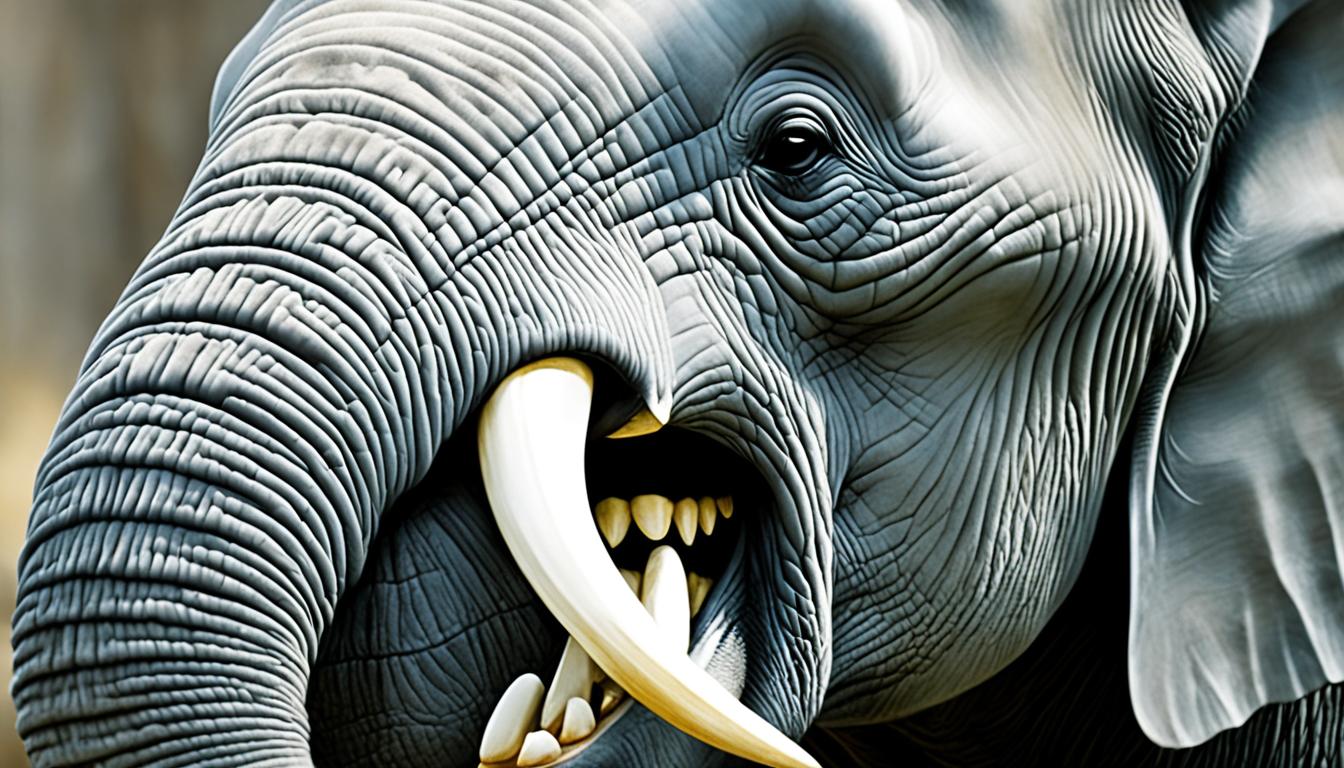
Did you know that there are animals with human teeth? It may sound bizarre, but it’s true! From canines to mountain lions, various animals in the animal kingdom exhibit dental characteristics that closely resemble those of humans. This intriguing phenomenon has captured the curiosity of many, offering a glimpse into the strange and fascinating visuals of nature.
Key Takeaways:
- Animals with human teeth are a surprising and intriguing phenomenon in the animal kingdom.
- Dental characteristics resembling human teeth can be found in a variety of animals, including canines and mountain lions.
- Exploring these unique visuals provides a deeper understanding of the wonders of nature.
- Canine teeth, also known as cuspid or fang teeth, play a crucial role in biting, tearing food, and speech formation.
- Other fascinating animal mouths include lampreys, leatherback sea turtles, tigers, and more.
What are Canine Teeth?
