Animals build their homes by creatively using available resources, tailoring structures to their environments. Birds weave nests from twigs and leaves, while beavers construct dams for safety. Social insects like ants and termites showcase complex teamwork, and foxes dig burrows for protection. Young animals learn these essential skills from their parents or through play, adapting quickly to thrive. Discovering the variety of techniques and communal strategies employed by different species can offer even more fascinating insights.
Key Takeaways
- Animals utilize various materials like twigs, leaves, and mud to construct their homes, tailored to their environmental needs.
- Birds build nests for their eggs using natural resources, while beavers create dams for underwater access and protection.
- Social insects, such as ants and termites, develop complex nests through cooperation, showcasing specific roles within their communities.
- Burrowing animals, like foxes and hamsters, dig extensive tunnels and chambers for safety and food storage, protecting against predators.
- Young animals learn essential home-building skills through observation, play, and instinct, adapting to their environments for survival.
Importance of Animal Homes

Animal homes play a crucial role in survival, as they provide essential resources like water, food, and shelter. These homes protect animals from predators and harsh weather, allowing them to thrive in their environments.
When animals build nests, they guarantee safety for their young and create spaces that trap heat, essential for nurturing offspring. Additionally, many species live together in complex structures, which enhances their chances of survival.
Social creatures like bees and ants exemplify this communal living, as they create intricate nests that house thousands, working together for the colony's success.
Types of Animal Homes

Across the animal kingdom, diverse types of homes are crafted to meet the unique needs of different species.
Birds build nests using twigs and leaves, providing warmth and safety for their eggs and chicks.
Birds skillfully weave twigs and leaves into nests, ensuring warmth and safety for their vulnerable eggs and chicks.
Beavers, on the other hand, create impressive dams from mud, stones, and sticks, forming ponds that protect their lodges with underwater entrances from predators.
Social insects like ants and termites construct complex nests and colonies from soil and wood pulp, featuring multiple chambers and tunnels for various purposes.
Some animals, including foxes and rabbits, dig burrows underground, offering shelter for families and protection from threats.
Each home type showcases the incredible adaptability of animals to their environments, ensuring their survival and success.
Unique Construction Techniques

When you explore the unique construction techniques of animals, you'll find some truly remarkable strategies.
From leafcutter bees crafting nests with leaves and saliva to ants coordinating their efforts in underground colonies, these methods showcase incredible ingenuity.
You'll also discover how material selection plays an essential role in creating safe and effective homes for various species.
Ingenious Nesting Strategies
While many creatures seem to rely on instinct alone, a closer look reveals that some have developed astonishingly intricate nesting strategies.
Take the Tailorbird, for instance; it uses its beak to stitch leaves together with spider silk, crafting camouflaged nests that blend seamlessly into their surroundings.
Leafcutter Bees demonstrate resourcefulness by cutting and gluing leaves with saliva to make nests that are small but secure.
Potter Wasps skillfully mold mud into pots, providing safe environments for their eggs.
Bumblebees dig tunnels to build homes underground, using wax to store food and protect their young.
Finally, Sociable Weavers showcase their ability to collaborate, constructing vast communal nests that accommodate multiple families, highlighting the diverse art of nest building across species.
Cooperative Building Efforts
Cooperative building efforts showcase the remarkable teamwork found in nature, where social insects and mammals come together to create intricate homes.
These animals demonstrate impressive building skills, forming structures that serve their communities.
- Ants construct complex underground tunnels and chambers, working tirelessly as a unit.
- Meerkats dig and maintain burrows, assigning roles to guarantee safety while others focus on construction.
- Termites create towering mounds, relying on the collective effort of their colony to regulate conditions inside.
Material Selection Techniques
Animals employ a variety of unique material selection techniques to construct their homes, showcasing their adaptability and ingenuity.
For instance, many birds, like hummingbirds and tailorbirds, intricately weave nests using leaves, grass, and spider silk, enhancing strength and camouflage.
Leafcutter bees cut specific shapes from leaves and glue them with saliva to create protective nests for their larvae.
Carpenter bees choose decayed wood for easy drilling, while hornets transform wood fibers into paper pulp for durable nests.
Ants gather soil and plant debris, even using their own secretions, to build complex underground nests with chambers and tunnels.
These clever strategies highlight how animals carefully select materials to build effective and resilient homes.
Social Structures in Animal Communities

