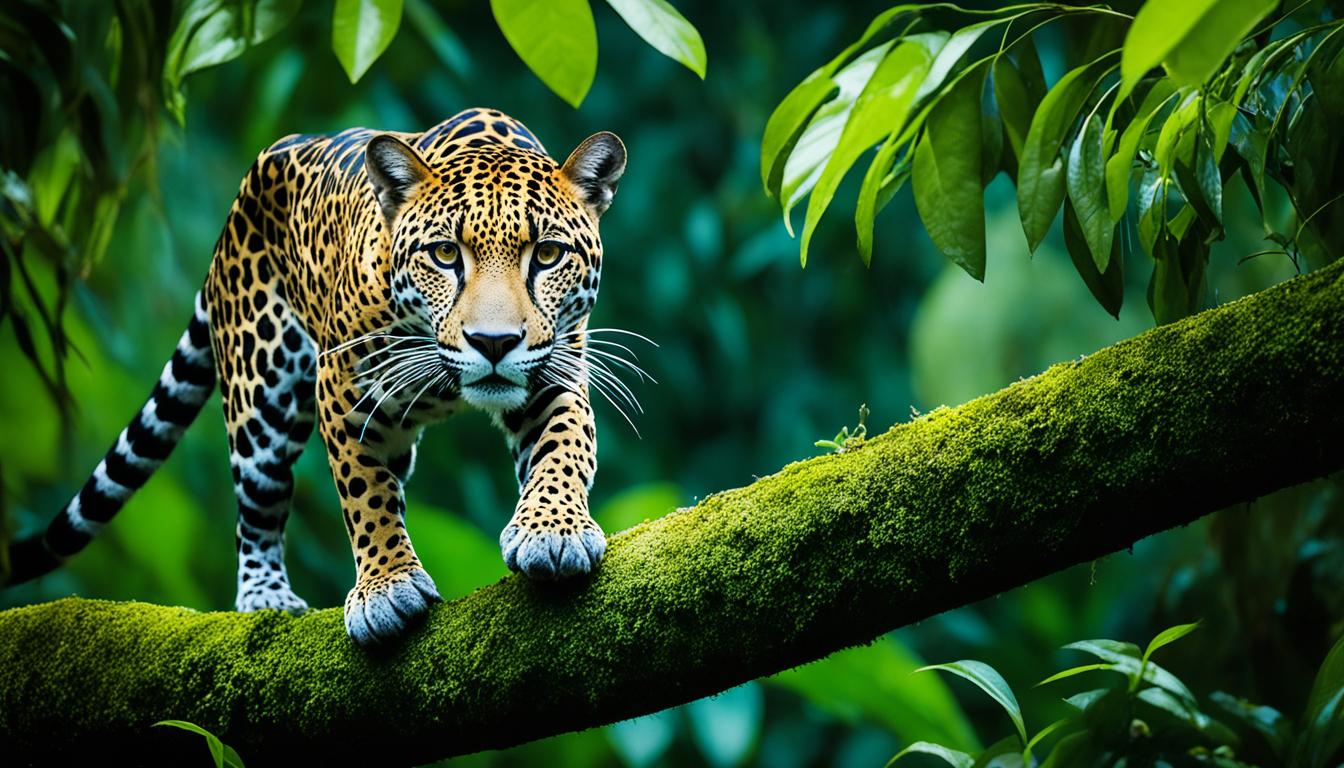
Colorado Chipmunk
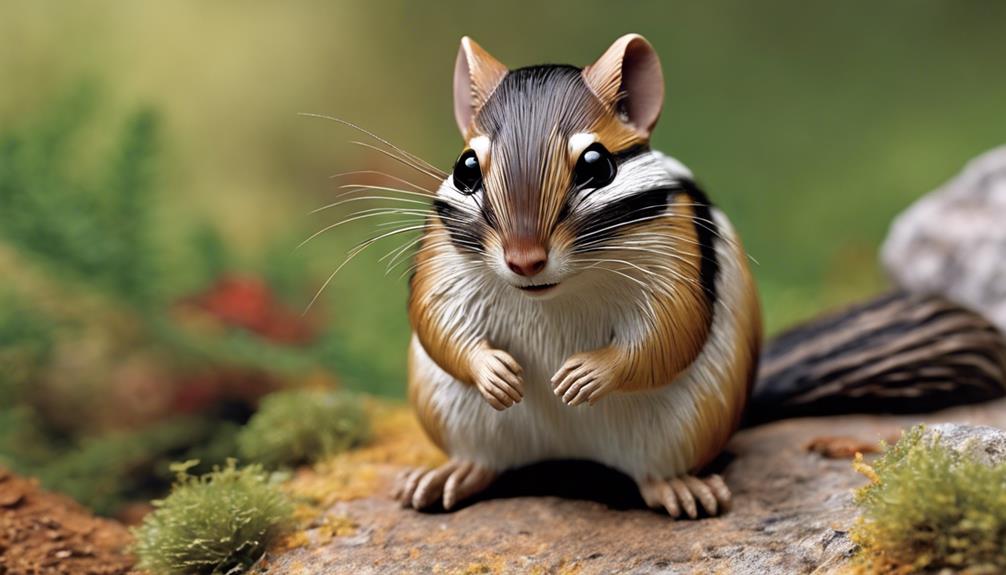

Scampering through the forests of Colorado, the Colorado Chipmunk showcases its larger size and distinctive stripes running from nose to tail. Unlike the Least Chipmunk, this species stands out with its significant markings, making it easily recognizable in its diverse habitats across Colorado. One key feature of Colorado Chipmunks is their cheek pouches, which they use to store food for later consumption. During the winter months, these chipmunks enter a state of torpor to conserve energy and survive the cold weather.
One of the most striking characteristics of Colorado Chipmunks is their stripes, which serve as a notable identifier for this species. These stripes not only add to their visual appeal but also play an important role in camouflage and protection from predators. By blending in with their surroundings, Colorado Chipmunks can stay safe while foraging for food. Next time you're exploring the forests of Colorado, keep an eye out for these charming creatures with their distinctive stripes!
Siberian Chipmunk
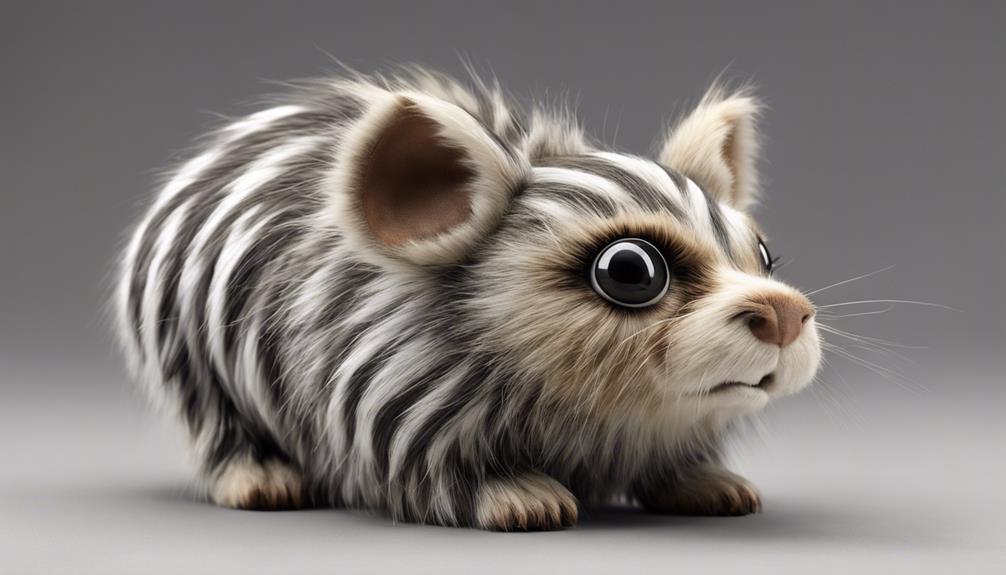

Sporting distinctive black and white stripes on its back, the Siberian Chipmunk, also known as the Korean Striped Chipmunk, hails from regions like Korea, China, and Russia. These chipmunks are smaller in size, typically measuring around 5 to 6 inches in length. With reddish-brown fur coloration, they're skilled climbers that forage for nuts, seeds, fruits, and insects in their natural habitat. Siberian Chipmunks aren't only known for their charming appearance but also for their playful and curious behavior, making them entertaining animals to observe.
In the wild, chipmunks like the Siberian Chipmunk play an essential role in their ecosystems by dispersing seeds and balancing insect populations. Their agility and quick movements help them evade predators, showcasing their adaptability in various environments. Observing these chipmunks in their natural habitat provides valuable insights into their behaviors and interactions with other species. By learning about the Siberian Chipmunk, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and uniqueness of chipmunks worldwide.
Red-Tailed Chipmunk
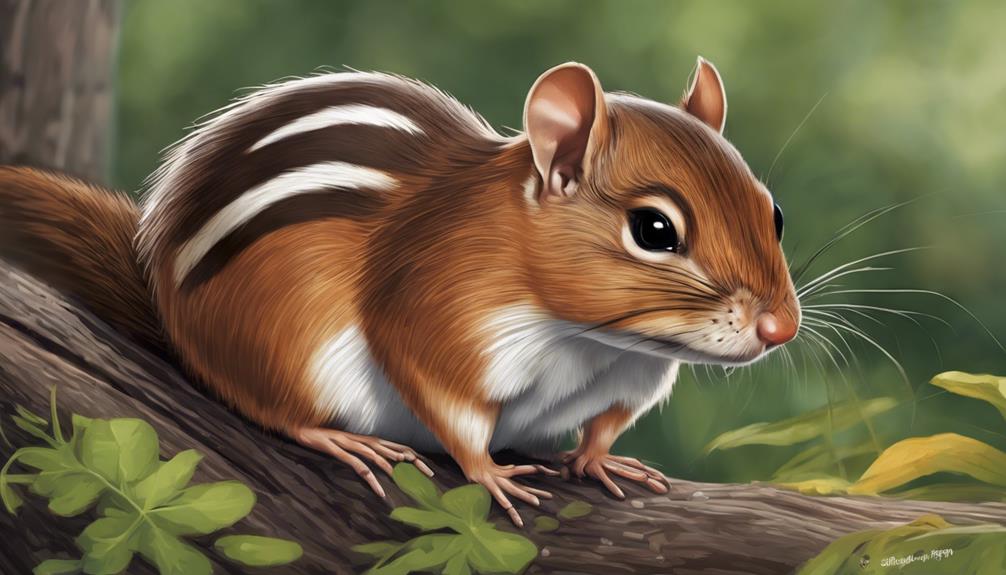

In comparison to the Siberian Chipmunk, the Red-Tailed Chipmunk, also known as the Uinta Chipmunk, inhabits the western United States and is characterized by its reddish-brown back and tail, along with distinct facial markings.
- Distinct Features:
- Red-Tailed Chipmunks stand out with their reddish-brown backs and tails, which sharply contrast with their grayish sides and white underparts.
- Facial Markings:
- These chipmunks sport unique facial stripes and markings, including dark lines that run from their eyes to their ears, giving them a distinctive appearance.
- Habitat and Behavior:
- Active during the day, Red-Tailed Chipmunks forage for a variety of foods like seeds, nuts, fruits, and insects in their forested habitats.
- Ecological Importance:
- Playing an essential role in their ecosystem, these chipmunks aid in seed dispersal and serve as prey for a range of predators, contributing to the balance of their natural environment.
Uinta Chipmunk
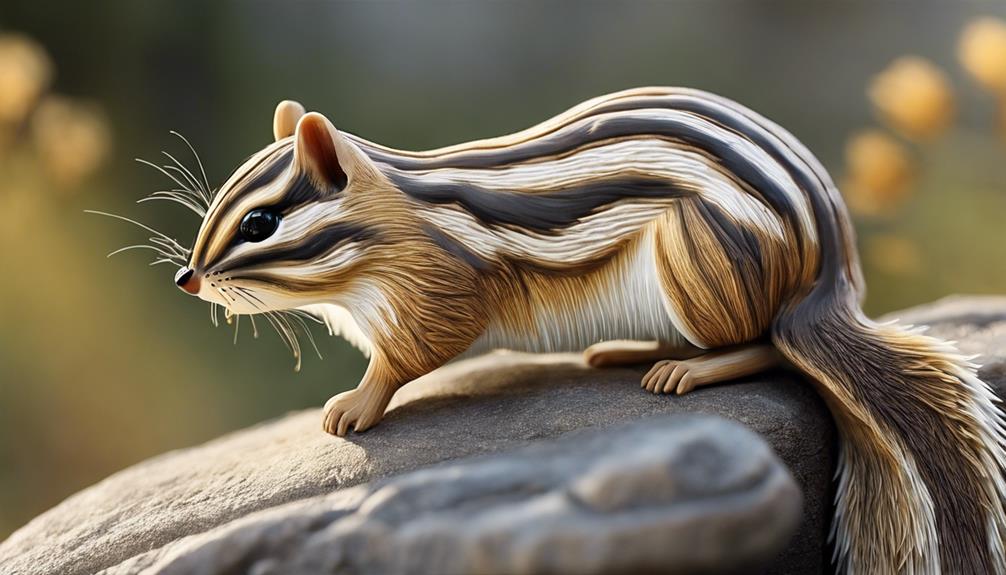