Canine teeth, also known as cuspid teeth or fangs, are longer pointed teeth found in most mammals, particularly predatory carnivores and omnivores. These teeth serve important functions in biting and tearing food, as well as speech formation. In humans, there are four canine teeth, two on the upper jaw and two on the lower jaw.
Canine teeth are named after dogs due to their resemblance to a dog’s long pointed canine teeth. They are designed to be sharp and sturdy, allowing for the efficient consumption of meat and other tough foods. In addition, canine teeth play a significant role in the social interactions of some animals, such as displays of aggression or submission.
Canine teeth play a crucial role in the biological makeup of various species, including humans, as they contribute to both physical and behavioral aspects of life.
Functionality and Features of Canine Teeth
Canine teeth are specifically adapted to perform specific tasks, such as puncturing and tearing flesh. The shape and size of canine teeth vary across species, depending on their dietary needs and hunting techniques.
- Predatory carnivores, such as lions and wolves, have long and sharp canine teeth that enable them to capture and kill their prey effectively. These teeth are essential for survival as they allow predators to immobilize and secure their food source.
- Omnivorous animals, such as bears and raccoons, also possess canine teeth, although they may not be as prominent as those of carnivores. For omnivores, their canine teeth aid in both plant and meat consumption.
The distinct morphology of canine teeth sets them apart from other types of teeth. Canine teeth have a single prominent cusp or point, which aids in piercing and tearing. Their shape, with a sharp and conical tip, allows for efficient biting and gripping. The root of the canine teeth is longer and stronger than that of incisor teeth, ensuring stability and durability in use.
Overall, canine teeth are an integral component of an animal’s dental anatomy, enabling them to thrive in their respective ecological roles.
| Species | Features of Canine Teeth |
|---|---|
| Lions | Prominent, long, and sharp canine teeth for effective prey capture and hunting. |
| Wolves | Long and strong canine teeth that assist in subduing and tearing prey. |
| Bears | Less pronounced canine teeth that aid in both plant and meat consumption. |
| Dogs | Varies depending on breed, but typically have moderately sized canine teeth for holding and tearing food. |
| Humans | Four canine teeth, two on the upper jaw and two on the lower jaw, contribute to biting, speech formation, and supporting the overall dental structure. |
Unique Features of Canine Teeth
Canine teeth possess several unique characteristics that differentiate them from other teeth. Understanding these distinctive features is essential in comprehending their role in dental function.
Eruption of Canine Teeth
Canine teeth typically erupt in children between the ages of 16 to 20 months. This eruption occurs after the incisors and first molars, marking an important developmental milestone. It is during this phase that the upper canines, often referred to as “eye teeth,” emerge beneath the eyes, contributing to their distinctive positioning in the dental arch.
Anchored by a Single Root
Unlike incisors that have a narrow and straight root, canine teeth possess a single root that is thicker and extends deeply into the bone. This robust root structure provides stability and firmly anchors the tooth, supporting its vital functions in biting, tearing, and chewing.
Positioning for Efficient Bite
The positioning of canine teeth is instrumental in achieving a smooth and efficient bite. Situated between the incisors and premolars, canines guide the alignment and positioning of all teeth when the jaws come together. This synchronized interaction ensures an optimal distribution of force during biting and chewing, enabling effective food processing.

Common Problems with Canine Teeth
Canine teeth, like any other dental feature, can encounter various problems. One common issue is the development of impacted canine teeth. Impacted teeth occur when a canine tooth fails to erupt properly, getting trapped beneath the gumline. This can lead to the tooth emerging in an incorrect position, causing discomfort and potential misalignment.
Impacted canine teeth often require orthodontic treatment to guide them into the correct alignment. Orthodontists may use braces, aligners, or other appliances to gradually shift the impacted tooth into its proper position. In some cases, a surgical procedure may be necessary to expose the impacted tooth and facilitate its eruption.
Another concern that can affect canine teeth is receding gums. When gums recede, the underlying tooth roots become exposed, leading to sensitivity and potential damage. Aggressive tooth brushing or poor dental hygiene practices can contribute to gum recession.
To prevent receding gums, individuals should practice gentle brushing techniques using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also crucial in maintaining healthy gums.
