Wolf reintroduction plays a vital role in restoring ecological balance by regulating prey populations and enhancing biodiversity. While it helps reduce overpopulated herbivore numbers, it also raises concerns about livestock predation, leading to economic worries for farmers. Communities often fear increased human-wolf encounters, but education can alleviate these anxieties. With effective management strategies and community engagement, coexistence is possible, balancing ecological health with local concerns. There’s more to uncover about these dynamics and their implications.
Key Takeaways
- Wolf reintroduction restores ecosystem balance by regulating prey populations, enhancing biodiversity, and promoting vegetation recovery.
- The absence of wolves can lead to overpopulation of herbivores, negatively impacting plant species and overall habitat health.
- Controversies arise from livestock predation concerns, with farmers fearing economic losses due to wolf attacks on sheep and cattle.
- Public safety worries exist, but education about wolf behavior and proper food source management can reduce human-wolf encounters.
- Community involvement and non-lethal deterrents are essential for managing challenges and promoting coexistence between wolves and livestock owners.
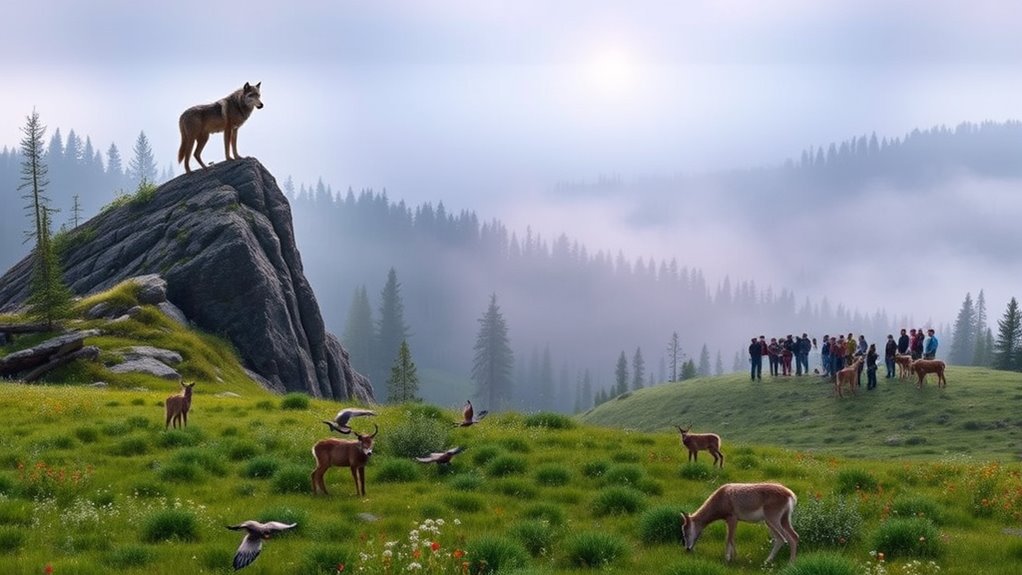

As you explore the concept of wolf reintroduction, you’ll discover that this ecological strategy aims to restore balance in ecosystems where these apex predators have been absent. Wolves play an essential role in maintaining the health of their habitats by regulating prey populations, which in turn can enhance biodiversity. When wolves are reintroduced, you might notice a notable decline in overpopulated herbivore species like deer. This helps vegetation recover, enabling various other species to thrive.
Wolf reintroduction is crucial for restoring ecological balance and enhancing biodiversity by regulating prey populations.
However, the conversation about wolf reintroduction doesn’t come without its controversies. One of the primary concerns people express is livestock predation. Farmers worry that wolves might attack their sheep and cattle, leading to economic losses. You can understand why livestock owners feel anxious about the presence of wolves near their farms. The fear is real, and in some cases, it’s justified. But it’s essential to contemplate how effective management strategies can mitigate these issues. Non-lethal deterrents, like fencing, guard animals, and better livestock management practices, can markedly reduce the risk of predation while allowing wolves to fulfill their ecological role.
Another concern that often arises is public safety. Many people worry that reintroducing wolves might lead to increased encounters between humans and these wild animals. While it’s true that wolves are powerful predators, they’re generally wary of humans and tend to avoid populated areas. Education plays a vital role here; understanding wolf behavior can alleviate fears. Most encounters can be avoided through proper measures, such as keeping food sources secured and educating the public on how to react if they encounter a wolf in the wild.
Ultimately, the challenges posed by livestock predation and public safety are real but manageable. Engaging communities in the wolf reintroduction process can foster understanding and collaboration. When people see the broader ecological benefits of wolves, like healthier ecosystems and increased biodiversity, they may become more amenable to coexistence. High refresh rates for monitoring wildlife populations can significantly enhance conservation efforts.
As you dive deeper into the topic, you’ll find that wolf reintroduction is not merely about bringing back a species; it’s about striking a balance between ecological health and the concerns of local communities. With thoughtful planning and community involvement, it’s possible to create a future where wolves and humans can coexist harmoniously.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Wolves Affect Local Livestock Populations?
Wolves can considerably impact local livestock populations through livestock predation. When wolves hunt livestock, it creates challenges for farmers and ranchers. However, many areas have implemented compensation programs to help offset these losses. These programs provide financial support to livestock owners who experience predation, aiming to balance conservation efforts with agricultural needs. By understanding these dynamics, you can better appreciate the complexities wolves bring to livestock management.
What Measures Are Taken to Prevent Wolf Attacks on Pets?
To prevent wolf attacks on pets, you can implement various pet safety strategies. Keep your pets indoors during dawn and dusk when wolves are most active. Use secure fencing to create a safe outdoor area and supervise pets during walks. Avoid leaving food outside, as it can attract wildlife. Educate yourself about local wolf populations and stay informed about any sightings in your area to take necessary precautions for your pets’ safety.
Are There Any Economic Benefits to Wolf Reintroduction?
Imagine standing on a misty mountain trail, the sound of a wolf’s howl echoing in the distance. Wolf reintroduction can bring significant economic benefits. You’ll see increased eco-tourism opportunities as nature enthusiasts flock to witness these majestic creatures in their habitat. Plus, hunting license revenue can rise as regulated wolf populations encourage sustainable hunting practices. These factors can boost local economies, creating jobs and fostering a deeper appreciation for wildlife conservation.
How Do Local Communities Feel About Wolf Reintroduction?
Local communities often have mixed feelings about wolf reintroduction. Some embrace it due to cultural perceptions that celebrate wolves as essential parts of the ecosystem, while others worry about livestock safety and potential economic impacts. Community engagement plays a critical role; when you involve locals in discussions and decision-making, it fosters understanding and support. By addressing concerns and highlighting benefits, communities can find common ground regarding wolf reintroduction and its implications.
What Is the History of Wolf Populations in the Area?
Like shadows fading at dusk, wolf populations once thrived in the area, only to face a historical decline due to habitat loss and hunting. As the years passed, their numbers dwindled, leaving a void in the ecosystem. However, conservation efforts emerged, aiming to restore balance. You’ll find that these initiatives have sparked renewed hope for wolf recovery, as communities and organizations unite to protect and reintegrate these majestic creatures into their rightful habitats.
Conclusion
In the grand game of nature, wolf reintroduction weaves a wondrous web of ecological balance. By embracing these majestic mammals, you’re not just witnessing wildlife return; you’re revitalizing the very heart of the ecosystem. Yet, it’s essential to confront the controversies and conflicts that accompany their comeback. Ultimately, you hold the power to protect and preserve this fascinating facet of flora and fauna, ensuring that harmony reigns in the wild, where wolves roam free.