The Uinta Chipmunk, scientifically known as Neotamias umbrinus, boasts reddish-brown fur marked by five dark stripes on its back and distinctive white stripes encircling its eyes.
Living in the western United States, these chipmunks thrive in mountainous terrains where they display impressive climbing skills while foraging for a diet of seeds, nuts, fruits, and insects.
Understanding the Uinta Chipmunk's characteristics, habitat preferences, and behaviors is essential to appreciating their significance in maintaining biodiversity within their ecosystems.
Uinta Chipmunk Features
With their distinctive black and white stripes and quick movements, Uinta chipmunks are small rodents native to western North America. Here are some key features that set them apart:
- Coloration: Uinta chipmunks sport black and white stripes on their faces and bodies, with reddish-brown fur and a grayish underside.
- Tail: These chipmunks have bushy tails that add to their charm and aid in balance.
- Movement: Known for their agility, Uinta chipmunks are quick on their feet, darting around their habitats with ease.
- Habitats: You can find these fascinating chipmunks in diverse environments like forests, meadows, and rocky areas, showcasing their adaptability and resourcefulness.
Habitat and Behavior
Nestled within the diverse landscapes of western United States, Uinta Chipmunks exhibit solitary behavior as they skillfully forage for seeds, nuts, and berries. These chipmunks are highly adaptable, inhabiting forests, meadows, and rocky areas with ease.
Agile climbers, they navigate tree branches and rocky terrain effortlessly. Uinta Chipmunks' reddish-brown fur and distinctive facial stripes provide excellent camouflage in their natural surroundings.
Active during the day, they retreat to their burrows at night for safety. Observing their diurnal habits can be a fascinating experience, as they go about their foraging and climbing activities.
Conservation Status
In the conservation efforts for the Uinta Chipmunk, focus remains on preserving its natural habitats to guarantee continued presence in the wild.
Here are four key points regarding the conservation status of chipmunks like the Uinta Chipmunk:
- IUCN Red List: Uinta chipmunks are classified as a species of least concern, indicating that their population is relatively stable.
- Habitat: Found in western U.S. mountainous regions, these chipmunks face threats from habitat loss due to human activities and climate change.
- Population Trend: Fortunately, the population trend for Uinta chipmunks is stable, with no immediate threats impacting their numbers.
- Conservation Focus: Efforts are directed towards safeguarding the natural habitats of chipmunks to ensure their survival in the face of potential challenges.
Yellow-Pine Chipmunk
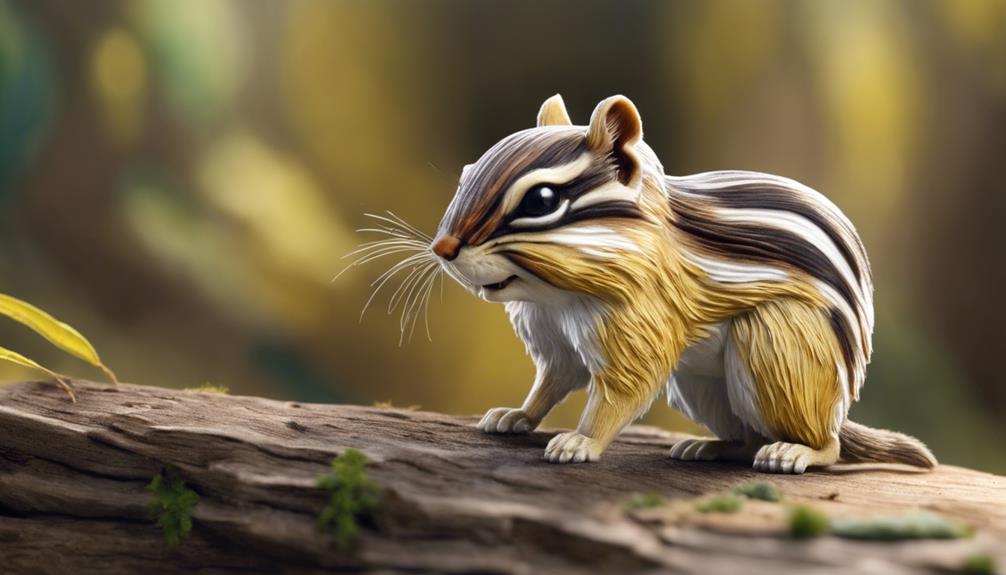

Yellow-Pine Chipmunks, commonly found in the western United States, boast distinctive yellow and gray striped fur patterns. These endearing chipmunks, smaller than other species at around 8 inches long, are known for their charming appearance and lively nature.
With their cheek pouches for storing food, Yellow-Pine Chipmunks are efficient gatherers, collecting seeds, nuts, fruits, and insects to sustain themselves. Their diurnal habits make them a delight to observe during the day, scurrying around in search of sustenance.
Found in various habitats ranging from forests to meadows, these chipmunks are adaptable creatures, showcasing their resilience in different environments. The yellow and gray stripes on their fur serve as excellent camouflage, helping them blend seamlessly into their surroundings.
Watching these agile creatures navigate their habitats is a true pleasure, offering a glimpse into the fascinating world of these charming Yellow-Pine Chipmunks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Animal Looks Like a Chipmunk but Isn T?
While sharing similarities with chipmunks, several small animals, like the thirteen-lined ground squirrel, red squirrel, and golden-mantled ground squirrel, differ in species but sport comparable features, leading to frequent mistaken identities.
What Is a Small Squirrel That Looks Like a Chipmunk?
I often mistake a small squirrel for a chipmunk. The one I see with similar features is the Aberts or Tassel-eared Squirrel. It's large with fluffy ears and inhabits Ponderosa forests in Evergreen.
What Resembles a Chipmunk?
Exploring nature's canvas, I find a creature resembling a chipmunk. Its stripes dance like shadows in sunlight, a tiny acrobat with cheeks full of secrets. Nature's artistry thrives in this small wonder.
Which Creature Is Actually a Rodent Often Mistaken to Be a Chipmunk?
Mistakenly identified as a chipmunk, the golden mantled ground squirrel shares similarities in size and appearance. However, its lack of distinct stripes sets it apart. Understanding these nuances aids in correctly identifying these small rodents.
Conclusion
To sum up, when searching for a small animal that resembles a chipmunk, consider the Thirteen-Lined Ground Squirrel, Eastern Chipmunk, Least Chipmunk, Colorado Chipmunk, Siberian Chipmunk, Red-Tailed Chipmunk, Uinta Chipmunk, or Yellow-Pine Chipmunk. Each of these creatures has unique characteristics that set them apart from one another, providing a fascinating glimpse into the diverse world of small mammals.
Just as each chipmunk species has its own distinct features, so too do these look-alike animals, showcasing the beauty of nature's diversity.
Dana is our Lead Content Writer, bringing a wealth of knowledge and expertise to our team. With a background deeply rooted in animal studies and a profound love for all creatures, Dana is dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that resonates with our audience. With Dana at the helm, you can trust that our content is accurate and engaging, catering to the diverse interests of animal enthusiasts everywhere.
Animals
Exploring Animals That Start With N: A Guide

Do you realize that there are multiple intriguing creatures that start with the letter N? From tiny worms to magnificent mammals, these animals highlight the amazing variety of the natural world. Come along on a quest to uncover some of the most captivating animals that start with N!
Key Takeaways:
- Animals that start with N encompass a wide range of species, including mammals, birds, fish, and invertebrates.
- Some notable animals that start with N include the nocturnal nightingale, the regenerating newt, and the adaptable Norwegian rat.
- These animals possess unique characteristics and adaptations that enable them to thrive in their respective habitats.
- Learning about animals that start with N provides a deeper appreciation for the incredible diversity of wildlife and the wonders of the natural world.
- Stay tuned as we explore each of these fascinating creatures in more detail!
List of Common Animals That Start With Letter N
This section provides a list of common animals that start with the letter N. From the amphibious newt to the nocturnal nightingale, these animals span different categories and habitats, showcasing their unique traits and behaviors. Whether you’re looking to expand your knowledge or engage young learners, this list is a valuable resource.
Common Animals That Start With N
- Newt
- Nuthatch
- Nightingale
- Numbat
- Nyala
- Nematode
- Nase
- Napu
- Norwegian Rat
- Nicator
- Noodlefish
- Nalolo
- Nightcrawler
Explore the fascinating world of these common animals that start with the letter N. Discover the unique adaptations, habitats, and behaviors that make them truly remarkable. Each animal has its own story to tell, showcasing the diversity and beauty of the natural world.
| Animal | Habitat | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Newt | Aquatic and terrestrial environments | Amphibious nature, ability to regenerate lost body parts |
| Nuthatch | Wooded areas | Unique ability to climb down trees headfirst |
| Nightingale | Various habitats | Melodic nocturnal song |
| Numbat | Australian woodlands | Termites as their primary food source |
| Nyala | Southern Africa | Distinct body markings, spiral horns in males |
| Nematode | Diverse environments | Microscopic roundworms, abundant in soil and oceans |
| Nase | European rivers | Adapted to fast-flowing streams, flattened body shape |
| Napu | Southeast Asian forests | Sharp fangs for defense, lesser mouse-deer |
| Norwegian Rat | Global distribution, often near human populations | Highly adaptable, common brown rat |
| Nicator | African forests | Loud and varied calls, dominant behavior |
| Noodlefish | North Pacific | Slender fish with noodle-like appearance |
| Nalolo | Indian Ocean | Gender-changing wrasse fish |
| Nightcrawler | Soil and compost | Large earthworms, commonly used as fishing bait |
Newt
Newts are small amphibians that belong to the salamander family. These fascinating creatures have a unique life cycle, spending part of their lives in water and part on land. They have a slender body, smooth skin, and a distinct tail that helps them navigate through water. Newts can be found in various habitats, including forests, ponds, and wetlands.
One of the most remarkable traits of newts is their ability to regenerate lost body parts. If a newt loses a limb, it has the incredible capability to regrow it. This regenerative power extends beyond limbs and includes other body parts such as heart tissues and even parts of their eyes. This remarkable ability makes newts one of the most fascinating creatures in the animal kingdom.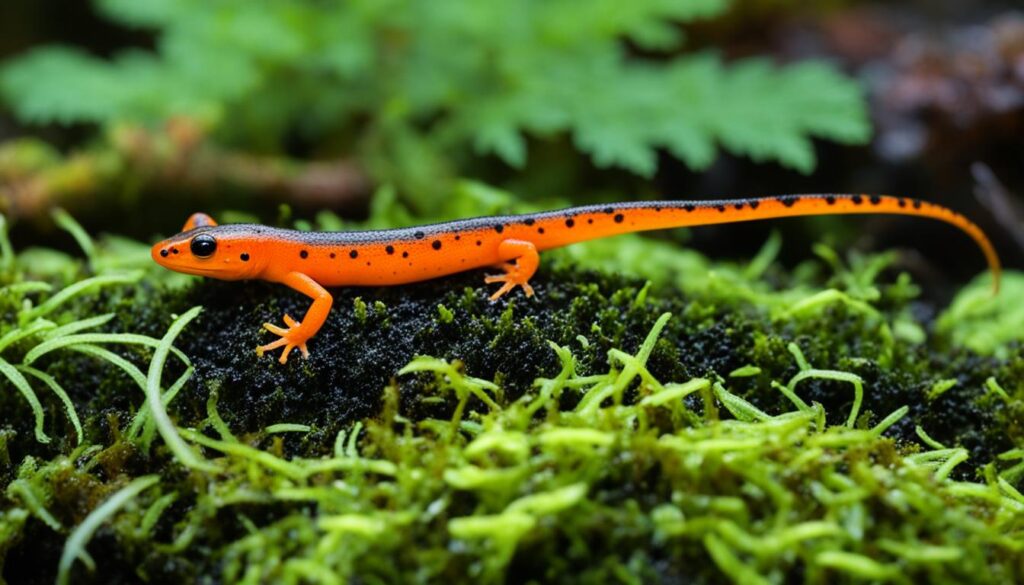
“Newts are fascinating creatures with the unique ability to regenerate lost body parts.”
Life Cycle of a Newt
Newts undergo a complex life cycle that involves distinct stages and transformations. It begins with the hatching of eggs in aquatic environments, where larvae develop and spend their early days as aquatic creatures. During this stage, they have gills for breathing and a tail that helps them swim.
As the larvae grow and develop, they undergo a remarkable metamorphosis known as “eft” stage. In this stage, they develop lungs, lose their gills, and begin to venture onto land. Efts have vibrant colors, ranging from bright orange to yellow or green, which serve as a warning to predators that they are toxic.
After spending a few years on land as efts, they transform into adult newts. Adult newts have fully developed lungs and spend most of their time in water, although they may come onto land during certain seasons, such as mating season. They are known for their distinctive mating rituals, which involve elaborate displays and courtship dances.
Newt Species
There are several species of newts, each with its unique characteristics. Here are a few notable examples:
| Newt Species | Habitat | Distinct Features |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern Newt | Eastern North America | Can change color depending on their surroundings |
| Palmate Newt | Europe | Distinctive black webbing between their hind toes |
| Japanese Fire-Bellied Newt | Japan and China | Has bright red or orange markings on its belly |
Whether it’s their ability to regenerate body parts or their unique life cycle, newts are truly remarkable creatures that continue to captivate nature enthusiasts and scientists alike.
Nuthatch
The nuthatch is a small songbird that stands out from the crowd with its exceptional ability to climb down trees headfirst. While most birds can only climb up, nuthatches possess the remarkable talent of descending tree trunks in search of food. This distinctive behavior sets them apart and makes them fascinating creatures to observe in the wild.
“Nuthatches demonstrate incredible agility as they navigate tree bark in a reverse orientation,” says ornithologist Dr. Amanda Johnson. “This adaptation allows them to access food sources that other birds cannot reach.”
With their short, sturdy legs and strong toes, nuthatches effortlessly maneuver upside down, thanks to an adaptation known as a “reversed hind-toe.” This physical trait gives them an advantage in finding insect larvae and hidden seeds tucked away in bark crevices.
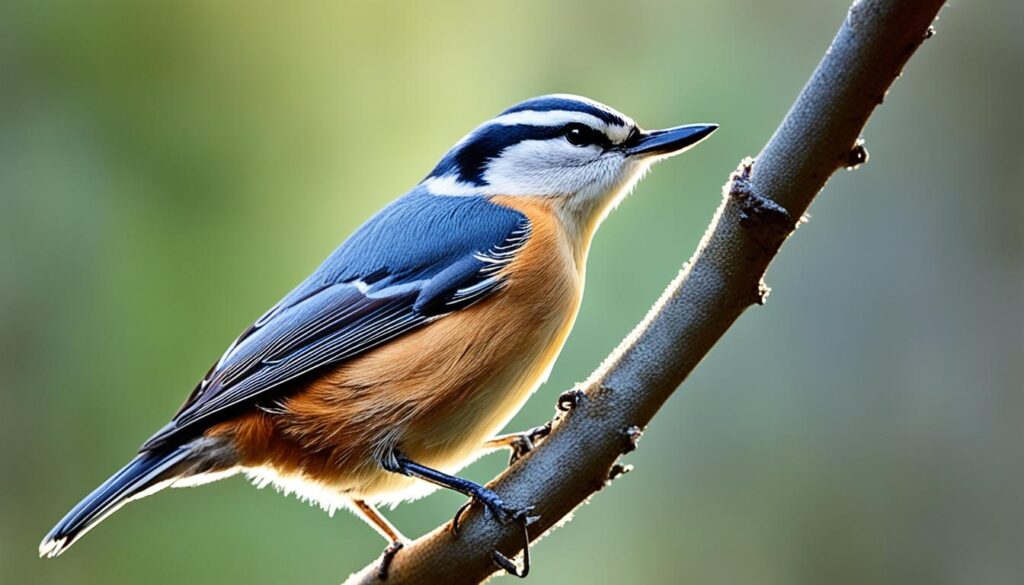