Misalignment of canine teeth can exacerbate gum recession. When canines are not properly aligned with the surrounding teeth, they can put excessive pressure on the gums, causing them to recede further. Early intervention through orthodontic treatment can correct misaligned canines and prevent complications.
Common Problems with Canine Teeth:
- Impacted canine teeth
- Receding gums
- Misalignment
Treatment for these common canine teeth problems varies depending on the severity of the condition. Orthodontic intervention, gum therapies, or a combination of both may be necessary to address the specific issue. Early detection and timely treatment are crucial in ensuring optimal oral health and avoiding further complications.
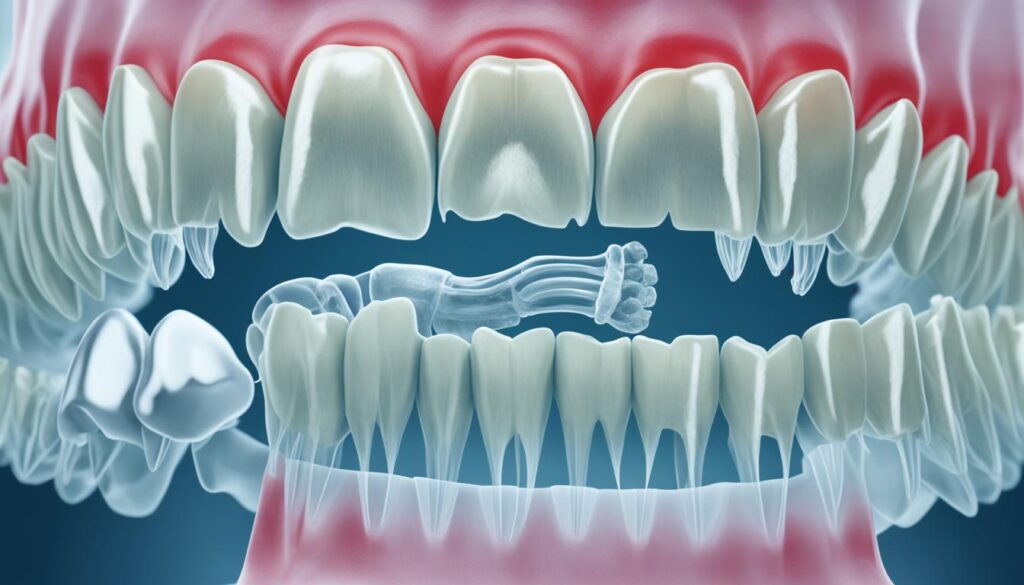
Canine Teeth in the Animal Kingdom
Canine teeth are not only found in humans, but they are also prevalent in the animal kingdom. Carnivorous animals like dogs, wolves, and big cats rely on their prominent canines for hunting and tearing apart prey. Even some omnivorous animals, such as bears, possess well-developed canine teeth. In contrast, herbivores have smaller and less pronounced canine teeth adapted to their diet. For example, deer, sheep, and cows usually have only two canines on the bottom jaw.

| Animal Group | Examples |
|---|---|
| Carnivores |
|
| Omnivores |
|
| Herbivores |
|
Unusual Cases of Canine Teeth in Animals
While most animals have typical canine teeth, some exhibit extraordinary dental characteristics. Let’s explore a few fascinating examples:
The Babirusa
The babirusa, a species of pig, boasts four canine teeth that grow upward and curl towards the head. These remarkable teeth often require grinding to prevent them from growing into the skull, creating a visually striking appearance.
The Saber-Tooth Tiger
The saber-tooth tiger, an extinct predator, possessed elongated upper canine teeth that transformed into large, intimidating fangs. These fearsome teeth were adapted for capturing and subduing prey, giving the saber-tooth tiger a formidable advantage in hunting.
The Musk Deer
Male musk deer develop fang-like upper canines during their mating season. These impressive teeth serve as a visual display to attract females and establish dominance among competing males, showcasing the unique role of canine teeth in reproductive strategies.
The Narwhal
Narwhals, often associated with mythical unicorns, possess canine teeth that grow into long spiraling tusks. These prominent tusks are actually elongated canine teeth and are believed to be primarily used for social communication and as a sensory organ in their Arctic environment.
