The Eastern Spotted Skunk is part of the Mephitidae family because it's classified under Spilogale genus, shares traits with other spotted skunks, and reveals insights into behavior, biology, and conservation status. Understanding its role in the skunk family's intricate evolution is valuable.
Key Takeaways
- Taxonomic classification under the genus Spilogale.
- Shares common characteristics with other spotted skunk species.
- Provides insights into behavior, biology, and conservation status.
- Helps in understanding evolutionary history and ecological role.
- Valuable for studying diversity and relationships among skunk species.
Physical Characteristics
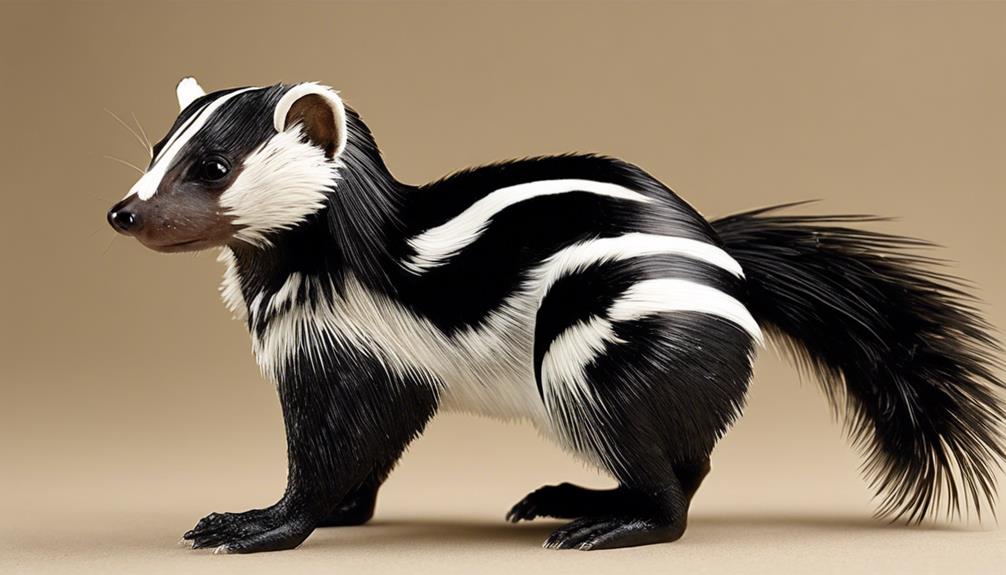
The Eastern spotted skunk's physical appearance sets it apart from other skunk species with its small weasel-like body covered in fine, dense black fur. What truly distinguishes this skunk is the 4 to 6 broken, white stripes running along its body, giving it a unique and striking look. These stripes are a signature feature of the Eastern Spotted Skunk, making it easily identifiable compared to its skunk relatives. The intricate pattern of these stripes adds a touch of elegance to its overall appearance, showcasing nature's creativity at its best.
Not only does the Eastern Spotted Skunk boast a sleek and weasel-like body, but its white stripes provide a touch of sophistication to its aesthetic. These distinctive markings are like nature's way of painting a masterpiece on this elusive creature, setting it apart in the skunk world. The combination of the small, sleek body and the striking white stripes truly makes the Eastern Spotted Skunk a marvel to behold.
Behavioral Traits
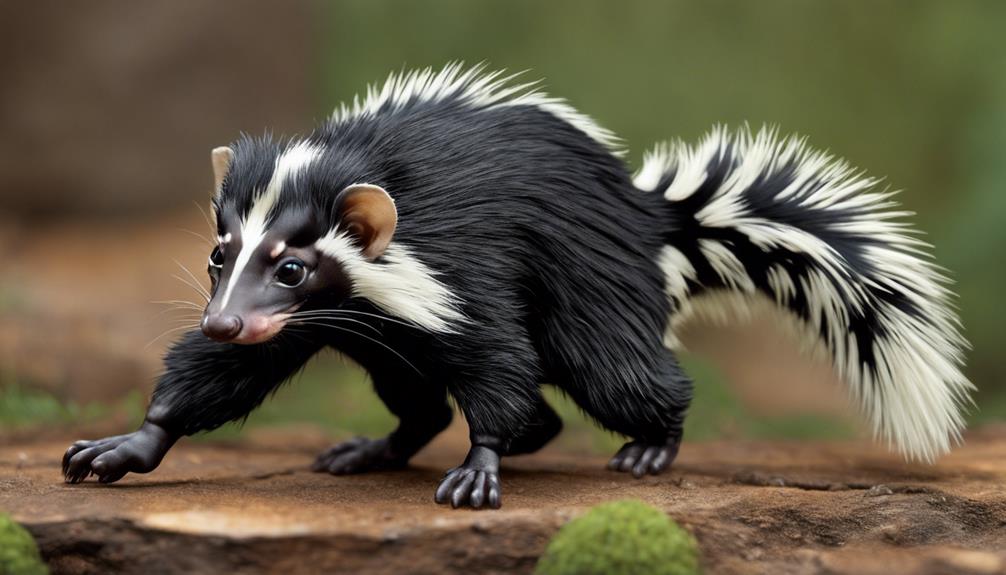