Contrary to their name, nuthatches don’t hatch nuts, but they do have a clever way of opening them. These resourceful birds wedge nuts into tree bark and then use their sharp bills to pry them open, revealing the tasty morsels inside. This unique feeding behavior earned them their distinctive moniker.
Types of Nuthatches
There are several species of nuthatches found around the world, each with its own characteristics and habitat preferences. Some notable species include:
- White-breasted nuthatch: This common North American species sports a vibrant white chest and a distinct black cap on its head.
- Red-breasted nuthatch: With its rusty-colored breast and bold black stripe across the eye, this species is a favorite among birdwatchers.
- Pygmy nuthatch: Found in western North America, these tiny nuthatches are highly social and travel in noisy flocks.
The Nuthatch’s Melodic Song
Although nuthatches are small birds, they boast a surprisingly powerful voice. Their songs are a symphony of whistles, trills, and bursts of melodious notes. These vocalizations are not only used for communication but also aid in defending territories and attracting mates.
Dr. Johnson explains, “Male nuthatches often serenade potential mates with their elaborate songs, showcasing their vocal prowess and ability to provide for a family.”
Conservation Status
Most species of nuthatches are relatively common and not currently considered to be at risk. However, habitat loss and fragmentation can pose challenges for these birds, particularly those reliant on specific forest ecosystems. Ongoing conservation efforts are crucial in maintaining healthy populations of nuthatches and preserving their unique behaviors in the wild.
| Nuthatch Species | Habitat | Conservation Status |
|---|---|---|
| White-breasted nuthatch | Deciduous and mixed forests of North America | Least Concern |
| Red-breasted nuthatch | Coniferous forests of North America | Least Concern |
| Pygmy nuthatch | Western pine forests of North America | Least Concern |
Nightingale
The nightingale, known for its melodic and powerful nocturnal song, captures the hearts of many with its captivating music. Males primarily sing these enchanting melodies to attract females. It’s fascinating to note that nightingales earned their name due to their propensity for serenading not only during the day but also throughout the night.
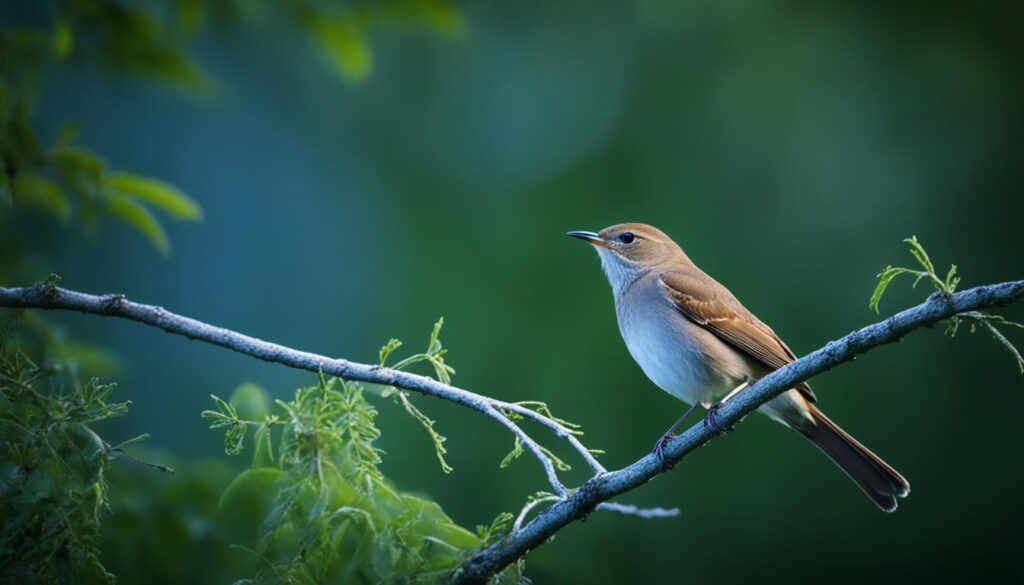

“The nightingale’s song is a testament to the beauty and harmony that nature offers. Its melodic notes echo through the darkness, enchanting all who listen.”
The Nocturnal Virtuosos
Nightingales are celebrated for their exceptional musical ability, which is most pronounced during the moonlit hours. Their captivating tunes fill the night air, blending with the tranquil ambiance of the nocturnal world. Their melodies create a symphony that resonates deeply with the listeners, evoking a sense of calm and wonder.
Magical Moments under the Stars
Imagine strolling through a moonlit garden, surrounded by the sweet scent of flowers, while the nightingale perches nearby, filling the silence with its magical song. The nocturnal serenade of the nightingale has inspired poets, artists, and lovers throughout history, evoking a sense of romance and connection to the natural world.
| Nightingale | Features |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Luscinia megarhynchos |
| Habitat | Woodlands, gardens, and parklands |
| Diet | Insects, worms, and berries |
| Size | Approximately 6-7 inches (15-18 cm) in length |
| Unique Fact | Nightingales can produce over 1,000 different song variations |
Numbat
The numbat is a small marsupial native to Australia. It is also known as the banded anteater due to its distinctive striped pattern. Despite its name, the numbat does not resemble traditional marsupials; instead, it bears a closer resemblance to squirrels or chipmunks. With its slender body, bushy tail, and pointed snout, the numbat is a unique and intriguing creature.
One of the most fascinating aspects of the numbat is its diet. This marsupial is a dedicated termite feeder, relying almost exclusively on termites for sustenance. In fact, it can consume up to 20,000 termites in a single day! The numbat’s method of capturing termites is equally intriguing. It uses its long, sticky tongue (which can extend up to 10 centimeters) to extract the insects from their underground tunnels.
The Numbat’s Adaptations
Unlike other marsupials, the numbat lacks a pouch for carrying its young. Instead, the female numbat constructs a nest made of fine grasses to provide a safe and cozy environment for her offspring. The young numbats, called joeys, stay in the nest until they are fully furred and able to venture out on their own.
The numbat is a testament to the marvels of evolution, with its specialized adaptations for termite feeding and survival in the Australian habitat. Its slender body, sharp claws for digging, and long tongue are all finely tuned for a life centered around termites.
The numbat population faces challenges due to habitat loss and predation by introduced species such as foxes and cats. Efforts are being made to conserve and protect this unique marsupial through initiatives such as habitat restoration and predator control programs.
By learning about and appreciating the numbat, we gain a greater understanding of the intricate web of life and the importance of preserving biodiversity.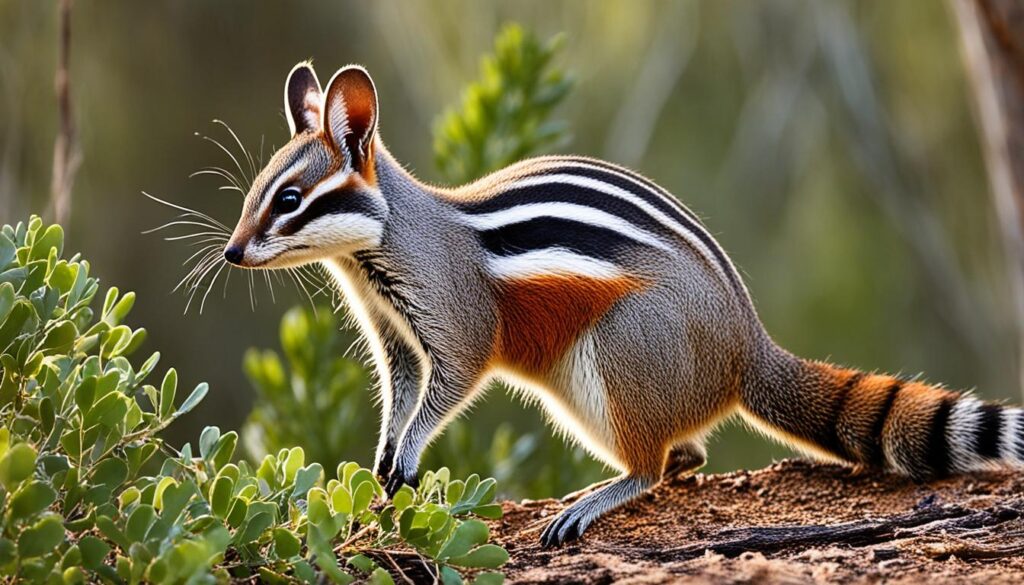
Nyala
The nyala is a beautiful antelope native to southern Africa. With its distinct body markings and spiral horns, the nyala is easily recognized in its natural habitat. Female nyalas have a warm orange or brown coat and lack horns, while males are darker and sport prominent spiral horns.
This antelope species is found in the dense woodlands of southern Africa, particularly in countries like South Africa, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe. Its habitat preference allows it to thrive in areas with abundant vegetation and water sources.
The nyala is a browser, meaning it primarily feeds on leaves, fruits, and other plant materials. It has a specialized digestive system that allows it to extract essential nutrients from the vegetation it consumes. This diet makes the nyala an important contributor to the ecosystem by helping to disperse seeds and control plant growth.
In addition to its striking physical appearance, the nyala has an intriguing social structure. Males are generally solitary or form small bachelor groups, while females and their offspring live in herds. During mating season, dominant males engage in fierce battles to establish their territory and breeding rights.
Key Features of Nyala:
- Distinct body markings
- Spiral horns in males
- Warm orange/brown coat in females
- Prevalent in southern Africa
- Browser diet of leaves and fruits
- Social structure with solitary males and herds of females
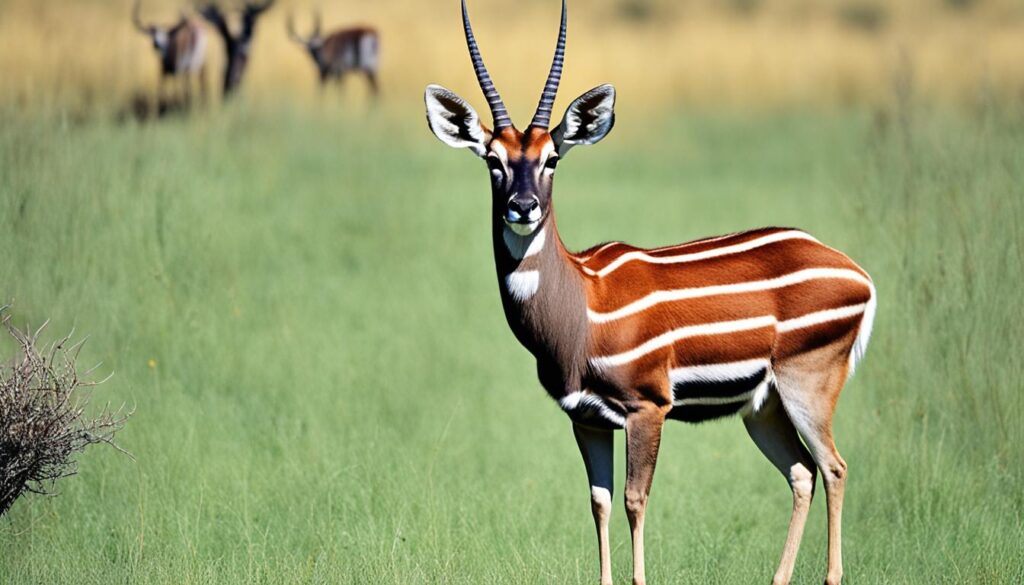

| Scientific Name | Tragelaphus angasii |
|---|---|
| Conservation Status | Least Concern |
| Habitat | Dense woodlands |
| Location | Southern Africa |
| Diet | Herbivorous (browsing on leaves, fruits, and plant materials) |
| Weight | Female: 120-240 lbs (55-110 kg) | Male: 220-280 lbs (100-125 kg) |
| Length | Female: 4-5 ft (1.2-1.5 m) | Male: 5-6 ft (1.5-1.8 m) |
Nematode
Nematodes, also known as roundworms, are microscopic worms that can be found in various environments, from soil to oceans. They are incredibly diverse and have adapted to survive in almost every habitat on Earth. These tiny creatures play vital ecological roles and have both beneficial and detrimental effects on plants, animals, and humans.
Nematodes are characterized by their slender, cylindrical bodies and pointed ends. Despite their small size, nematodes are incredibly abundant and widespread. In fact, scientists estimate that four out of every five animals on Earth are nematodes! Due to their ubiquity, nematodes are considered one of the most successful animal groups on the planet.
Some nematodes are parasitic, while others are free-living. Parasitic nematodes can infect plants, animals, and even humans, causing various diseases and health issues. They can harm crops, livestock, and humans alike, making them a significant concern in agriculture, veterinary medicine, and public health.
Roundworms come in a wide range of shapes and sizes. Some are barely visible to the naked eye, while others can reach several meters in length. Their diversity is truly remarkable, with nematodes occupying almost every ecological niche imaginable. They can be found in freshwater habitats, ocean sediments, soil, and even inside the bodies of other organisms.
Despite their tiny size, nematodes play crucial roles in ecosystems. They contribute to nutrient cycling, as some species feed on decaying organic matter and help break it down. Other nematodes are important predators, preying on bacteria, fungi, and other microscopic organisms. Their activities help maintain the balance of microbial communities and influence the overall health of ecosystems.
Nase
The nase is a freshwater fish commonly found in the rivers of Europe. With its flattened body and strong swimming abilities, the nase has successfully adapted to life in fast-flowing streams.
Known for its sleek and streamlined shape, the nase is built for navigating through swift currents. Its body structure allows it to minimize drag and maintain stability while swimming. The nase also possesses a powerful caudal fin, which enables it to propel itself with speed and agility.
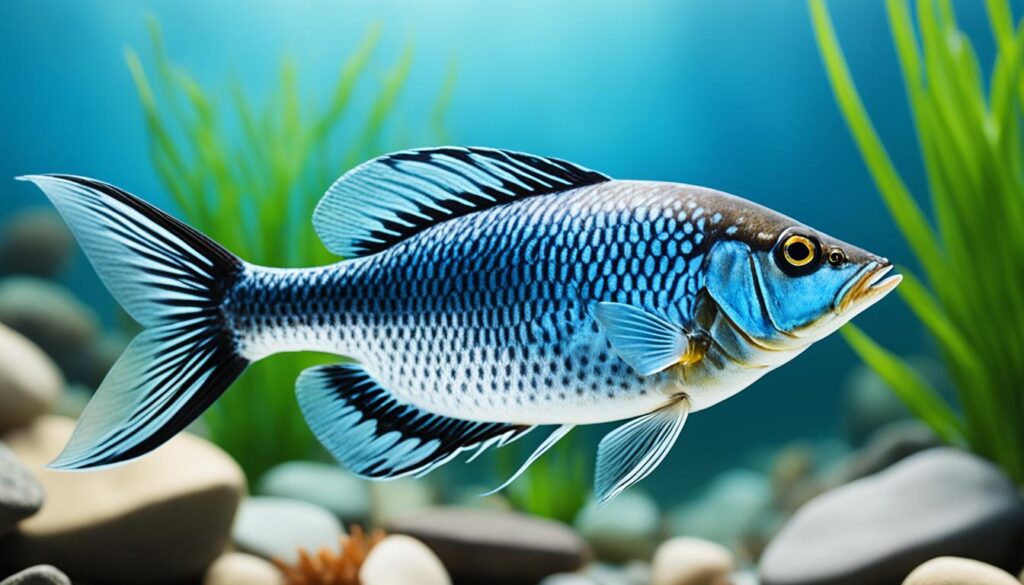