The Hippopotamus
The hippopotamus possesses enormous canine teeth that continually grow throughout its life. These formidable teeth play a crucial role in territorial displays, warding off rivals, and combat. The immense size and strength of a hippo’s canines reflect the power and aggression it possesses.
To visualize the remarkable canine teeth of these unusual animals, take a look at the image below:
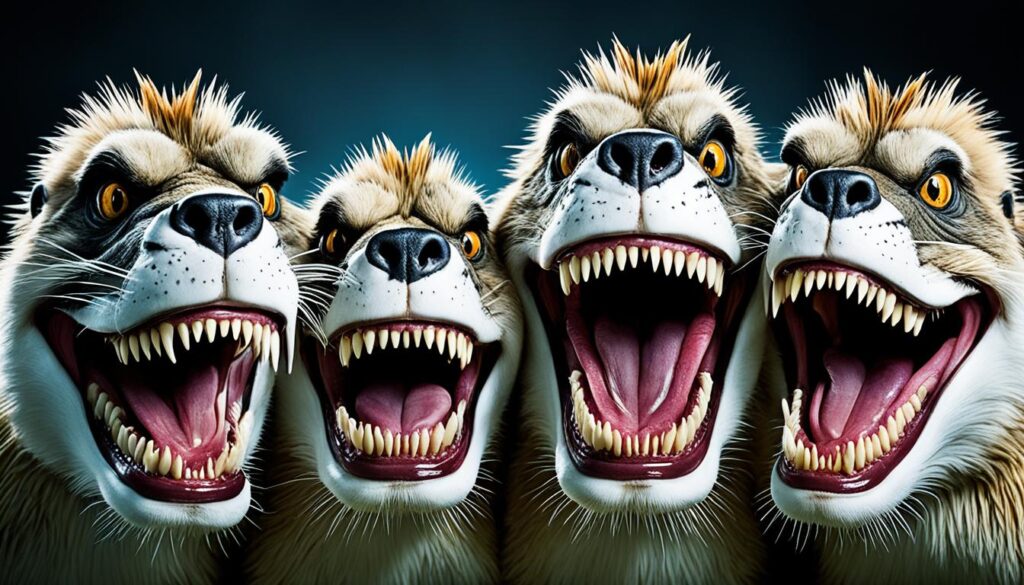

These exceptional examples highlight the diversity and ingenuity of nature’s design, showcasing how canine teeth can evolve to fulfill various functions in different species.
Humans’ Fear of Animal Mouths
Animal mouths have an innate ability to evoke fear in humans. The mere sight of a mountain lion’s teeth can send shivers down one’s spine. There is something primal and intimidating about the sharp, menacing dental structure of wild creatures.
Recently, a peculiar and perplexing occurrence added to the biological mystery surrounding animal mouths. In Idaho, a mountain lion was discovered with a full set of teeth and whiskers growing out of its forehead. This abnormality has left scientists baffled, seeking answers to unravel this enigmatic phenomenon.
One possible explanation for this extraordinary occurrence is the presence of a remnant of a twin lion absorbed in the womb. It is not uncommon for absorbed twins to leave traces or remnants within an individual’s body, resulting in unusual characteristics. Another hypothesis put forth by scientists is the presence of a teratoma tumor, a type of tumor that can develop teeth and hair. The growth of teeth and whiskers on the forehead of the mountain lion could be an aberration caused by such a tumor.
While scientists continue to investigate and study this biological anomaly, it serves as a testament to the complexities and mysteries that exist within the natural world. Animal mouths, with all their power and mystery, continue to captivate our imaginations and instill a sense of primal fear within us.

Other Terrifying Animal Mouths
Apart from animals with human-like teeth, there are other creatures with terrifying mouths. From lampreys to leatherback sea turtles, tigers to pacu fish, these animals possess unique dental structures that are both fascinating and frightening.