In animal communities, social structures play an essential role in home-building efforts.
You'll see how cooperation among members leads to efficient nest construction, with specific roles assigned to each individual.
From family units working together to raise young to colonies communicating through chemical signals, these dynamics shape their living environments.
Cooperative Nest Building
While many creatures instinctively build their homes alone, some form intricate social structures that enhance survival through cooperative nest building.
You'll find that these animals work together to create nests that provide safety and efficiency.
Consider the benefits of cooperative nest building:
- Communication: Ants use chemical signals to coordinate their efforts, ensuring a well-structured colony.
- Shared Responsibilities: Meerkats take turns watching for predators, allowing others to dig and maintain their underground homes.
- Collaborative Structures: Termites build massive mounds, managing airflow and creating breeding grounds for the colony.
These social behaviors not only strengthen their communities but also increase their chances of survival.
Roles Within Colonies
Understanding the roles within animal colonies reveals fascinating social structures that promote survival and efficiency. In these communities, individuals work together, each with specific tasks. For instance, in ant colonies, workers build nests and forage, while the queen focuses on reproduction. Meerkats take turns as sentinels, guaranteeing safety as others dig their underground homes. Badgers create shared burrows, showcasing communal living.
Here's a quick overview of roles within different animal colonies:
| Animal | Roles | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Ants | Workers, queen | Build nests, reproduce |
| Meerkats | Sentinels, diggers | Watch for predators, maintain homes |
| Hornets | Workers, nurses, foragers | Guarantee survival of the colony |
These roles highlight the importance of teamwork in their habitats.
Family Structures and Care
Animal communities often showcase complex family structures that play an essential role in nurturing and teaching the young. These structures help animals make their homes together, ensuring safety and cooperation.
Here are some key features of these social dynamics:
- Cooperative Care: In species like foxes, vixens often receive help from other females in raising their pups.
- Division of Labor: Ant colonies highlight this with worker ants focusing on nest maintenance while the queen reproduces.
- Shared Responsibilities: Meerkats take turns as lookouts while constructing burrows, ensuring everyone's safety.
These family structures not only provide care but also enhance survival, showcasing the importance of cooperation in animal communities.
Survival Strategies Through Burrowing
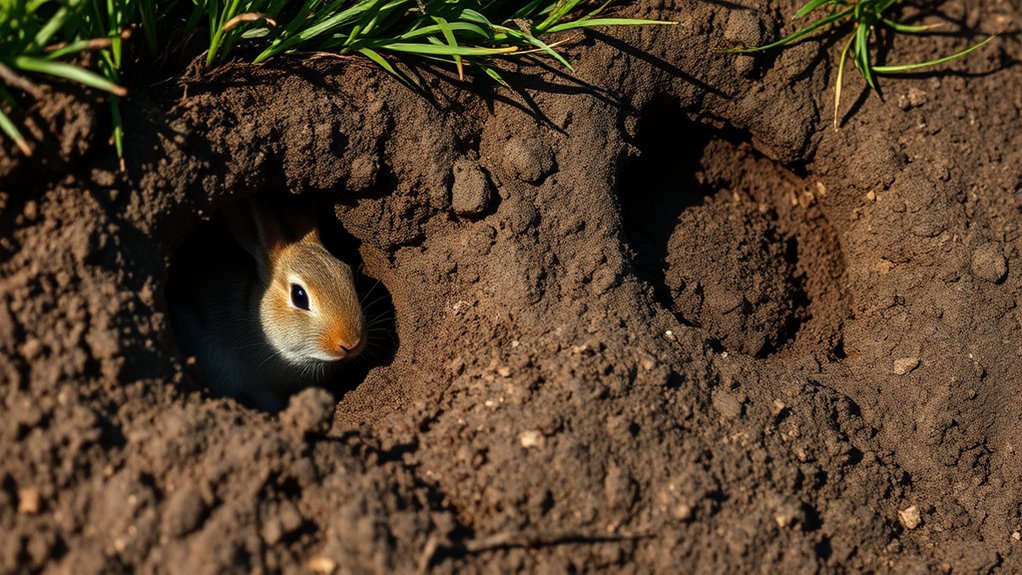