Exploring the Eastern Spotted Skunk's Behavioral Traits reveals intriguing insights into its nocturnal activities and unique survival strategies. Eastern spotted skunks, like many species in the Mephitidae family, exhibit fascinating behaviors that contribute to their classification within this distinct group. Here are three key behavioral traits that characterize the Eastern spotted skunk:
- Nocturnal Lifestyle: These skunks are primarily active during the night, using their keen senses and agility to navigate the darkness. This behavior aligns with the nocturnal tendencies commonly observed in Mephitidae species.
- Essential Mating Behaviors: Eastern spotted skunks display unique mating rituals and reproductive strategies that set them apart within the Mephitidae family. These behaviors play a vital role in their survival and the continuation of their species.
- Social Interactions: The Eastern spotted skunk's social interactions and denning habits offer valuable insights into their communication methods and group dynamics, shedding light on their evolutionary adaptations as Mephitidae members.
Nocturnal Habits
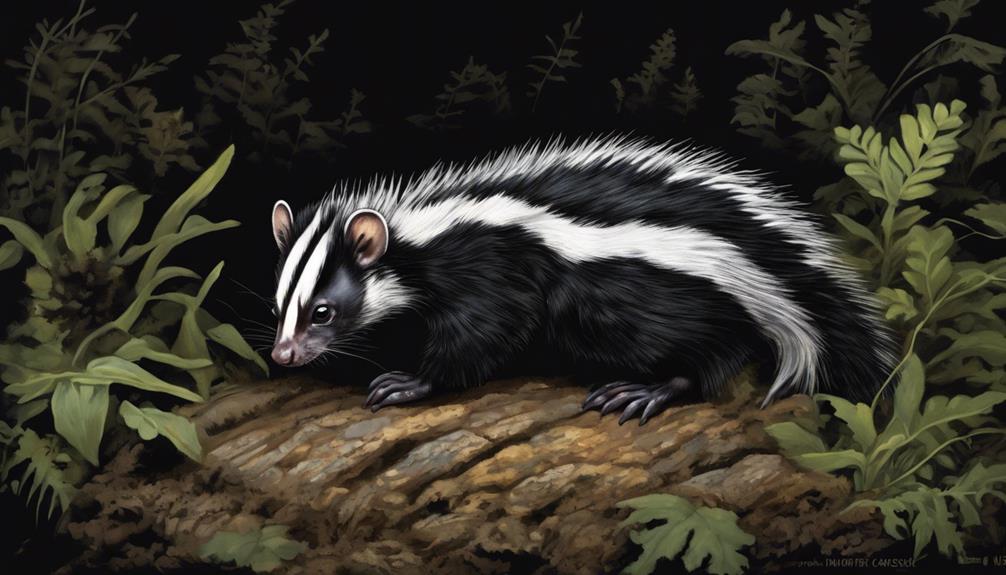

Moving through the darkness with agility, the Eastern Spotted Skunk displays its nocturnal habits to evade predators and effectively hunt for food. Being most active during the night, this skunk species has adapted to utilize the cover of darkness for protection and to minimize interactions with diurnal animals.
Vital is a crucial adaptation that allows the Eastern Spotted Skunk to navigate its environment successfully. By hunting at night, these skunks can take advantage of their keen senses to locate prey while avoiding potential predators. Their nocturnal behavior showcases their ability to thrive in low-light conditions, giving them a competitive edge in the wild.
Understanding the Eastern Spotted Skunk's nocturnal lifestyle sheds light on the fascinating ways in which animals have evolved to survive and thrive in their habitats. This adaptation not only helps them secure food sources but also enables them to stay one step ahead of potential threats lurking in the darkness.
Reproductive Patterns