Lampreys
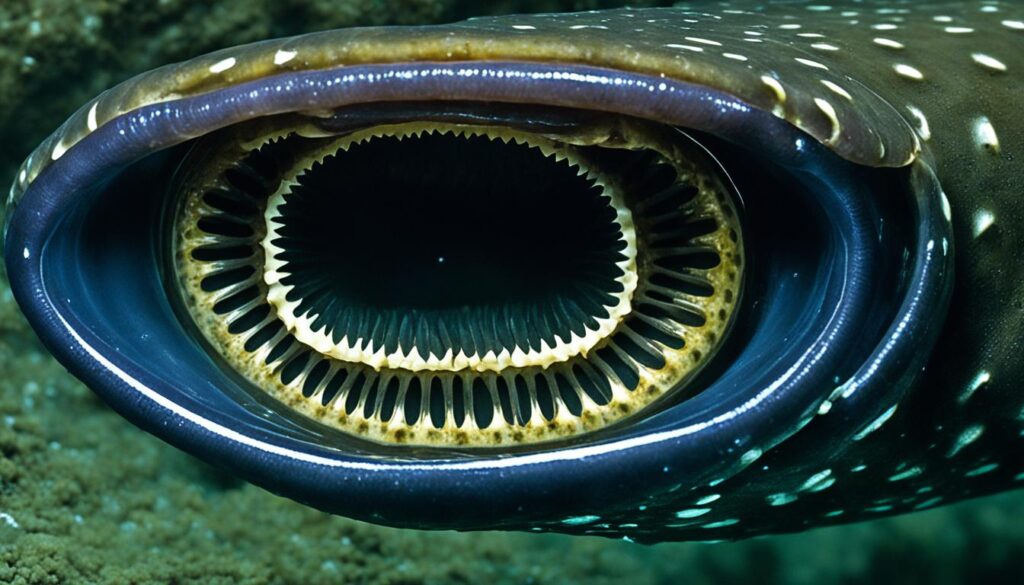

Lampreys, known as jawless parasitic fish, have thorny, suction cup-like mouths that they use to latch onto their prey. They feed by consuming the blood and body fluids of other fish, making their mouths a menacing sight.
Leatherback Sea Turtles
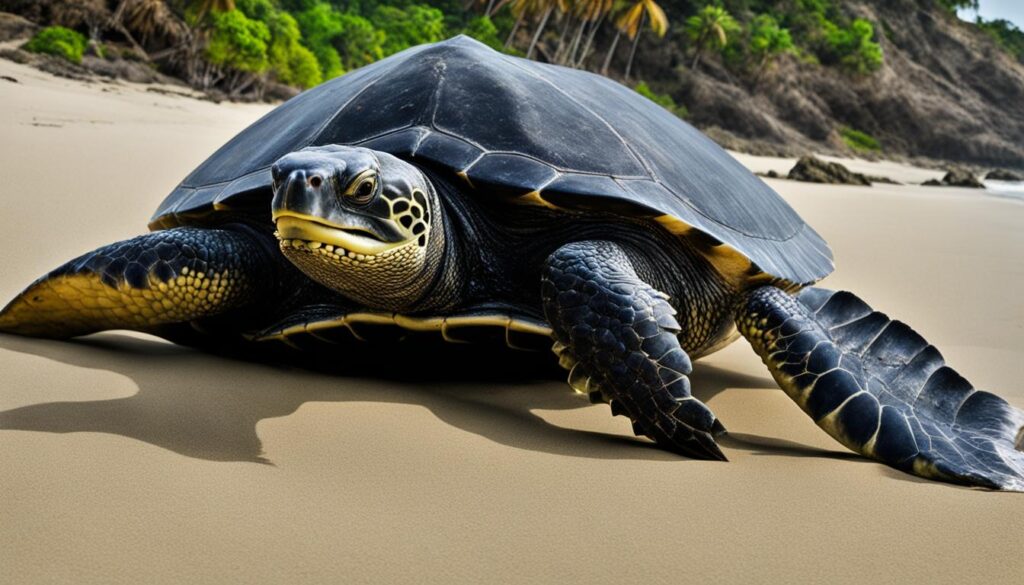

Leatherback sea turtles have backward-facing cartilage spikes called papillae in their throats. These unique structures help them trap and consume jellyfish, showcasing their incredible adaptation for their diet.
