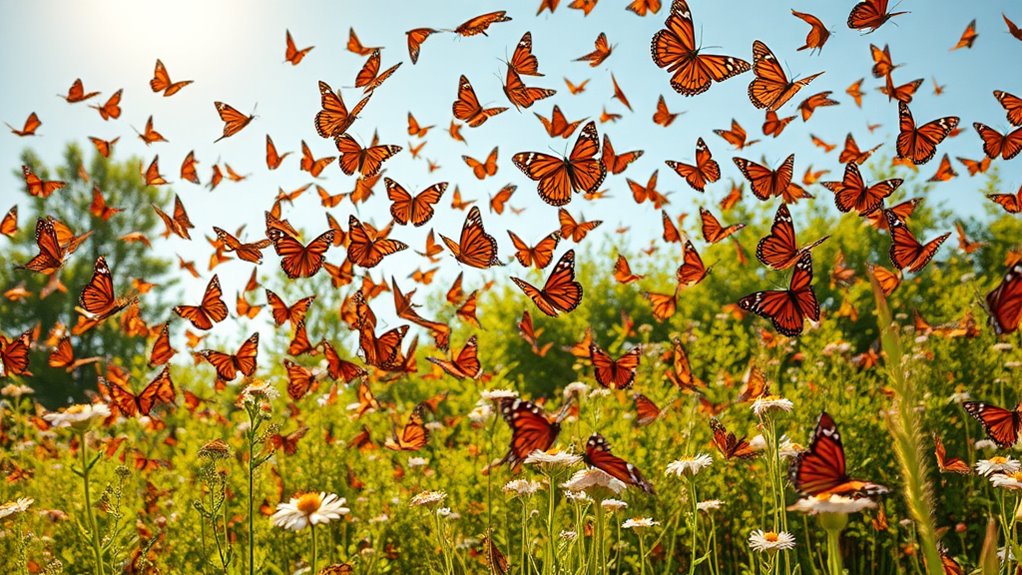
Monarch butterflies commence on an incredible migration each year, traveling thousands of miles from North America to their winter habitats in Mexico and California. They rely on community science for tracking, using celestial cues and internal clocks for navigation. Over the winter, they cluster in trees to survive harsh conditions. Conserving their population is essential, and genetic factors enhance their migratory capabilities. There's so much more to discover about their fascinating journey and the challenges they face ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Monarch butterflies migrate thousands of miles from North America to central Mexico and California for overwintering, utilizing specific roosting sites.
- Community science initiatives, like Monarch Watch, have tagged over one million butterflies, aiding in tracking migration patterns and recovery insights.
- Navigation relies on celestial cues, internal body clocks, and possibly the earth's magnetic field to guide their long-distance journey.
- Genetic adaptations, including 536 identified genes, enhance flight efficiency and endurance, crucial for the migratory process.
- Conservation efforts are vital to support monarch habitats and monitor population changes for the sustainability of their migration routes.
Tracking Monarch Migration Through Community Science
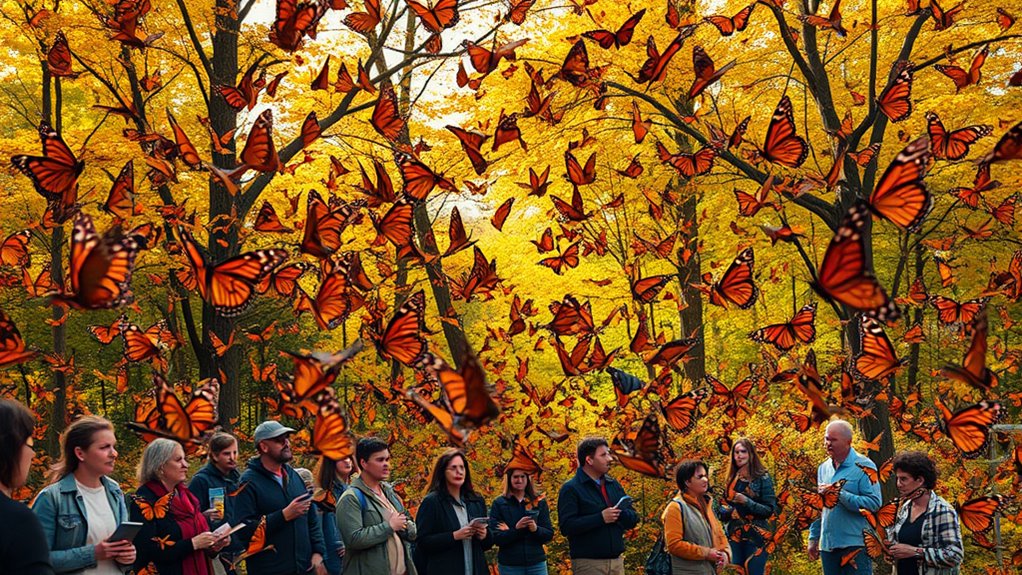