Eastern spotted skunks have fascinating mating behavior where they engage in multiple breeding seasons throughout their lives.
Following mating, these skunks experience a gestation period lasting around 60-75 days before giving birth to a litter of 4-6 kits on average.
Understanding these reproductive patterns sheds light on the unique life cycle of the Eastern spotted skunk within the Mephitidae family.
Mating Behavior
Understanding the mating behavior of the eastern spotted skunk involves observing their polygynous tendencies and iteroparous nature during the breeding season. These unique behaviors contribute to the reproductive success of this fascinating species.
- Polygynous Behavior: Males engage in mating with multiple females, increasing genetic diversity within the population.
- Iteroparity: The ability to breed multiple times in a season allows eastern spotted skunks to maximize their reproductive output.
- Delayed Implantation: This reproductive strategy guarantees that the fertilized egg implants in the uterus at the best time for the development of healthy offspring.
These mating behaviors showcase the complex and innovative ways in which eastern spotted skunks navigate their reproductive processes.
Gestation Period
Observing the gestation period of the Eastern spotted skunk reveals key insights into their reproductive patterns and breeding strategies.
The Eastern spotted skunk typically carries its young for 60 to 75 days before giving birth to 4 to 6 kits. This critical gestation period is vital for the survival of the species.
Female Eastern spotted skunks exhibit seasonal breeding behavior, ensuring that their offspring are born during ideal times for survival.
Within the Mephitidae family, these skunks display iteroparous reproduction, meaning they can have multiple litters in a single breeding season.
Understanding the gestation period of the Eastern spotted skunk is crucial for comprehending their unique reproductive biology and the challenges they face in sustaining their population.
Conservation Challenges
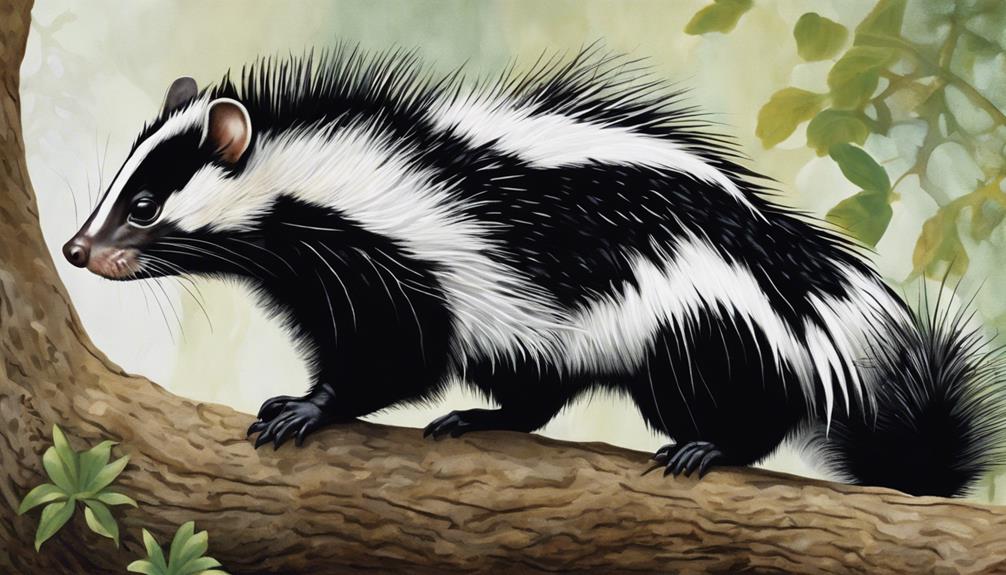

Facing significant threats from factors like pesticide use, farming practices, and over-trapping, the conservation of eastern spotted skunks presents a critical challenge. These challenges include:
- Population Declines: Eastern spotted skunks are experiencing declines in their numbers due to various human activities like pesticide use and over-trapping, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts.
- Conservation Efforts: With Appalachian spotted skunks facing a 3% decline per year and a high 50% mortality rate, targeted conservation strategies are essential to reverse these trends and guarantee the survival of the species.
- Monitoring Difficulties: The secretive nature of eastern spotted skunks makes it challenging to monitor and protect their populations effectively. Developing innovative monitoring techniques is vital to understanding their populations and implementing conservation measures promptly.
Addressing these conservation challenges requires a holistic approach that combines scientific research, community involvement, and policy changes to safeguard the eastern spotted skunk population and ensure its long-term survival.
Genetic Similarities