Tigers
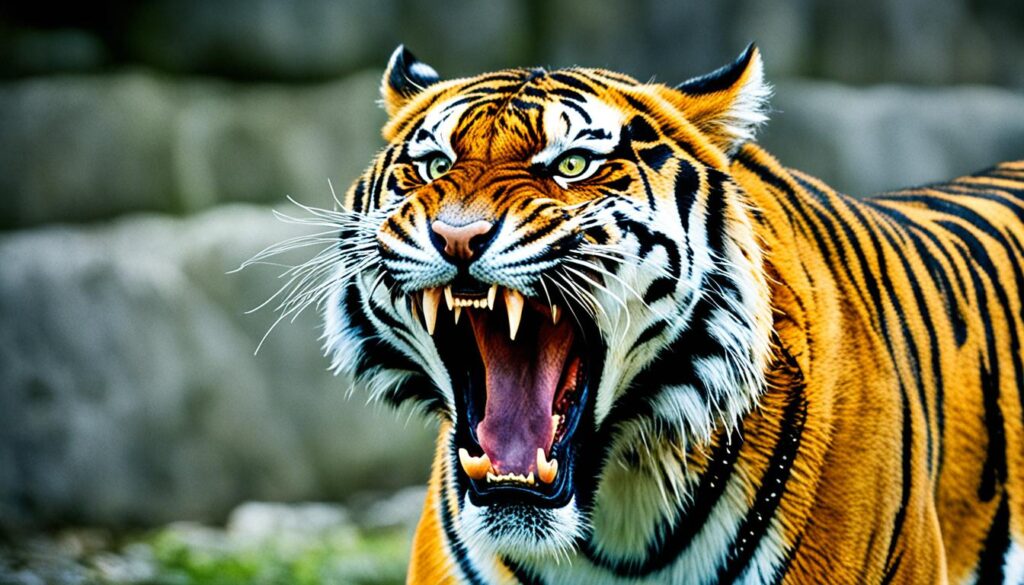

Tigers have needle-like backward-facing papillae on their tongues that serve a specific purpose. These papillae assist tigers in stripping flesh from their prey, highlighting their incredible hunting abilities.
Pacu Fish
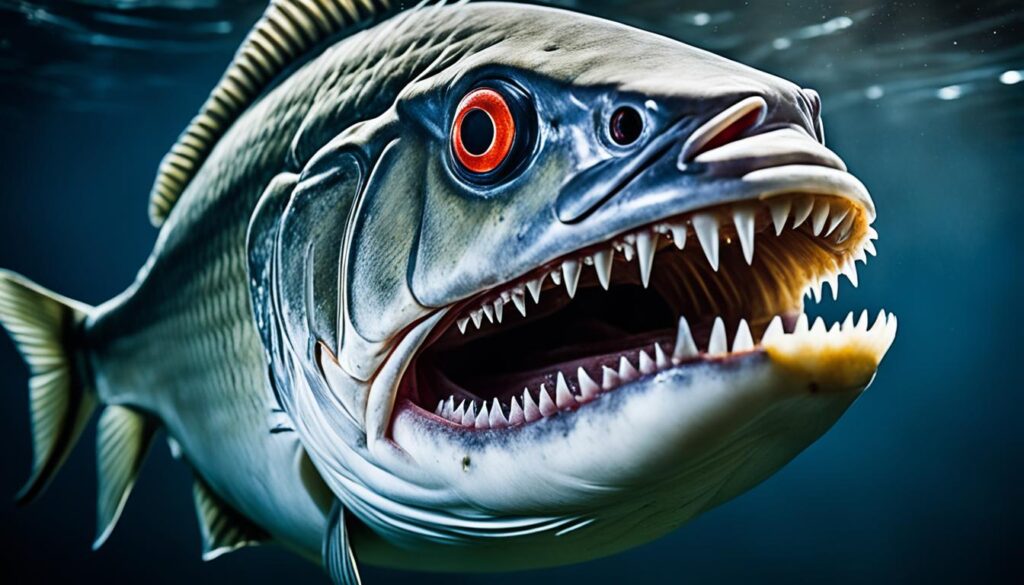

Despite being related to the notorious piranhas, pacu fish have squarer and straighter teeth that resemble human teeth. These teeth are designed for crushing hard fruits and nuts, but they can still be unsettling to behold.
These animals with terrifying mouths showcase the diverse adaptations found in nature. From their specialized structures for feeding to their formidable hunting capabilities, they remind us of the incredible diversity and intricacies of the animal kingdom.