As you explore the fascinating world of monarch butterflies, you'll find that community science plays an essential role in tracking their migration. Programs like Monarch Watch have tagged over one million butterflies, leading to more than 16,000 recoveries that help scientists understand migration patterns.
Initiatives such as Journey North invite you to participate as a citizen scientist, tracking seasonal changes through interactive maps. Correo Real focuses specifically on monarchs migrating through northern Mexico, gathering significant data on their journey.
Project Monarch enhances our understanding of their movements with small tracking devices. Meanwhile, the Monarch Monitoring Project documents fall migration along the Atlantic coast in Cape May, NJ, showcasing how community science is fundamental for conservation efforts.
Overwintering Sites and Survival Strategies
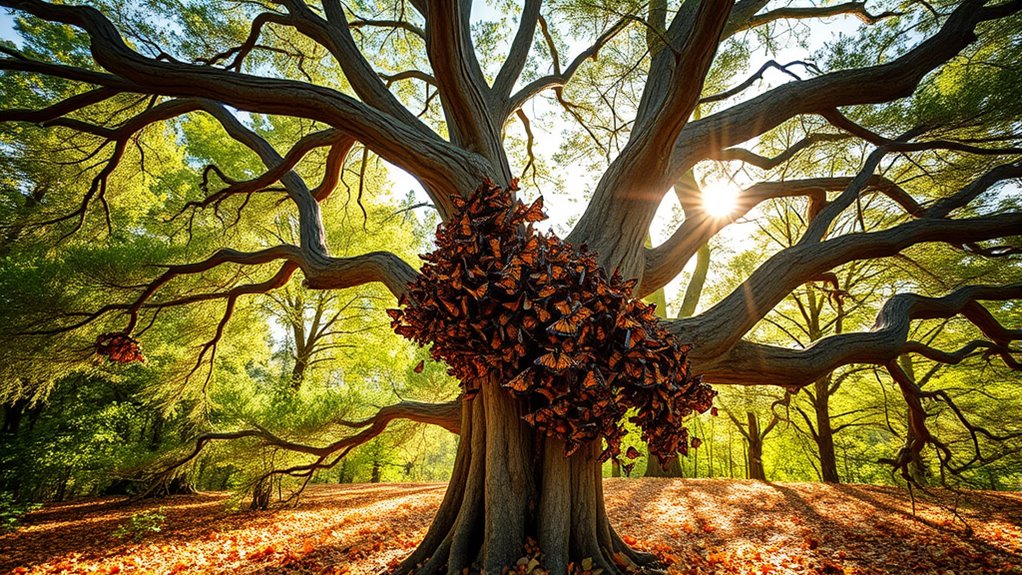

While many butterflies fade away in the winter, monarchs find refuge in specific overwintering sites that are vital for their survival.
Eastern monarchs roost in oyamel fir trees at high elevations in central Mexico, while western monarchs choose eucalyptus and other trees along the California coast.
These locations provide cool temperatures, water, and shelter from predators, important for their survival during the winter months.
These vital locations offer essential cool temperatures, water, and protection from predators, ensuring survival through the winter months.
By clustering in high-elevation oyamel fir forests, you help protect yourself from harsh weather, boosting your odds of survival.
During this time, you don't reproduce; instead, you focus on finding water and nectar sources in your habitat.
Key elements for your winter survival include roosting trees, protective vegetation, cool air, and moisture sources.
Navigation and Orientation Mechanisms
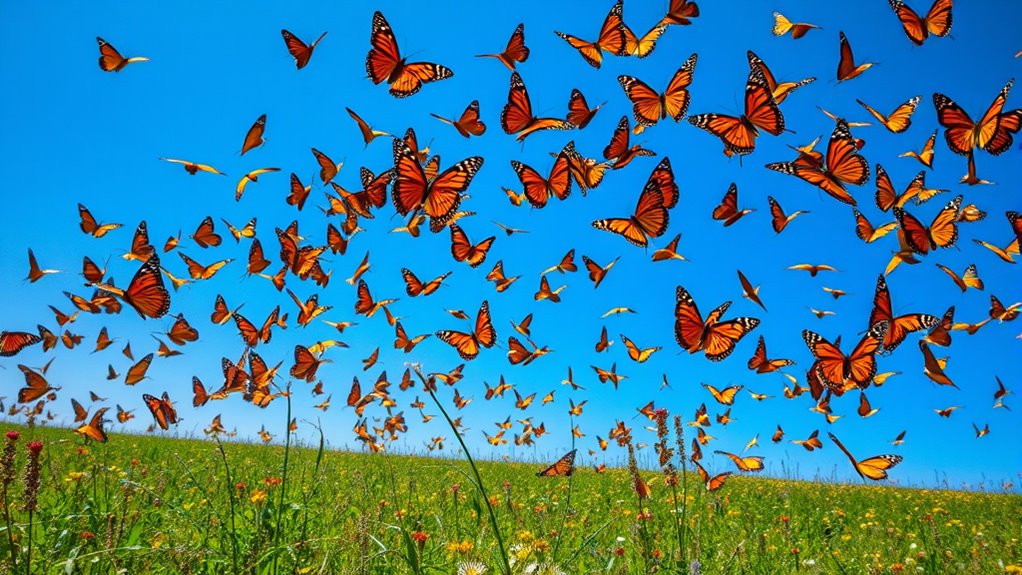