In addition to its physical adaptations, the nase has developed specialized feeding habits to thrive in its environment. It primarily feeds on small invertebrates, algae, and other plant matter found in the rivers of Europe.
The nase plays a significant ecological role in freshwater ecosystems, contributing to the balance of populations and food webs. This species serves as both predator and prey, interacting with various organisms in its habitat.
Understanding the biology and behavior of the nase is crucial for the conservation of freshwater ecosystems in Europe. By studying its adaptations and ecological interactions, scientists can develop strategies to preserve the nase and the delicate balance of the rivers it inhabits.
Overall, the nase is a remarkable freshwater fish that showcases nature’s ability to adapt and thrive in diverse environments. Its presence in European rivers is not only a testament to its resilience but also a reminder of the rich biodiversity found across the continent.
Napu
The napu, also known as the lesser mouse-deer, is a small hoofed mammal found in Southeast Asia. Despite their tiny size, they are known to stand their ground and use their sharp fangs in defense against threats.
The napu, scientifically known as Tragulus napu, belongs to the family Tragulidae. These fascinating creatures are native to the dense forests and swampy areas of Southeast Asia, including countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
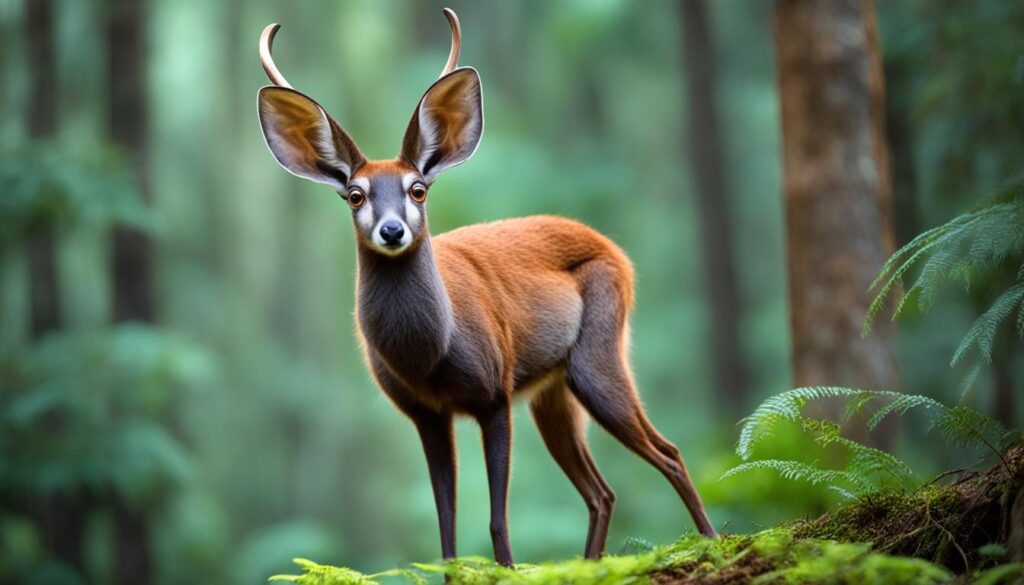

With a height of only about 40-45 centimeters and weighing around 5-8 kilograms, napus are one of the smallest hoofed mammals in the world. Their compact body and delicate limbs allow them to maneuver effortlessly through the dense foliage of their habitat.
The napu is recognized for its slender, deer-like body, pointed snout, and large, round eyes. Its fur varies in color, ranging from reddish-brown to gray or dark brown, providing excellent camouflage within its natural surroundings.
These remarkable creatures are predominantly herbivorous, feeding on a variety of leaves, grasses, shoots, and fruits. Due to their smaller size, napus have the advantage of being able to access lower vegetation that larger herbivores cannot reach.
The lesser mouse-deer is primarily a solitary creature, coming together only during mating season. Females give birth to a single offspring after a gestation period of about six months. The young napu, known as fawn, is precocial, meaning it is capable of walking and running shortly after birth.
The napu’s survival is threatened by habitat loss and fragmentation due to human encroachment and deforestation. Conservation efforts are in place to protect their natural habitats and ensure their survival in the wild.
Norwegian Rat
The Norwegian rat, also known as the brown rat, is one of the most widespread rat species globally. These rats are highly adaptable and are often found living near human populations.
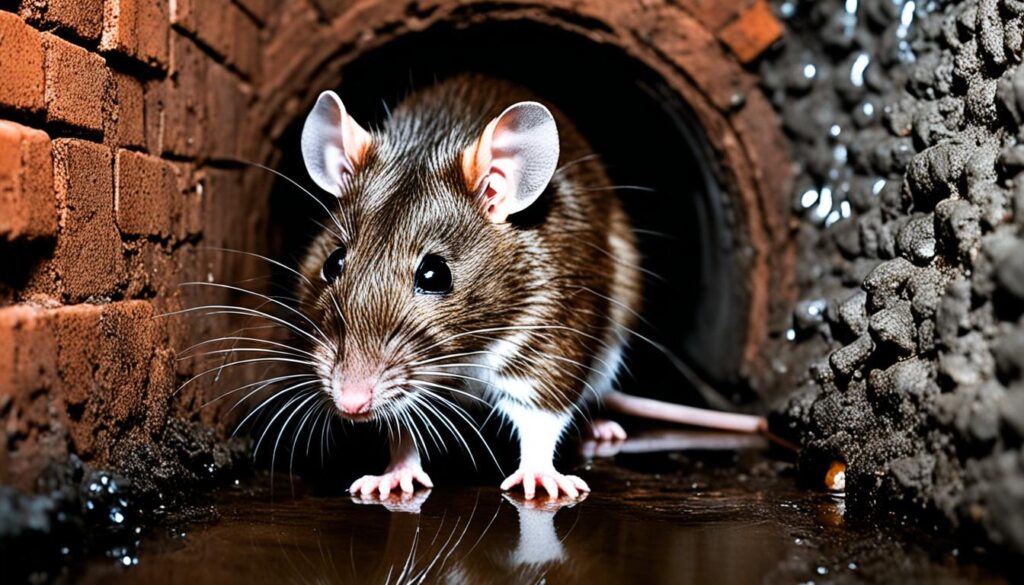

Key Characteristics of the Norwegian Rat:
- Color: Brown
- Size: Up to 10 inches in length
- Weight: Can weigh between 11 to 18 ounces
- Tail: Typically shorter than the head and body length
- Habitat: Found in urban and rural areas
- Adaptability: Thrives in various environments and climates
“The Norwegian rat, with its adaptability and ability to coexist with humans, has earned its reputation as a resilient and agile survivor.” – RatExpert22
Distribution of the Norwegian Rat:
The Norwegian rat is native to northern China and Mongolia but has since spread to all continents except Antarctica. It has successfully colonized urban areas around the world, thriving in environments where it can scavenge for food and find shelter. These rats are particularly common in large cities and areas with dense human populations.
Impacts on Humans:
The adaptability of the Norwegian rat poses various challenges for humans. They are known to cause damage to buildings, contaminate food supplies, and spread diseases through their droppings and parasites. In agricultural settings, they can destroy crops and stored grain.
Efforts to Control the Norwegian Rat:
Due to the negative impacts of the Norwegian rat, efforts have been made to control their populations. Pest control methods often include the use of traps, bait stations, and rodenticides. Public education campaigns emphasizing proper waste disposal and sanitation practices also play a crucial role in preventing rat infestations.
Rat Fact vs. Fiction:
| Fact | Fiction |
|---|---|
| 1. Norwegian rats are excellent swimmers. | 1. Rats can chew through concrete walls. |
| 2. They are social animals, living in colonies. | 2. Rats are carriers of the bubonic plague. |
| 3. Norwegian rats have poor eyesight but a strong sense of smell. | 3. Rats are attracted to cheese. |
Nicator
Nicators are songbirds native to Africa. They are known for their loud and varied calls. Despite their pleasant songs, nicators can be aggressive and often dominate other birds in their habitat.
If you ever find yourself in Africa, keep your ears open for the enchanting melodies of the nicator. These talented songbirds have a unique ability to captivate listeners with their melodic tunes, filling the air with their rich and vibrant voices.
With their striking plumage and graceful movements, nicators are a true delight to observe in the wild. Their vibrant colors, ranging from deep blues to earthy browns, make them a visual spectacle against the African landscape.
One fascinating aspect of nicators is their ability to command attention through their calls. Their vocal repertoire consists of a wide range of sounds, each serving a different purpose. From melodic tunes that attract potential mates to territorial calls that assert dominance, nicators communicate their presence and intentions in distinct ways.
Although nicators are known for their harmonious songs, they can also exhibit a fierce side. These songbirds can be territorial and aggressive, especially when defending their nests or asserting dominance over other birds. Their assertive behavior allows them to maintain control over their preferred habitat, ensuring their survival in the competitive African ecosystem.
Notable Characteristics of Nicators
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Geographical Range | Africa |
| Family | Nicatoridae |
| Habitat | Forests, woodlands, and savannas |
| Size | Varies depending on species, ranging from 15 to 23 centimeters in length |
| Diet | Insects, fruits, and seeds |
| Reproduction | Monogamous breeding pairs construct cup-shaped nests and raise their young together |

Despite their occasional aggression, nicators play a vital role in their ecosystem as pollinators and seed dispersers. Their feeding habits contribute to the health and diversity of African plant life, making them an essential part of the continent’s delicate balance of nature.
So, the next time you find yourself in the vast and diverse landscapes of Africa, take a moment to listen for the enchanting songs of the nicator. These melodious birds will surely leave an indelible mark on your heart and remind you of the incredible wonders that nature has to offer.
Noodlefish
The Noodlefish, also known as the Slender Fish, is a small species found in the North Pacific. These fish are known for their unique appearance and long, noodle-like bodies.
Despite their slender shape, Noodlefish are agile swimmers and are well adapted to their marine environment. They have streamlined bodies and powerful caudal fins that enable them to maneuver swiftly through the water.
Noodlefish primarily feed on small crustaceans, zooplankton, and other small marine organisms. Their elongated bodies and sharp teeth allow them to capture their prey with precision.
These fish are an important part of the North Pacific ecosystem, serving as a food source for larger predators and helping to maintain the balance of marine life.
Characteristics of the Noodlefish:
- Slender body shape
- Long, noodle-like appearance
- Powerful caudal fin for swimming
- Sharp teeth for capturing prey
It is fascinating to observe the Noodlefish in their natural habitat, gracefully gliding through the water with their unique body structure. Their distinct shape and behavior make them an intriguing species within the diverse marine ecosystem.
| Noodlefish Facts | |
|---|---|
| Habitat | North Pacific |
| Diet | Small crustaceans, zooplankton, marine organisms |
| Physical Characteristics | Slender body, long and noodle-like |
Nalolo
Nalolos are a type of wrasse fish mainly found in the Indian Ocean. They inhabit the vibrant coral reefs and tropical waters of this vast oceanic expanse. Nalolos are known for their vibrant colors and intricate patterns, making them a captivating sight for divers and snorkelers.
One fascinating aspect of nalolos is their ability to change their gender as they mature. They start their lives as females and then transition into males as they grow older. This unique reproductive strategy, known as sequential hermaphroditism, allows nalolos to optimize breeding opportunities within their social groups.
Their behavior and appearance also change as they undergo this gender transformation. Female nalolos typically have a vibrant orange or yellow coloration, while males exhibit more subdued hues of blue, green, and red. This color variation serves as a visual signal to potential mates and rivals within their ecosystem.
To showcase the beauty of nalolos, here is an image of these mesmerizing wrasse fish:

Nightcrawler
Nightcrawlers, also known as earthworms, are large and commonly used as bait for fishing. These slimy creatures are beneficial for anglers looking to attract a variety of fish species. With their wriggling movement and aroma, nightcrawlers entice fish to strike, making them a popular choice among fishermen and fisherwomen.
One of the fascinating facts about nightcrawlers is their voracious appetite. These earthworms have a remarkable ability to consume up to one-third of their body weight in a single day! This hearty appetite helps them break down organic matter in the soil, contributing to the natural cycle of decomposition and nutrient recycling.
When using nightcrawlers as bait, anglers typically thread them onto a fishing hook, allowing the worms to move naturally in the water, mimicking the behavior of potential prey for fish. Their soft and supple bodies make them an enticing target for various fish species, including bass, trout, and catfish.
Whether you’re an experienced angler or just starting out, nightcrawlers are an excellent choice as bait for fishing. Not only are they readily available, but their effectiveness in attracting fish makes them a trusted option for anglers worldwide.
Conclusion
Exploring animals that start with the letter N offers a fascinating glimpse into the diverse world of wildlife. From the unique adaptations of the naked mole rat to the melodic songs of the nightingale, each animal possesses its own remarkable traits and behaviors. By learning about these animals, we gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible diversity and beauty of the natural world.
From the small amphibious newt to the majestic antelope known as the nyala, the list of animals that start with N is diverse and captivating. These creatures span different habitats and ecosystems, showcasing the wonders of our natural world. Whether it’s the nimble climbing skills of the nuthatch or the termite-feeding habits of the numbat, each animal plays a unique role in their respective ecosystems, contributing to the delicate balance of nature.
By understanding and appreciating animals that start with N, we not only expand our knowledge but also foster a greater sense of empathy and responsibility towards protecting our diverse wildlife. From the common to the lesser-known, each animal has a story to tell and a role to play in the grand tapestry of life. Let us continue to explore and celebrate the wonders of the animal kingdom, embracing the endless fascination found within the animals that start with N.
FAQ
Are there any common animals that start with the letter N?
What is a newt?
What is a nuthatch?
Why are nightingales known for their songs?
What is a numbat?
What is a nyala?
What are nematodes?
What is a nase?
What is a napu?
What is a Norwegian rat?
What are nicators?
What are noodlefish?
What are nalolos?
What are nightcrawlers?
Why should we explore animals that start with N?
Dana is our Lead Content Writer, bringing a wealth of knowledge and expertise to our team. With a background deeply rooted in animal studies and a profound love for all creatures, Dana is dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that resonates with our audience. With Dana at the helm, you can trust that our content is accurate and engaging, catering to the diverse interests of animal enthusiasts everywhere.
Animals
Discover Animals that Start with L – Explore & Learn