More Frightening Animal Mouths
When it comes to terrifying animal mouths, the hippopotamus takes the crown. Although its mouth may not look particularly menacing, its power is not to be underestimated. Hippos have the ability to open their jaws nearly 180 degrees, showcasing a set of massive incisors and canines. With a bite force of approximately 1,800 pounds per square inch, these formidable creatures mean business.
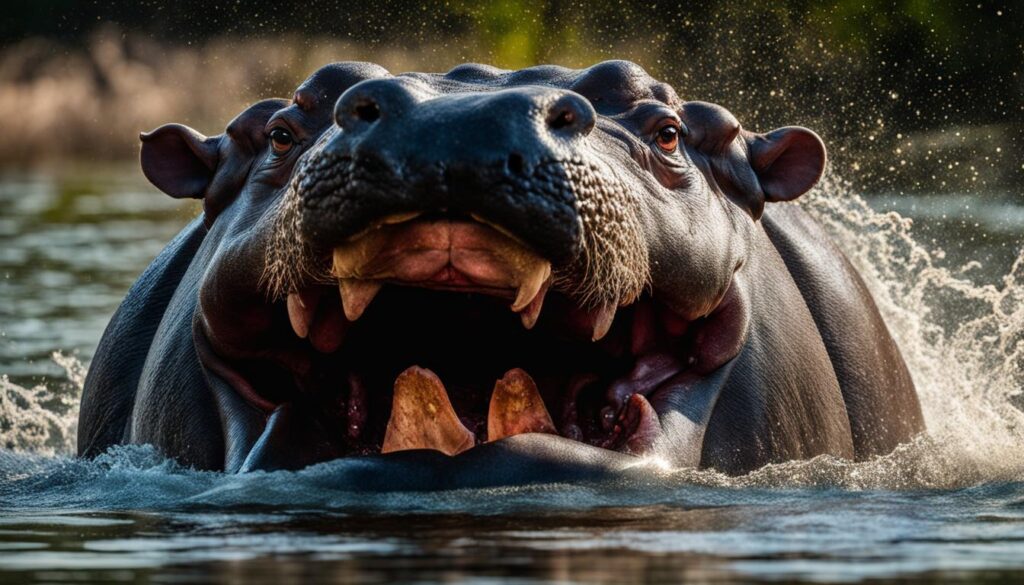

The goblin shark is another creature with a jaw that will give you shivers. This deep-sea dweller possesses highly protrusible jaws that extend from its head to snatch prey. This unique adaptation allows the goblin shark to surprise its unsuspecting victims in the dark depths of the ocean.
Mandrills: A Friendly Greeting with Fierce Canines
While the mandrill may seem like a friendly and colorful primate, don’t be fooled by its appearance. Male mandrills sport impressive canine teeth that they use not only for self-defense but also as a form of social communication. During friendly encounters, mandrills may display their impressive canines as a non-threatening greeting among themselves.
“The mandrill’s canine teeth not only serve as formidable weapons but also play a vital role in social interactions.”
On the theme of fearsome teeth, the hagfish is a master of survival. These primitive marine creatures have comb-shaped teeth that may not look impressive individually but are collectively powerful. Aggregating in large numbers, hagfish sink their teeth into carcasses, tearing through flesh and consuming their meals with efficiency.
The payara fish, also known as the vampire fish, possesses long fangs that make it a true predator. With its saber-like teeth, the payara skewers its prey, ensuring a secure catch. These formidable fangs allow the payara fish to thrive in its natural habitat, the rivers of South America.
Conclusion
Animals with human teeth are an intriguing phenomenon that captivate our curiosity. Whether it’s the canines of a carnivorous predator or the dental peculiarities of a mountain lion, these unique dental characteristics serve various purposes in the animal kingdom.
From the efficient bite of canine teeth to their role in hunting and tearing food, animals with human-like teeth showcase the remarkable diversity of nature. Observing the intriguing world of animal mouths not only provides us with a deeper understanding of these creatures but also highlights the wonders of our natural world.
As we explore and discover more about animals with human teeth, we come to appreciate the amazing adaptations that have evolved over time. The presence of these unique dental features is a testament to the complexity and diversity of life on Earth. It reminds us that even in the realm of teeth, there is still much to explore and marvel at.