Burrowing serves as an essential survival strategy for many creatures, allowing them to create safe havens in their environments.
Animals like European hamsters and foxes dig extensive burrows with multiple chambers, providing a secure place to live, store food, and protect themselves from predators.
Ants construct underground tunnels that double as escape routes during emergencies, such as forest fires, showcasing their collective survival tactics.
Meanwhile, beavers build lodges and dams to form ponds, ensuring safety and access to food sources.
Social insects like meerkats and badgers collaborate to maintain their burrows, enhancing communal survival through shared resources.
These burrowing habits enable animals to thrive, avoiding harsh weather and predator threats while ensuring their young remain safe.
Learning and Adaptation in Young Animals

As young animals grow, they quickly learn essential skills for survival in their environments. This learning process is important for building homes and adapting to their surroundings.
Here are a few ways they achieve this:
- Young hamsters adapt rapidly, reaching sexual maturity in just 43 days, which helps them thrive in burrowing habitats.
- Beavers teach their young significant skills through play, with older siblings actively participating in maintaining their lodges.
- Coati youngsters venture out of their nests after six weeks, learning to forage and navigate their world.
Through observation and instinct, young animals master home-building techniques and survival strategies, ensuring their safety and success in the wild.
This adaptability is key to their long-term survival.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Animals Make Homes?
You might be surprised at how creatively animals make homes. They gather materials from their surroundings, like twigs, mud, and leaves, to create shelters that provide safety and comfort.
Social insects build elaborate nests, while birds use unique techniques to weave their homes. From beavers constructing dams to solitary insects crafting small nests, each creature adapts its building methods to suit its environment and needs, showcasing incredible ingenuity in their home-making skills.
Which Animal Builds the Best Home?
When you think about which animal builds the best home, consider the complexity and functionality of their creations.
For instance, termites construct towering mounds with intricate tunnels, while beavers create robust dams that provide safety and habitat.
Sociable Weavers build massive communal nests that offer insulation and protection.
Each animal showcases unique skills, but ultimately, the best home depends on what features you value most—safety, complexity, or communal living.
What Animals Can Make Their Own Home?
You'll find many animals that can make their own homes, showcasing impressive building skills.
Birds gather twigs and leaves to create nests, while beavers construct dams and lodges from mud and sticks.
Ants and bees collaborate to build intricate hives and nests, each serving thousands.
Even solitary insects like leafcutter bees create small nests from leaves and mud.
Don't forget mammals like foxes and rabbits, who dig burrows for safety and shelter.
How Do Animals Get Their Shelter?
Did you know that over 90% of bird species build nests for shelter?
Animals get their shelter by using materials found in their environment. You'll see birds gathering twigs, leaves, and mud to create cozy nests.
Beavers use tree trunks to construct lodges, while ants collaborate to form intricate colonies.
Each species adapts its building techniques based on available resources, ensuring their homes provide safety and comfort for themselves and their young.
Conclusion
So, next time you marvel at a bird's nest or a beaver's dam, remember that these homes are more than just cozy spots. They're masterpieces of engineering built by critters with some serious skills. Ironically, while we humans often complicate our living spaces, animals keep it simple, proving that sometimes the best homes are the ones that blend seamlessly into nature. Who knew that in the quest for comfort, it's the animals who've got it all figured out?