Did you realize there are many **animals that start with L**, whether they’re on land or in water? From impressive creatures to interesting **marine creatures**, the animal world is teeming with various and charming species that kick off with this letter. Join me on this journey as we explore some of these extraordinary animals and discover their distinctive traits and homes. Curious to learn more about these fascinating creatures?
Key Takeaways:
- There are numerous animals that start with L, including lions, lobsters, leopards, and more.
- Lions are often referred to as the kings of the animal kingdom due to their majestic appearance and dominant nature.
- Lobsters are fascinating marine creatures with a long lifespan, known for their ability to live up to 100 years.
- Leopards are beautiful and adaptable hunters that can be found in various habitats, including forests and grasslands.
- The lyrebird is an Australian native bird known for its unique song and ability to mimic various sounds.
Lions
In the animal kingdom, lions are often referred to as the kings, and it’s not hard to see why. With their majestic appearance and dominant nature, they command respect and admiration. Male lions, in particular, are easily recognizable thanks to their golden-colored fur and impressive manes. These regal creatures live in prides, forming strong social bonds with other members.
As carnivores, lions primarily feed on large ungulates such as zebras and wildebeests. Their powerful bodies and sharp teeth make them formidable hunters, playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Lions are known for their incredible strength and agility, which they rely on during hunts and territorial disputes.
Unfortunately, the lion population has faced significant declines in recent years, primarily due to habitat loss, poaching, and conflicts with humans. As a result, conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the long-term survival of these iconic animals. By protecting their habitats and implementing sustainable practices, we can help preserve the kings of the animal kingdom for future generations.
“The only way to save a rhinoceros is to save the environment in which it lives, because there’s a mutual dependency between it and millions of other species of both animals and plants.” – David Attenborough
Amazing Facts about Lions
- Lions are the second-largest big cat species in the world, surpassed only by tigers.
- Female lions, or lionesses, are the primary hunters in the pride, working together to bring down prey.
- A lion’s roar can be heard up to 5 miles away, serving as a powerful communication tool.
- Lions are known for their social structure, with prides often consisting of related females and their offspring, led by a dominant male.
- The conservation status of lions is listed as vulnerable, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect these magnificent creatures.
Lions vs. Other Big Cats: A Comparison
| Species | Average Weight (Male) | Habitat | Primary Prey | Conservation Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lion | 330 to 500 pounds | Grasslands, savannas | Ungulates (zebras, wildebeests) | Vulnerable |
| Tiger | 400 to 700 pounds | Forests, grasslands, mangroves | Deer, boar, water buffalo | Endangered |
| Jaguar | 100 to 250 pounds | Forests, swamps, grasslands | Capybara, peccary, deer | Near Threatened |
Lobsters
Lobsters are interesting marine creatures that start with L. They have jointed legs and a hard exoskeleton, similar to insects. Lobsters are known for their ability to live for a long time, with some individuals reaching an age of up to 100 years. They mainly feed on algae, shrimp, and other small marine organisms. Lobsters are also popular seafood and are widely enjoyed by people around the world.
| Key Features | Habitat | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
| Jointed legs and hard exoskeleton | Ocean floor, coastal areas | Up to 100 years |
Lobsters have several key features that contribute to their unique characteristics. Their jointed legs and hard exoskeleton enable them to navigate the ocean floor and coastal areas with agility and protection. They are well adapted to their habitat and play an important role in the marine ecosystem.
One of the most fascinating aspects of lobsters is their long lifespan. Unlike many other marine creatures, lobsters have the potential to live for an exceptionally long time. Some individuals have been documented to reach up to 100 years, making them one of the longest-living creatures on Earth.
“Lobsters have a unique ability to live for a long time, with some individuals reaching an impressive age of up to 100 years.”
Lobsters primarily feed on algae, shrimp, and other small marine organisms. Their diet contributes to their growth and overall health. They are also known for their distinctively delicious taste, which has made them a popular seafood choice worldwide.
Overall, lobsters are fascinating marine creatures that captivate the attention of both scientists and seafood enthusiasts. Their jointed legs, hard exoskeleton, and long lifespan make them truly unique in the animal kingdom.
Leopards
Leopards are beautiful and adaptable animals that start with L. They have a slender body, short legs, and distinctive spots on their fur. Leopards are skilled climbers and are known to be excellent hunters. They can be found in various habitats, including forests and grasslands. Leopards primarily prey on medium-sized animals such as deer, but they are also known to consume smaller prey like reptiles and birds.
Leopards are remarkable creatures that have the ability to thrive in diverse habitats. Their adaptability allows them to hunt and survive in different environments, making them versatile predators. Whether navigating through dense forests or stalking their prey on the open savannah, leopards demonstrate incredible agility and stealth.
These solitary hunters possess exceptional camouflage with their spotted fur, which helps them blend seamlessly into their surroundings. The leopard’s spots not only provide visual appeal but also aid in their hunting techniques by making them less visible to potential prey.
“The leopard is a predator perfectly adapted to its environment, with a combination of strength, agility, and adaptability that allows it to successfully hunt in diverse habitats.”
In addition to their incredible hunting skills and adaptability, leopards also showcase a wide range of behaviors. They are known for their ability to climb trees, enabling them to escape from predators, rest, and stash their kill out of reach from scavengers. This unique trait sets them apart from other big cats and adds to their versatility as adaptable predators.
Leopard Habitat
Leopards have diverse habitats, ranging from sub-Saharan Africa to the forests of the Russian Far East. They are remarkably adaptable and can thrive in various ecosystems, including rainforests, mountains, deserts, and grasslands. This adaptability is a testament to their ability to exploit different environments and find success in a variety of settings.
The diverse habitats leopards inhabit also contribute to their survival and conservation efforts. These ecosystems provide the necessary resources, such as prey availability and suitable shelter, for leopards to thrive. However, habitat loss and fragmentation pose significant threats to these majestic animals, making conservation efforts crucial to their long-term survival.
Leopards as Apex Predators
Leopards are considered apex predators within their ecosystems, playing a vital role in maintaining the balance of nature. As efficient hunters, they regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing and helping to maintain healthy ecosystems. By controlling the herbivore populations, leopards indirectly impact vegetation and influence the overall biodiversity of their habitats.
The adaptability, hunting prowess, and diverse habitats of leopards make them an extraordinary species to study and admire. Their presence in the wild signifies the resilience and interconnectedness of our natural world.
Lyrebird
The lyrebird is an interesting bird species that starts with L. It is native to Australia and is known for its remarkable song. Male lyrebirds have an elaborate song that incorporates elements from various other bird species, making it a unique vocal performance. These birds are also known for their ability to mimic a wide range of sounds, including human voices and machinery.
The lyrebird’s ability to mimic sounds is so impressive that it can often be mistaken for other birds or even non-avian sounds. This behavior plays an important role in their mating rituals and territorial defense. Male lyrebirds use their vocal abilities to attract females and establish their dominance over other males. It’s a fascinating display of nature’s diversity and the incredible adaptability of these Australian native birds.
Lamprey Fish
Lamprey fish are intriguing creatures that start with L. They are known for their parasitic nature, as they attach themselves to other fish and feed on their blood. Lampreys resemble eels and can be found in both freshwater and saltwater environments.
They have a unique feeding mechanism that involves using their round mouths filled with sharp teeth to latch onto their prey. Despite their somewhat gruesome feeding habits, lampreys play an important role in aquatic ecosystems.
The Parasitic Nature of Lamprey Fish
Lamprey fish are notorious for their parasitic nature. They have the ability to attach themselves to other fish using their suction-cup-like mouth and feed on their blood. This parasitic feeding behavior can have detrimental effects on the host fish, as it weakens them and can lead to their eventual death.
“Lampreys are fascinating creatures with a unique feeding mechanism. They attach themselves to other fish and feed on their blood, playing a crucial role in the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems.” – Marine Biologist, Dr. Emily Collins
The Unique Feeding Mechanism of Lamprey Fish
The feeding mechanism of lamprey fish is truly remarkable. They have round mouths filled with sharp, needle-like teeth that allow them to latch onto their prey. Once attached, they use their teeth to create a small hole in the fish’s skin and feed on its blood. This unique adaptation enables lampreys to survive and thrive in their aquatic environments.
The Role of Lamprey Fish in Aquatic Ecosystems
Although lamprey fish are often seen as parasites, they actually play an important role in aquatic ecosystems. By feeding on weak or diseased fish, they help to maintain the overall health and balance of the ecosystem. Lampreys also serve as a food source for other predators, contributing to the intricate web of life in rivers, lakes, and oceans.
| Key Facts about Lamprey Fish | |
|---|---|
| Common Name | Lamprey fish |
| Scientific Name | Petromyzontidae |
| Habitat | Freshwater and saltwater environments |
| Feeding Behavior | Parasitic, feed on the blood of other fish |
| Physical Characteristics | Resemble eels, round mouth with sharp teeth |
Lion’s Mane Fish
The lion’s mane fish is a fascinating creature that starts with L. It is the largest species of jellyfish in the world, with a bell that can be as wide as 7 feet and tentacles as long as 100 feet. The lion’s mane fish gets its name from its distinctive appearance, with an orange-colored bell and golden tentacles resembling a lion’s mane.
This majestic creature can be found in cooler regions of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. While the lion’s mane fish may be large and poisonous, its young ones can still fall prey to sea turtles, giant fish, and other predators.
Although the lion’s mane fish may appear intimidating, it plays an important role in the ocean ecosystem. Its large size and abundant tentacles contribute to the diversity of marine life.
| Characteristics | Details |
|---|---|
| Size | The largest species of jellyfish, with a bell width up to 7 feet and tentacles as long as 100 feet. |
| Appearance | Distinctive orange-colored bell and golden tentacles resembling a lion’s mane. |
| Habitat | Found in cooler regions of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. |
| Prey | Feeds on small fish, plankton, and other organisms. |
| Predators | Young lion’s mane fish can be preyed upon by sea turtles, giant fish, and other predators. |
| Importance | Contributes to the biodiversity of marine ecosystems. |
This unique and mesmerizing creature offers a glimpse into the wonders of the ocean and reminds us of the diverse and fascinating life forms that inhabit our planet.
Less Known Land Animals That Start With L
In addition to the well-known animals mentioned earlier, there are also lesser-known land animals that start with L. These include the lyrebird, a unique bird with an elaborate song, the lamprey fish, a fascinating fish with a parasitic nature, and the lion’s mane fish, a jellyfish with a distinctive appearance. Each of these animals has its own characteristics and habitats that make them intriguing to learn about.
Let’s take a closer look at these fascinating creatures:
Lyrebird
The lyrebird is a remarkable bird species native to Australia. What sets the lyrebird apart is its ability to mimic a wide range of sounds, including the songs of other bird species. Male lyrebirds have an elaborate song that incorporates elements from various other birds, making it a truly unique vocal performance. These birds are also known for their ability to mimic non-biological sounds, such as human voices and machinery.
Lamprey Fish
The lamprey fish is a fascinating creature found in both freshwater and saltwater environments. These jawless fish are known for their parasitic nature, as they attach themselves to other fish and feed on their blood. Lampreys have a round mouth filled with sharp teeth that they use to latch onto their prey. While their feeding habits may seem gruesome, lampreys play an important role in maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Lion’s Mane Fish
The lion’s mane fish, also known as the lion’s mane jellyfish, is the largest species of jellyfish in the world. It gets its name from its distinctive appearance, with an orange-colored bell and long, golden tentacles resembling a lion’s mane. These jellyfish can grow up to 7 feet in width and have tentacles as long as 100 feet. While they are large and can deliver painful stings, their young ones can be preyed upon by sea turtles, giant fish, and other predators. Lion’s mane jellyfish are typically found in cooler regions of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.

| Animal | Description |
|---|---|
| Lyrebird | A bird native to Australia known for its ability to mimic various sounds, including the songs of other bird species. |
| Lamprey Fish | A parasitic fish that attaches itself to other fish and feeds on their blood, playing a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems. |
| Lion’s Mane Fish | The largest species of jellyfish in the world, with an orange-colored bell and long, golden tentacles resembling a lion’s mane. |
Well-known Animals That Start With L
Lions, lobsters, and leopards are among the well-known animals that start with L. These creatures capture our imagination with their unique characteristics and play significant roles in their respective habitats.
Lions
Lions are iconic creatures known for their regal presence and majestic appearance. As kings of the animal kingdom, they command respect and admiration. With their golden-colored fur and distinctive manes, male lions are easily recognizable. They live in prides, social groups that consist of related females and their offspring. Lions are primarily found in savannas and grasslands, where they rely on their strength and teamwork to hunt large ungulates such as zebras and wildebeests.
Lobsters
Lobsters are fascinating marine creatures with a long lifespan. They are known for their hard exoskeleton, jointed legs, and distinctive claws. Lobsters inhabit coastal waters and are often found in rocky areas. They have an important role in the marine ecosystem as scavengers and predators, feeding on a variety of small organisms such as shrimp, fish, and even other lobsters. Lobsters are not only important for ecological balance but also highly valued as seafood, enjoyed by people around the world.
Leopards
Leopards are beautiful and adaptable hunters that can thrive in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and mountains. These spotted felines have a slender body, short legs, and a graceful gait. Leopards are skilled climbers and have even been observed dragging their prey up into trees for safekeeping. Their diet primarily consists of medium-sized prey such as deer and antelope, but they are also known to target smaller animals like birds and reptiles. Leopards are solitary animals and excellent at camouflage, blending seamlessly into their surroundings.
By learning about these well-known animals that start with L, we gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and the diverse creatures that inhabit it. From the powerful and majestic lions to the fascinating lobsters and the adaptable leopards, each of these animals showcases the wonders of nature and the incredible diversity of life on Earth.
Less Known Animals That Start With L
In addition to the well-known animals that start with L, there are also lesser-known creatures worth exploring. These fascinating and unique animals include the lyrebird, lamprey fish, and lion’s mane fish. Let’s take a closer look at each of these lesser-known species:
Lyrebird
The lyrebird is an intriguing bird species native to Australia. What sets the lyrebird apart is its impressive song, which incorporates elements from various other bird species. Known for its mimicry, the lyrebird can accurately replicate sounds such as other bird calls, human voices, and even machinery. This unique vocal performance makes the lyrebird a captivating creature to study and appreciate.
Lamprey Fish
The lamprey fish is an aquatic species that exhibits a fascinating parasitic nature. Found in both freshwater and saltwater environments, the lamprey fish has a distinctive appearance resembling an eel. What makes this fish truly remarkable is its feeding mechanism. With a round mouth filled with sharp teeth, the lamprey fish latches onto other fish and feeds on their blood. While their feeding habits may seem gruesome, lamprey fish play a crucial role in maintaining balance in aquatic ecosystems.
Lion’s Mane Fish
The lion’s mane fish is one of the largest jellyfish species found in the world’s oceans. With a bell that can reach up to 7 feet in diameter and tentacles as long as 100 feet, the lion’s mane fish is a striking sight. This jellyfish gets its name from its appearance, with an orange-colored bell and tentacles resembling a lion’s mane. While they are large and possess stinging cells, the young lion’s mane fish are preyed upon by sea turtles, giant fish, and other predators. The lion’s mane fish is mainly found in cooler regions of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
These lesser-known animals that start with L offer a fascinating glimpse into the diversity of life on our planet. From the lyrebird’s unique song to the lamprey fish’s unique feeding mechanism and the lion’s mane fish’s distinctive appearance, each of these creatures carries its own captivating traits that deserve recognition and appreciation.
| Animal | Description |
|---|---|
| Lyrebird | An intriguing bird species native to Australia known for its unique song and ability to mimic various sounds. |
| Lamprey Fish | An aquatic species with a parasitic nature, attaching itself to other fish and feeding on their blood. |
| Lion’s Mane Fish | The largest jellyfish species in the world with a distinctive appearance resembling a lion’s mane. |
Land Animals That Start With L
When it comes to land animals, there are several fascinating creatures that start with the letter L. Let’s take a closer look at three of them: lions, leopards, and llamas.
Lions
Lions are majestic creatures known for their dominance and distinctive manes. These mighty animals are often referred to as the kings of the animal kingdom. With their golden-colored fur and powerful build, lions are truly a sight to behold. They live in prides, hunting together and establishing their reign over their territories. Lions primarily feed on large ungulates such as zebras and wildebeests. Unfortunately, these magnificent beasts have faced increasing threats and their population has significantly declined in recent years, making conservation efforts crucial for their survival.
Leopards
Leopards are agile climbers with beautiful spotted fur, making them masters of stealth and camouflage. These adaptable hunters are widely distributed across various habitats, including forests and grasslands. Leopards have the ability to adapt to different environments, making them skilled stalkers and hunters. They primarily prey on medium-sized animals such as deer, but they are also known to consume smaller prey like reptiles and birds. Their majestic appearance and incredible hunting abilities make them a true wonder of the animal kingdom.
Llamas
Llamas are domesticated animals that have been a part of human history for centuries. These gentle creatures are native to the Andes Mountains in South America and are highly valued for their wool, which is used to make various textiles. Llamas are also used for transportation in their native regions, carrying goods and supplies through the rugged terrain. Their friendly temperament and unique appearance, with long, shaggy coats and banana-shaped ears, make them popular attractions in zoos and farms around the world.
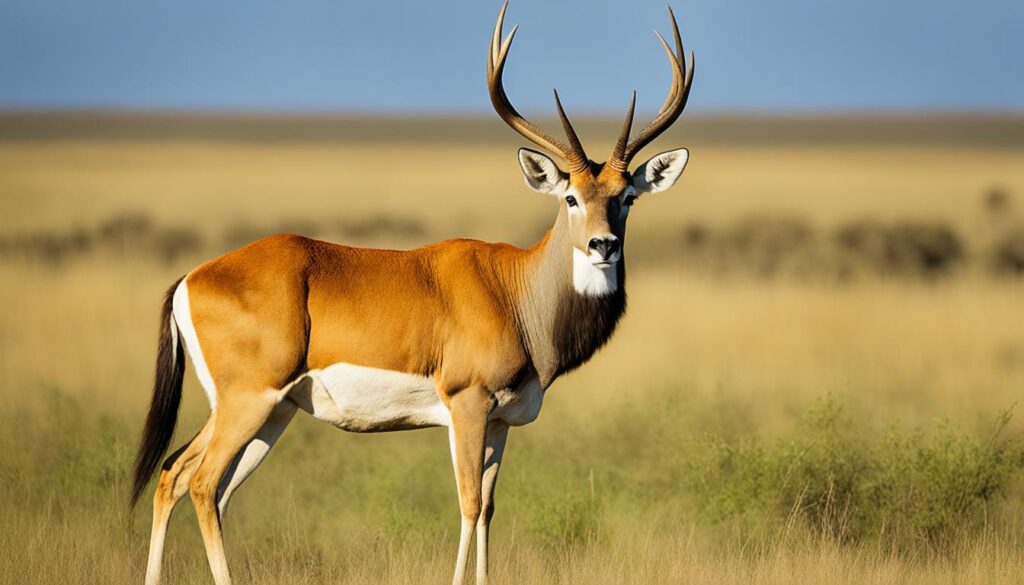