Analyzing the genetic makeup of the Eastern spotted skunk reveals significant similarities with other members of the Mephitidae family. Through DNA analysis, scientists have uncovered shared genetic markers and sequences that align the Eastern spotted skunk with its skunk relatives. This genetic similarity provides concrete evidence of the evolutionary relationship between the Eastern spotted skunk and other species within the Mephitidae family.
To illustrate the genetic similarities further, consider the table below:
| Genetic Marker | Shared by Eastern Spotted Skunk and Other Mephitidae Members |
|---|---|
| DNA Sequence X | Present in Eastern spotted skunk, Striped skunk, Hog-nosed skunk |
| Gene Y | Found in Eastern spotted skunk, Hooded skunk, Western spotted skunk |
| Chromosome Z | Shared by Eastern spotted skunk, American hog-nosed skunk, Sunda stink badger |
The analysis of these genetic markers through DNA studies solidifies the Eastern spotted skunk's placement within the Mephitidae family, showcasing its close genetic ties to other skunk species.
Taxonomic Classification

Let's talk about the taxonomic classification of the Eastern spotted skunk within the Mephitidae family.
This classification places the Eastern spotted skunk under the genus Spilogale, distinguishing it from other skunk species.
Understanding where the Eastern spotted skunk fits within this family helps us appreciate its unique characteristics and evolutionary relationships.
Family Mephitidae Overview
Belonging to the family Mephitidae are skunks and stink badgers, known for their potent anal scent glands used for defense. The Mephitidae family is a diverse group with unique characteristics that set them apart from other mammals:
- Mephitidae consists of 12 extant species in four genera, showcasing the family's biodiversity.
- Skunks exhibit warning coloration with black and white patterns, a visual alert to predators of their toxicity.
- These mammals primarily feed on invertebrates but also consume other animal material, demonstrating their adaptable diet within the family Mephitidae.
The family Mephitidae encompasses fascinating species with specialized adaptations, making them intriguing subjects for further exploration.
Eastern Spotted Skunks Classification
The Eastern spotted skunk's taxonomic classification under the genus Spilogale distinguishes it within the family Mephitidae. This specific placement highlights its genetic relationship with other skunk species.
As Spilogale putorius, the Eastern spotted skunk shares common characteristics with other spotted skunk species, such as its small weasel-like body, fine black fur, and broken white stripes.
Understanding its taxonomic classification aids in unraveling its behavior, biology, and conservation status within the skunk family.
By studying the Eastern spotted skunk's unique classification under Mephitidae, scientists can uncover more about its evolutionary history and ecological role.
This classification system provides valuable insights into the diversity and relationships among different skunk species, contributing to the broader understanding of wildlife biology.
Evolutionary History

Considering the Eastern Spotted Skunk's evolutionary past within the Mephitidae family sheds light on its unique adaptations and lineage.
- The Eastern Spotted Skunk's evolution from a common ancestor with other skunk species is supported by genetic studies, which have provided insights into its genetic makeup and relationship within the Mephitidae family.
- Fossil evidence plays an essential role in tracing the evolutionary history of the Eastern Spotted Skunk, offering a glimpse into its past and the changes it has undergone over time.
- By examining molecular phylogeny, scientists have confirmed the placement of the Eastern Spotted Skunk in the Mephitidae family, highlighting the connections it shares with other skunk species and its position in the evolutionary tree of life.
Understanding these evolutionary aspects not only enriches our knowledge of the Eastern Spotted Skunk's origins but also underscores the intricate relationships that exist within the Mephitidae family.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Family Does the Eastern Spotted Skunk Belong To?
The Eastern Spotted Skunk belongs to the Mephitidae family, recognized for its distinctive traits. Skunks in this family possess potent anal scent glands, warning coloration, and feed on invertebrates. These features contribute to their classification within the Mephitidae group.
What Are the Characteristics of the Mephitidae Family?
Exploring the Mephitidae family reveals fascinating adaptations like well-developed anal scent glands used for defense. Skunks and stink badgers stand out in this family, showcasing unique evolutionary traits that make them distinct.
Is a Skunk a Mephitidae?
Yes, a skunk is a mephitidae. Skunks' distinct anal scent glands for defense and their black and white warning coloration are key traits. Their diet and ecological niche align with the Mephitidae family characteristics.
What Family Does the Skunk Belong To?
Skunks, with their distinct black and white patterns, belong to the family Mephitidae. They're known for their potent scent glands. These features, along with their diet and habitat, tie them to this unique family of mustelids.
Conclusion
To sum up, the eastern spotted skunk's inclusion in the family Mephitidae is like a hidden key that reveals the secrets of its physical appearance, behavior, and genetic makeup. By grasping these distinctive characteristics, we can better understand the significance of conserving this captivating species.
So let's continue to learn about and protect these elusive creatures, ensuring they remain an essential part of our natural world for generations to come.