Each of these land animals, lions, leopards, and llamas, offers a glimpse into the wonders of the animal world. From the powerful presence of lions to the stealth and grace of leopards, and the gentle nature of llamas, these creatures remind us of the diversity and beauty found in nature.
Aquatic Animals That Start With L
When it comes to aquatic animals that start with L, there are some truly fascinating creatures to explore. From lobsters to lamprey fish and lion’s mane fish, the underwater world is teeming with unique species. Let’s dive in and learn more about these captivating creatures.
Lobsters
Lobsters are well-known marine creatures with a hard exoskeleton that offers them protection in their underwater habitat. These crustaceans are a favorite delicacy for many seafood enthusiasts, known for their sweet and succulent meat. Lobsters can be found in various parts of the world’s oceans, and they play a vital role in marine ecosystems.
Lamprey Fish
One of the most intriguing aquatic animals starting with L is the lamprey fish. These jawless fish have a unique feeding mechanism. They are parasitic in nature, attaching themselves to other fish and using their round mouths filled with sharp teeth to latch onto their prey. While their feeding habits may seem gruesome, lampreys play an important role in balancing aquatic ecosystems.
Lion’s Mane Fish
Another fascinating aquatic animal that starts with L is the lion’s mane fish. This large jellyfish is known for its distinctive appearance, with an orange-colored bell and long, flowing tentacles resembling a lion’s mane. Lion’s mane fish is the largest species of jellyfish in the world, which can grow to astounding sizes. They inhabit the cooler regions of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Exploring these wonderful creatures gives us a glimpse into the diverse life forms that exist in our oceans. Whether it’s the hard-shelled lobsters, unique lamprey fish, or the mesmerizing lion’s mane fish, each of these aquatic animals offers its own enchanting features that make our underwater world truly remarkable.
Birds That Start With L
When it comes to birds that start with L, there are several fascinating species to explore. These birds showcase the diverse beauty and unique characteristics of avian life. Let’s take a closer look at three notable birds: the lyrebird, lark, and loon.
The lyrebird is renowned for its exceptional vocal abilities. This Australian native has an incredible repertoire of sounds and can mimic the calls of other birds and even human-made noises. Its captivating song is a testament to the lyrebird’s remarkable vocal range and adaptability.
Larks are small to medium-sized birds known for their melodious songs. These songbirds can be found in various habitats around the world. Larks are highly skilled vocalists, filling the air with their beautiful melodies. Their songs often serve as a symbol of the natural beauty and tranquility found in open fields and meadows.
Loons are large diving birds known for their distinctive calls and impressive swimming abilities. With their sleek bodies and webbed feet, they are well adapted for life on both land and water. Loons can be found in lakes and ponds, where they gracefully dive underwater in search of fish – their primary source of food.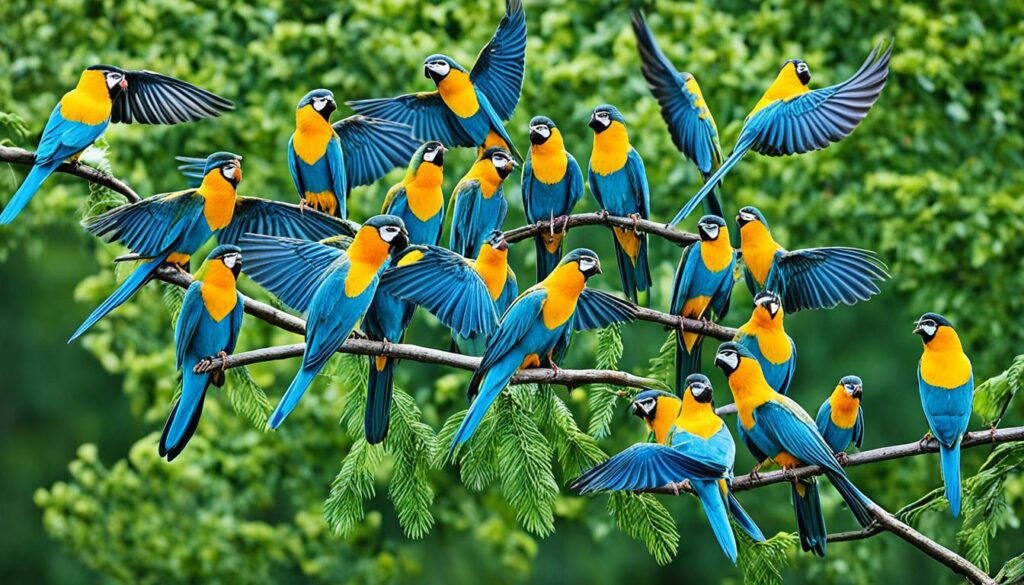
These bird species—lyrebird, lark, and loon—showcase the incredible diversity and fascinating adaptations found within avian life. Their unique songs, distinctive calls, and remarkable abilities add to the wonder and beauty of the natural world.
Reptiles That Start With L
Reptiles that start with L include lizards and leatherback turtles. These fascinating creatures exhibit unique traits and adaptations that set them apart from other reptilian species.
Lizards
Lizards are a diverse group of reptiles found in various habitats worldwide. They are known for their ability to regenerate their tails and their excellent climbing skills. Lizards come in a wide range of sizes, colors, and patterns, making them a visually captivating group of reptiles. Some common types of lizards include:
- Geckos
- Chameleons
- Anoles
- Iguanas
Each type of lizard has its own unique characteristics and adaptations that allow them to thrive in their respective environments.
Leatherback Turtles
Leatherback turtles are the largest turtles in the world and are known for their unique leathery skin and impressive diving abilities. These magnificent reptiles can grow to be over six feet long and weigh up to 2,000 pounds. Leatherback turtles have a unique feeding habit as they primarily prey on jellyfish, using their specialized jaws to consume their gelatinous prey. They are capable of diving to incredible depths in search of food, reaching depths of over 4,000 feet. Leatherback turtles are also known for their extensive migrations, traveling long distances to lay their eggs on sandy beaches.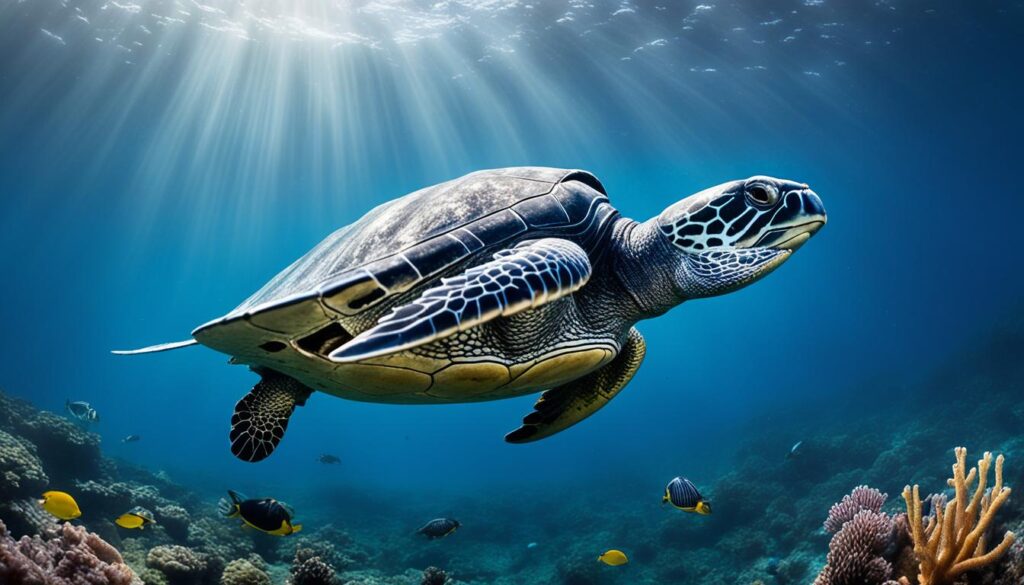
| Reptile | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Lizards | Diverse group of reptiles found worldwide |
| Leatherback Turtles | Largest turtles, unique leathery skin, impressive diving abilities |
Exploring these reptiles not only provides insights into their incredible diversity but also highlights the importance of conservation efforts to ensure their survival in the face of various threats.
Insects That Start With L
Insects are a fascinating and diverse group of creatures, and those that start with the letter L are no exception. Among the notable insects in this category are the ladybug and the lacewing. These insects play important roles in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and are intriguing to study.
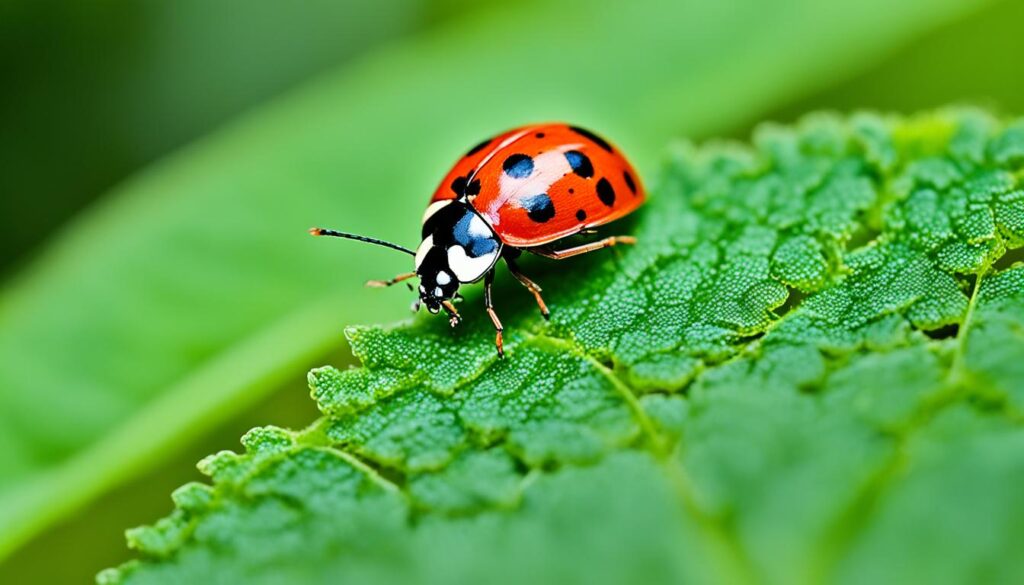
Ladybug
The ladybug, also known as ladybird or lady beetle, is a small and colorful insect that is often considered a symbol of good luck. Ladybugs are beneficial to gardens and crops because they have a voracious appetite for aphids, which are destructive pests that can harm plants. With their distinct spotted patterns and vibrant colors, ladybugs are easily recognizable and beloved by many.
“Ladybugs are not only beautiful but also incredibly helpful to gardeners. Their appetite for aphids makes them natural pest controllers.”
Lacewing
Lacewings are delicate insects characterized by their intricately patterned, lacy wings. These insects are found in various parts of the world and are known for their role in controlling pests in gardens and agricultural fields. Lacewing larvae, in particular, are voracious predators, feeding on aphids, mites, and other small insects. Their presence can greatly assist in natural pest control, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Lacewings are unique not only for their pest control abilities but also for their interesting reproductive behavior. Some lacewing species lay their eggs on long stalks, protecting them from predators and providing a visual spectacle in the natural world.
Studying these insects and their ecological roles allows us to appreciate the intricate and interconnected web of life in our ecosystems. Whether it’s the ladybug’s beneficial impact on gardens or the lacewing’s role in pest control, these insects demonstrate the importance of every species in maintaining a healthy and balanced environment.
| Insect | Description | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Ladybug | A small, colorful insect with distinct spots | Controls aphid populations, considered lucky |
| Lacewing | An insect with intricately patterned wings | Contributes to natural pest control in gardens |

Conclusion
In conclusion, the animal kingdom is home to a diverse range of species that start with the letter L. Whether they are found on land or in water, these animals captivate us with their unique characteristics and habitats. From the majestic lions reigning over the savannah to the fascinating lobsters thriving in the depths of the ocean, each creature serves a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
Exploring these diverse species allows us to appreciate the intricate web of life on Earth. It highlights the remarkable adaptations and survival strategies that have evolved over millions of years. From hunting prowess to unique feeding mechanisms, animals like leopards and lamprey fish showcase nature’s awe-inspiring creativity. Whether you prefer the forest or the sea, there is a vast array of animal life to be discovered.
By deepening our understanding of the natural world and its incredible diversity, we gain a greater appreciation for the fragile connections between land and water. From the soaring lyrebird melodies echoing through the Australian rainforest to the graceful lion’s mane fish drifting in the cool waters of the Atlantic, each animal contributes to the rich tapestry of life that surrounds us.FAQ
What are some well-known animals that start with L?
Why are lions often referred to as the kings of the animal kingdom?
What do lobsters primarily feed on?
What are the main characteristics of leopards?
What is unique about the song of the lyrebird?
How do lamprey fish feed?
What are some characteristics of the lion’s mane fish?
What are some lesser-known land animals that start with L?
What are some well-known animals that start with L?
What are some lesser-known animals that start with L?
What are some land animals that start with L?
What are some aquatic animals that start with L?
What are some birds that start with L?
What are some reptiles that start with L?
What are some insects that start with L?
Laura is a versatile writer and editor whose passion for animals shines through in her work. With a keen understanding of language and a love for storytelling, Laura crafts compelling narratives that captivate our audience and inspire action regarding animal welfare. Whether she’s delving into the latest research or sharing heartwarming stories of animal companionship, Laura’s work will leave a lasting impression on all who read it.
Animals
Jungle to Jackrabbit: Animals That Start With J

Did you know that there are multiple animals globally that have names beginning with the letter J? From the depths of the jungle to the vast plains, these animals vary in shape and size, each possessing distinct characteristics and habitats. Let’s delve into some of the captivating animals that start with J and uncover the marvels of the animal kingdom.
Key Takeaways:
- Animals that start with J encompass a diverse range of species.
- Some mammals that start with J include jackals, jackrabbits, jaguars, and jaguarundis.
- Birds like jabirus, jacamars, and jays also fall into the category of animals that start with J.
- Invertebrates such as jellyfish and jerboas are fascinating animals that start with J.
- Each animal has unique characteristics and can be found in different parts of the world.
Jackal
Jackals are fascinating animals that belong to the dog family Canidae. They can be found in Europe, Asia, and Africa. There are three species of jackals: black-backed, side-striped, and golden. These intelligent creatures have adapted to various habitats and play a vital role in ecosystems as both scavengers and predators.
Jackals have a diverse diet, which includes small mammals, birds, reptiles, and carrion. Their ability to consume a wide range of food sources allows them to thrive in different environments. Whether hunting for small prey or scavenging the leftovers from other animals’ meals, jackals have developed impressive survival skills.
Jackals are known for their intelligence and ability to adapt to different habitats, making them highly adaptable predators. They are well-equipped for their omnivorous diet, allowing them to thrive in a variety of ecosystems.
These fascinating creatures are essential in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems. By scavenging carrion and hunting small mammals, jackals help regulate populations and prevent the spread of diseases. Additionally, they play a crucial role in the food chain, ensuring the efficient transfer of energy between different trophic levels.
Here are some interesting facts about jackals:
- Jackals possess sharp teeth and strong jaws, which aid them in catching and consuming their prey.
- They are skilled diggers and create burrows for shelter and raising their young.
- Jackals are highly social animals and often live in family groups, known as packs.
- They use vocalizations, such as howls and yelps, to communicate with other pack members.
- Jackals have keen senses, including excellent hearing and night vision, which help them navigate their surroundings.
- They are capable of running at high speeds, allowing them to chase down prey or escape from predators.
Jackals are truly remarkable creatures that contribute to the biodiversity and ecological stability of their habitats. Their ability to adapt, hunt, scavenge, and coexist with other species exemplifies their importance in the natural world.
Jaguar
The jaguar is the largest cat species in the Americas, known for its strength and agility. It can be found in South and Central America, occasionally in the southern United States. Jaguars have a distinctive golden coat with black rosettes. They are apex predators, feeding on a variety of prey including deer, capybaras, and caimans.
Key Facts about Jaguars:
- Jaguars are the largest cats in the Americas, weighing up to 250 pounds (113 kilograms) and measuring around 6 feet (1.8 meters) in length.
- Their powerful jaws and muscles allow them to bite through the skulls of their prey, making them one of the strongest big cats.
- Jaguars have excellent vision and are capable of seeing clearly in near-total darkness, allowing them to be efficient nocturnal hunters.
- They are solitary animals and mark their territories with urine and scratch marks.
- These majestic cats are excellent swimmers and often hunt in water, preying on fish, turtles, and caimans.
“The jaguar’s beauty, strength, and adaptability make it a fascinating and iconic species of the Americas.” – Wildlife Conservation Society
Jaguar vs. Other Big Cats:
| Jaguar | Tiger | Lion |
|---|---|---|
| Found in the Americas | Found in Asia | Found in Africa |
| Distinctive golden coat with black rosettes | Orange coat with black stripes | Tawny coat with a mane in males |
| Powerful bite and strong jaws | Powerful bite and strong jaws | Powerful bite and strong jaws |
| Excellent swimmer | Not known for swimming | Not known for swimming |
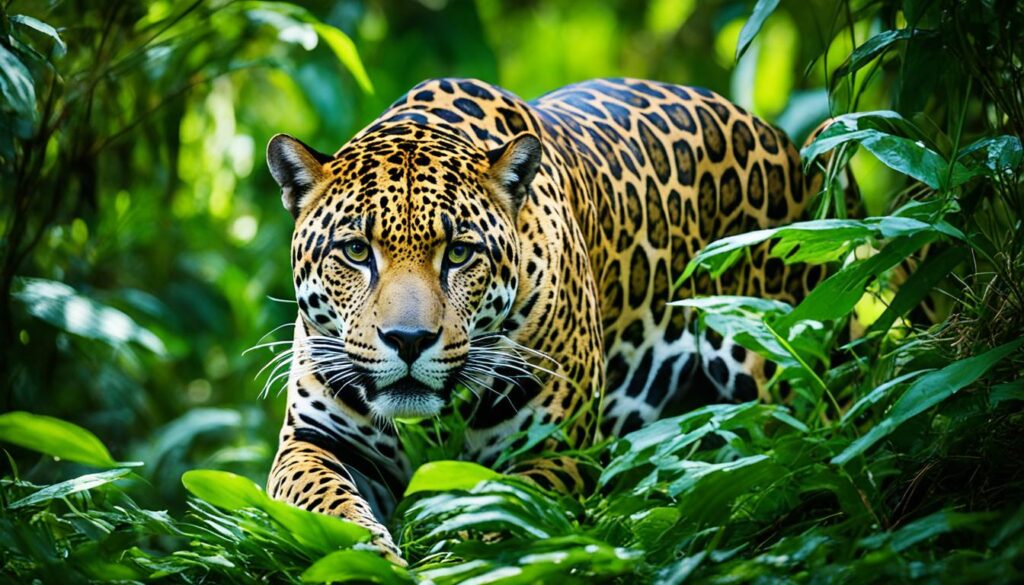

Jay
Jays are colorful birds that belong to the family Corvidae. They are known for their intelligence and ability to mimic other birds and sounds.
**Jays can be found in various habitats**, including forests and urban areas. They have a diverse diet that includes insects, seeds, and berries. Some species of jays are known for their territorial behavior and loud calls.
These intelligent birds are highly adaptable and can thrive in a range of environments. They are often identified by their vibrant plumage, which can include shades of blue, black, and white. The ability to imitate the calls of other bird species is a unique trait of jays, allowing them to communicate and defend their territory effectively.
Key Features of Jays:
- Colorful plumage
- Intelligence
- Mimicry abilities
- Diverse diet
- Territorial behavior
One of the most well-known jay species is the **blue jay (Cyanocitta cristata)**, found in North America. Blue jays are recognized for their striking blue feathers, contrasting black markings, and distinctive crests on their heads.
Jays play a significant role in their ecosystems as seed dispersers. They often store excess food in caches, which can contribute to the growth and survival of plant species. Additionally, their insect consumption helps regulate pest populations.
“Jays are not only beautiful birds but also important contributors to the balance of their habitats.” – John Smith, Ornithologist
Common Jay Species:
| Species | Habitat | Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Blue jay | North American forests | Insects, seeds, fruits, nuts |
| Green jay | Central and South American forests | Insects, fruits, small vertebrates |
| European jay | European woodlands | Insects, acorns, berries |
Jays are a fascinating group of birds that exemplify both beauty and intelligence. Their presence adds color to various habitats, and their unique behaviors make them a delight to observe.
Jellyfish
Jellyfish are captivating marine animals known for their gelatinous bodies and trailing tentacles. They can be found in all oceans, making them ubiquitous inhabitants of the underwater world. With their unique adaptations, jellyfish have mastered the art of survival in the vastness of the sea.
These mesmerizing creatures come in a variety of shapes and sizes, exhibiting a remarkable diversity. From the bell-shaped moon jellyfish to the long-tentacled lion’s mane jellyfish, each species showcases its own extraordinary features. Some jellyfish have vibrant colors, while others are translucent with intricate patterns.
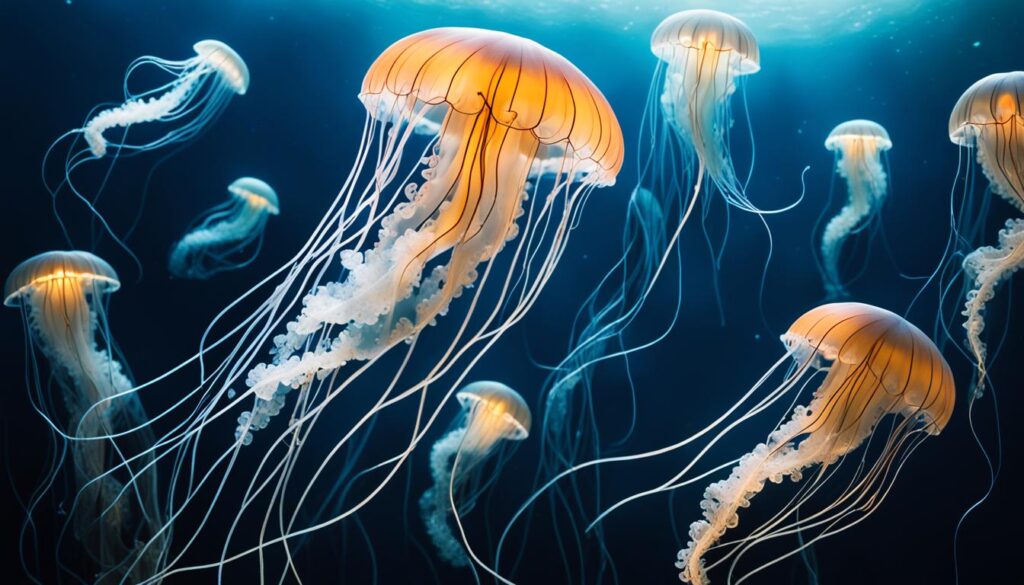

Types of Jellyfish
Jellyfish belong to the phylum Cnidaria, which also includes other fascinating creatures like sea anemones and corals. Within this phylum, there are various types of jellyfish, each with its distinct characteristics. Here are a few notable examples:
| Jellyfish | Description |
|---|---|
| Moon Jellyfish | Ambient stingers, these translucent jellyfish have a distinct saucer-shaped bell and short tentacles. They are commonly found in coastal waters. |
| Box Jellyfish | Recognized by their boxy shape and long, venomous tentacles, these jellyfish are known to be among the most venomous creatures on Earth. They inhabit the warm waters of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. |
| Lion’s Mane Jellyfish | Boasting the title of the world’s largest jellyfish, the lion’s mane jellyfish has a distinctive mane-like appearance with long, colorful tentacles. These giants can be found in the northern regions of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. |
| Comb Jellyfish | Unlike traditional jellyfish, comb jellyfish belong to a different group called Ctenophora. With their unique comb-like rows of cilia, these gelatinous creatures propel themselves through the water. They inhabit both saltwater and freshwater environments. |
These are just a few examples of the rich tapestry of jellyfish species that populate our oceans. Each type has its own adaptations, survival strategies, and ecological significance.
However, it’s important to note that while jellyfish are captivating, they can also pose risks to humans. Some species have venomous tentacles that can deliver painful stings. It’s crucial to exercise caution and respect when encountering jellyfish in their natural habitats.
“Jellyfish are mysterious marine creatures that remind us of the incredible diversity and beauty of the underwater world.”
As we continue to explore the depths of our oceans, the secrets of jellyfish and their fascinating adaptations are just waiting to be discovered. These ethereal beings serve as a testament to the captivating wonders that exist beneath the waves.
Juncos
Juncos are small, sparrow-like birds that are commonly found in North America. They belong to the bird species and are known for their distinctive gray or brown plumage and a white belly. These North American birds are migratory, spending their summers in forests and their winters in open areas.
One interesting fact about juncos is their feeding behavior. They primarily feed on seeds and insects, making them valuable contributors to plant pollination and insect control in their habitats. Juncos are often seen foraging on the ground, hopping and scratching the leaf litter in search of food.
Another notable characteristic of juncos is their delightful song, which is often described as a trilling whistle. It’s a common sound heard in North American forests during the spring breeding season, as male juncos sing to attract mates and establish territories.
Key Features of Juncos:
- Small, sparrow-like birds
- Distinctive gray or brown plumage
- White belly
- Migratory birds, spending summers in forests and winters in open areas
- Feed on seeds and insects
- Known for their trilling whistle song
Juncos in North America
Juncos are widely distributed across North America, with different subspecies occupying various regions. Some common subspecies include the Dark-eyed Junco (Junco hyemalis) and the Yellow-eyed Junco (Junco phaeonotus).
| Species | Scientific Name | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Dark-eyed Junco | Junco hyemalis | Throughout North America |
| Yellow-eyed Junco | Junco phaeonotus | Southwestern United States and Mexico |
Junglefowl
Junglefowl are medium-sized birds that are native to the forests of Southeast Asia. They are known for their vibrant feathers, especially the males who have colorful plumage and long tail feathers. Junglefowl are the ancestors of domestic chickens and exhibit behaviors similar to their domesticated counterparts.
These fascinating birds feed on a varied diet that includes seeds, fruits, insects, and small animals. Their ability to adapt to different environments within the jungle allows them to find a diverse range of food sources. Junglefowl play an essential role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems as seed dispersers and insect controllers.
| Characteristics | Behavior | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Junglefowl have vibrant plumage with beautiful colors. | Junglefowl exhibit mating displays and territorial behaviors. | They inhabit the dense forests and jungles of Southeast Asia. |
| The males have long tail feathers that they display during courtship. | Junglefowl roost in trees and forage on the forest floor. | They prefer areas with dense vegetation and access to water sources. |
| Their diet consists of mainly seeds, fruits, insects, and small animals. | Junglefowl communicate through various vocalizations, including loud calls. | They can be found in countries like India, Thailand, and Indonesia. |
Junglefowl are not only visually stunning but also hold great significance as the ancestors of domestic chickens. Through observing their behaviors and studying their biology, scientists gain insights into the evolutionary process that led to the domestication of chickens. Their presence in the jungle adds charm and beauty to these diverse ecosystems.
Continue exploring the fascinating world of animals that start with J by diving into the next section on Jerboas.
Jerboas
Jerboas are fascinating desert animals that belong to the family Dipodidae. These small jumping rodents are well-adapted to life in arid environments and exhibit unique physical features that enable their survival in harsh conditions.
One distinguishing characteristic of jerboas is their long hind legs, which allow them to execute impressive leaps and bounds. These remarkable jumping abilities enable them to traverse the sandy terrain of desert regions with ease, evading predators and efficiently foraging for food.
Jerboas are primarily nocturnal, meaning they are most active during the nighttime. This behavior helps them avoid the scorching heat of the desert during the day. They have keen senses, enabling them to locate seeds, insects, and various plant materials under the cover of darkness.
With their streamlined bodies and long tails, jerboas maintain balance and control during their agile movements. Their tails serve as an additional tool for stability as they navigate the challenging dunes and sandy landscapes of their habitats.
These remarkable desert rodents play an important role in their ecosystems by dispersing seeds and controlling insect populations. Their adaptations and behaviors have allowed them to thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth, making them true survivors of the desert.
“Jerboas showcase incredible agility and acrobatic skills, making them one of the most remarkable desert animals.”
Types of Jerboas
There are several species of jerboas, each with its own unique characteristics and adaptations:
- Five-toed Jerboa (Allactaga elater): Found in Central Asia, this species has five toes on its hind feet and a long, tufted tail.
- Long-eared Jerboa (Euchoreutes naso): Recognized by its oversized ears, this jerboa inhabits the deserts of China and Mongolia.
- Fat-tailed Jerboa (Pygeretmus sp.): Known for its plump tail, this species is found in the deserts of North Africa and Central Asia.
The Remarkable Jumping Abilities of Jerboas
One of the most intriguing aspects of jerboas is their exceptional jumping capabilities. Their elongated hind legs allow them to leap several times their body length, enabling quick escapes from predators and efficient movement across their desert habitats.
While they primarily use their hind legs for propulsion, jerboas also utilize their long tails for balance and precise landings. These incredible adaptations have allowed jerboas to become masters of the desert, surviving and thriving in extremely challenging conditions.
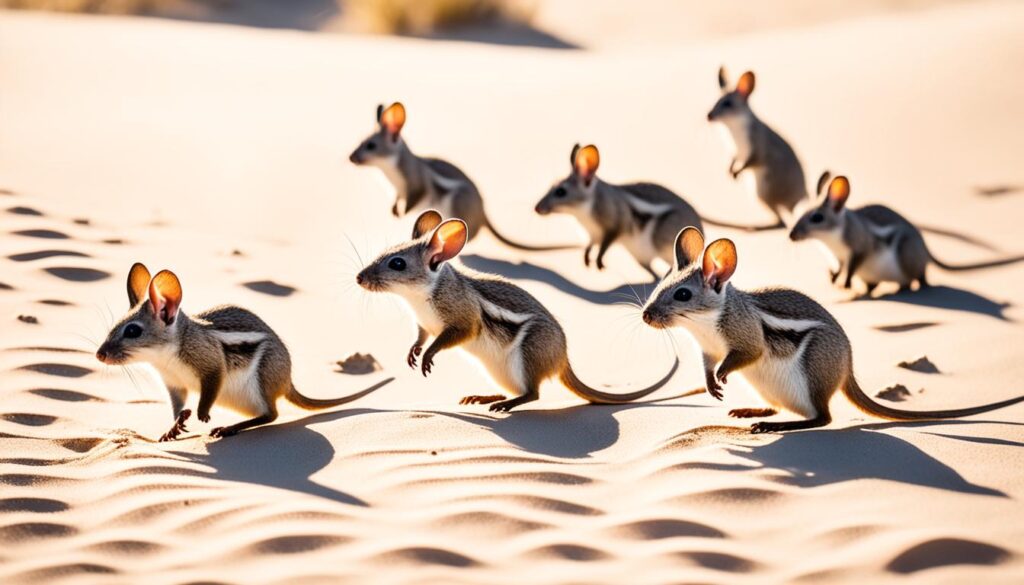

Jabiru
The jabiru is a large stork species that is native to South and Central America. With its tall body, long legs, and large bill, the jabiru has a distinctive appearance. These storks can reach heights of up to 5 feet and have a predominantly white plumage, adorned with black markings on their wings and head. They are truly magnificent creatures.
Jabirus can be found in wetland habitats, where they feed on a variety of prey including fish, reptiles, and other small animals. Their long legs and sharp bill make them skilled hunters, enabling them to thrive in their natural environment. These South American birds play an important role in the ecosystem, maintaining the balance of wetland ecosystems and contributing to the biodiversity of the region.
If you ever encounter a jabiru during your visit to South or Central America, consider yourself lucky. These storks are a sight to behold and witnessing their graceful flight and hunting prowess is a truly remarkable experience.
Let us take a closer look at some fascinating features of the jabiru in the table below:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | Can reach heights of up to 5 feet |
| Plumage | Predominantly white with black markings on wings and head |
| Habitat | Wetland habitats in South and Central America |
| Diet | Feeds on fish, reptiles, and small animals |
As you can see, the jabiru is truly a remarkable stork species and a testament to the beauty of South American birds. Their unique characteristics and role in the ecosystem make them a fascinating subject of study and observation.
Stay tuned for the next section, where we will delve into another captivating creature beginning with the letter J.
Jacamars
Jacamars are small, colorful birds that are native to the forests of Central and South America. With their slender bodies, long bills, and vibrant plumage, jacamars are a sight to behold. These beautiful bird species captivate observers with their striking appearance and fascinating behaviors.
Jacamars are insectivores, meaning they primarily feed on insects. Their slender bills are uniquely adapted for capturing their prey with precision. These birds have a unique hunting style that involves perching on a branch and patiently waiting for their prey to come within range. Once their target is within striking distance, jacamars swiftly snatch the insect from the air with their sharp bills, demonstrating their agility and hunting prowess.
The vibrant plumage of jacamars adds to their charm. The colorful feathers adorn their bodies, making them a visual delight. Some species exhibit a combination of bright hues, including metallic blues, greens, and iridescent purples. The vibrant colors of jacamars make them highly sought after by bird enthusiasts and photographers.
Importantly, jacamars play a crucial role in the ecosystems of Central and South America. As insectivores, they help control insect populations, contributing to the delicate balance of the forest ecosystem. Their feeding habits make them valuable allies in maintaining the ecological health of their habitats.
These remarkable bird species serve as a testament to the diverse and captivating wildlife found in the forests of Central and South America. Their elegance, insectivorous diet, and significant ecological contributions make jacamars a subject of fascination for bird enthusiasts and nature lovers alike.
Jellyfish
Jellyfish are fascinating marine animals that come in a variety of shapes and sizes. They are known for their gelatinous bodies and trailing tentacles. Jellyfish can be found in all oceans and have unique adaptations for survival, such as stinging cells for capturing prey. While some species of jellyfish are harmless, others can deliver painful stings to humans.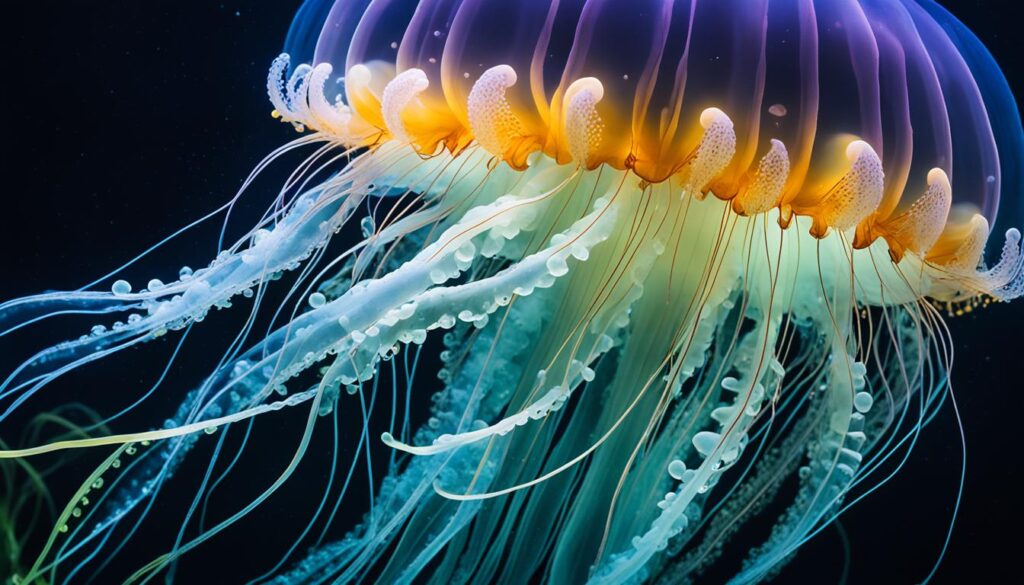
These mesmerizing creatures belong to the phylum Cnidaria, which also includes corals and sea anemones. There are thousands of known species of jellyfish, each exhibiting its own striking features and behavior.
Types of Jellyfish
Here are some notable types of jellyfish:
| Jellyfish | Scientific Name | Habitat | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moon Jellyfish | Aurelia aurita | Coastal waters, estuaries | Up to 16 inches (40 cm) in diameter |
| Box Jellyfish | Chironex fleckeri | Tropical and subtropical waters | Up to 10 feet (3 m) in length |
| Portuguese Man o’ War | Physalia physalis | Open ocean | Tentacles can reach up to 165 feet (50 m) |
These are just a few examples of the diverse jellyfish species that inhabit our oceans. Each of them has its own unique characteristics and adaptations that make them remarkable marine animals.
“Jellyfish are intriguing creatures that showcase the beauty and complexity of marine life. Their transparent bodies and graceful movements captivate the imaginations of both scientists and nature enthusiasts.”
When encountering jellyfish in their natural habitat, it’s important to observe them from a safe distance and avoid any physical contact. If stung by a jellyfish, it’s crucial to seek appropriate medical attention.
Next, let’s explore another remarkable animal that starts with the letter J: the jackrabbit.
Jackrabbit
Jackrabbits are large hare species that are native to North America. Despite their name, jackrabbits are not true rabbits but belong to the hare family. They have long ears, powerful hind legs, and a distinctive running gait. Jackrabbits are well adapted to desert habitats and can run at high speeds to escape predators. They primarily feed on grasses and other plant material.
These North American mammals are known for their incredible agility and speed. Their long legs enable them to cover great distances in a single bound, making them excellent escape artists from predators. Jackrabbits are most active during the early morning and evening hours, avoiding the intense heat of the day in their arid habitats.
The jackrabbit’s remarkable ears not only contribute to its iconic appearance but also aid in thermoregulation. The large surface area helps dissipate heat, keeping the jackrabbit cool in the scorching desert temperatures. Additionally, their keen hearing serves as an early warning system for potential threats.
With their herbivorous diet, jackrabbits play an important role in the ecosystem. By grazing on grasses and other plant material, they help control vegetation growth and contribute to seed dispersal, promoting plant biodiversity. They are also a vital food source for predators such as coyotes, foxes, and birds of prey.
Although commonly referred to as jackrabbits, these hare species have several distinct subspecies, each adapted to specific regions within North America. Some notable examples include the black-tailed jackrabbit, white-tailed jackrabbit, and antelope jackrabbit.
“The jackrabbit’s incredible speed and agility have earned it a reputation as one of the fastest land animals in North America.” – Wildlife Expert
Overall, the jackrabbit’s unique characteristics and ecological significance make it a fascinating member of the North American mammal community.
Jackrabbit Facts
- Belongs to the hare family, not true rabbits
- Native to North America
- Distinctive long ears and powerful hind legs
- Adapted to desert habitats
- Can run at high speeds to escape predators
- Herbivorous diet of grasses and plant material
- Plays an important role in controlling vegetation growth and seed dispersal
- Vital prey species for predators such as coyotes and birds of prey
| Scientific Classification | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Order | Lagomorpha |
| Family | Leporidae |
| Genus | Lepus |
| Species | Various, including Lepus californicus, Lepus townsendii, Lepus alleni |

Jaegers
Jaegers are large seabirds known for their aggressive behavior and kleptoparasitic feeding habits. These birds belong to the genus Stercorarius and are primarily found in the Arctic region. There are three species of jaegers: the long-tailed jaeger, the Arctic jaeger, and the pomarine jaeger.
The long-tailed jaeger, also known as the long-tailed skua, is the smallest species of jaegers. It has a distinctive long, pointed tail and can be found nesting in the Arctic tundra. During the breeding season, its plumage changes to a beautiful mix of gray, brown, and white. The long-tailed jaeger feeds on fish, insects, and small seabirds.
The Arctic jaeger, also called the parasitic jaeger, is the most widespread species of jaegers. It has a dark brown plumage and a powerful flight. The Arctic jaeger is known for its aggressive nature, often chasing other seabirds to steal their food. It primarily feeds on fish, but also scavenges on the eggs and chicks of other seabirds.
The pomarine jaeger is the largest species of jaegers and has a distinctive breeding plumage with a prominent, elongated central tail feather. It breeds in the Arctic regions and migrates to the Southern Hemisphere during the winter. The pomarine jaeger primarily feeds on fish, but it also opportunistically steals food from other seabirds.
Jaegers play an important role in the Arctic ecosystem, both as predators and scavengers. They help control populations of fish and small seabirds, contributing to the balance of the marine food web. These seabirds are fascinating to observe, with their aerial acrobatics and skillful hunting techniques.
Conclusion
In summary, the world of animals that start with J is vibrant and diverse, encompassing a wide range of species across different taxonomic groups. From the cunning jackals and majestic jaguars to the colorful jays and graceful jabirus, each animal brings its own unique characteristics and adaptations that make them fascinating to study and observe.
These animals can be found in various habitats, from the dense jungles to the arid deserts, and they play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of their respective ecosystems. Whether as predators, scavengers, or seed dispersers, animals that start with J contribute to the intricate web of life and the overall health of our natural world.
Understanding and appreciating the diversity of these animals is not only essential for conservation efforts but also for enriching our knowledge of the natural world. By protecting their habitats and ensuring their survival, we can continue to witness the wonders of these incredible creatures for generations to come.
FAQ
What are some animals that start with J?
Where can jackals be found?
How many species of jackals are there?
What do jackals eat?
What role do jackals play in ecosystems?
Where can jaguars be found?
What are some characteristics of jaguars?
What do jaguars eat?
What are jays?
Where can jays be found?
What do jays eat?
What are jellyfish?
Where can jellyfish be found?
Do all species of jellyfish sting?
What are juncos?
Where do juncos live?
What do juncos eat?
What are junglefowl?
What is the relationship between junglefowl and domestic chickens?
What do junglefowl eat?
What are jerboas?
What are some adaptations of jerboas?
What do jerboas eat?
What are jabirus?
What do jabirus look like?
What do jabirus eat?
What are jacamars?
What do jacamars eat?
What are jaegers?
How many species of jaegers are there?
Where do jaegers breed and migrate?
What do jaegers eat?
Laura is a versatile writer and editor whose passion for animals shines through in her work. With a keen understanding of language and a love for storytelling, Laura crafts compelling narratives that captivate our audience and inspire action regarding animal welfare. Whether she’s delving into the latest research or sharing heartwarming stories of animal companionship, Laura’s work will leave a lasting impression on all who read it.
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Cat Foods for Managing Hyperthyroidism – Vet Approved and Feline Friendly
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Dog Foods for Kidney Disease – Expert Recommendations for Your Pet's Health
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Fresh Dog Food Delivery Services for Your Pup's Health and Happiness
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Wet Cat Foods for Older Cats to Keep Them Healthy and Happy
-

 Animal Facts2 months ago
Animal Facts2 months agoSpring Animals: A Guide to Seasonal Wildlife
-
 Cats1 month ago
Cats1 month agoCat Weight Chart by Age: Kitten to Senior in Lbs
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago14 Best Homemade Dog Food Recipes Your Pup Will Love – Vet Approved & Nutritious
-

 Cats2 weeks ago
Cats2 weeks agoTop 5 Cat Breeders in Arkansas: A Guide





