Monarch butterflies rely on a remarkable set of navigation and orientation mechanisms to guide them during their epic migrations. They utilize celestial cues like the sun and moon, adjusting their flight direction based on the sun's angle using an internal body clock. Additionally, monarchs may harness the earth's magnetic field and recognize geographical landmarks. A proposed sun compass mechanism helps them orient correctly towards specific overwintering sites. Genetic studies have revealed 536 genes linked to their migratory behavior, demonstrating a complex biological foundation. As they migrate, lower metabolic rates enhance flight efficiency, and adjustments in specific genes improve flight muscle performance.
| Mechanism | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Celestial Cues | Use sun and moon for navigation | Guides long-distance flight |
| Magnetic Field | Sense earth's magnetic field | Aids in directional orientation |
| Genetic Factors | 536 genes linked to migration | Underpins migratory behavior |
Population Statistics and Conservation Efforts
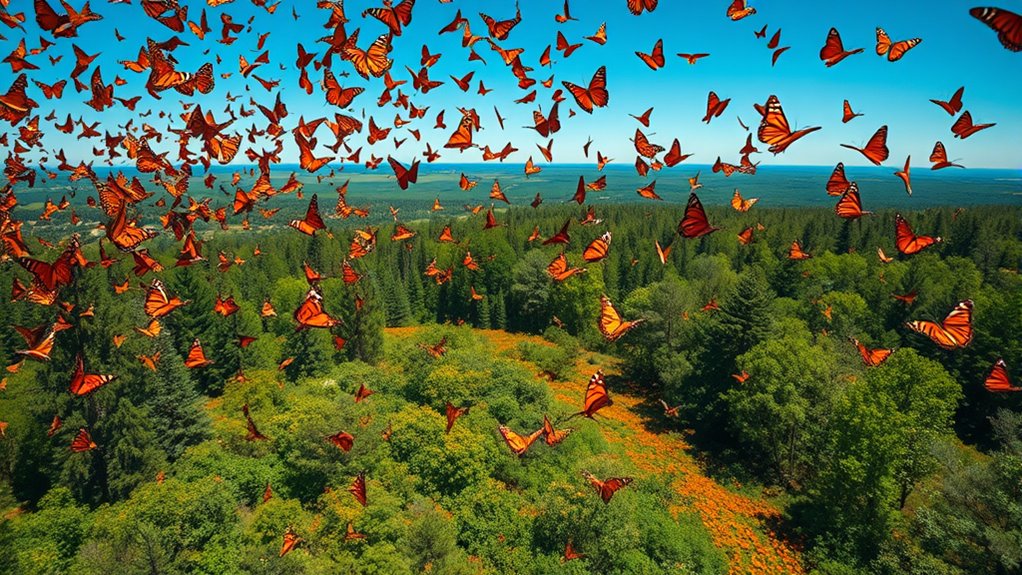

Approximately 5% of the global monarch population resides in California, underscoring the need for effective conservation efforts.
You can help maintain their numbers by supporting initiatives that focus on breeding and overwintering habitats. Monitoring efforts are essential for tracking population changes and health, allowing for targeted conservation strategies.
Organizations like the Xerces Society play a key role in mapping these habitats, providing valuable data for effective actions. Raising awareness through campaigns helps educate the public about monarch migration, fostering community support for conservation initiatives.
By collaborating with local communities, you can enhance habitat protection efforts, ensuring that these strategies are sustainable and effective for the future of monarch butterflies.
Together, we can make a difference!
The Role of Genetic Adaptations in Migration

Understanding the genetic adaptations that facilitate migration reveals fascinating insights into the monarch butterfly's remarkable journey. Research shows 536 genes linked to migration, highlighting a genetic foundation for this behavior. Remarkably, the Collagen IV alpha-1 gene diverges appreciably between migratory and non-migratory populations, suggesting it plays a role in flight efficiency. Migrating monarchs also display lower metabolic rates, an adaptation that conserves energy for long distances. This downregulation of the Collagen IV alpha-1 gene enhances the efficiency of their flight muscles, vital for survival amid environmental changes.
| Gene | Function | Importance in Migration |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen IV alpha-1 | Flight muscle efficiency | Enhances long-distance travel |
| 536 migration-associated genes | Overall migratory behavior | Genetic basis for migration |
| Metabolic rate regulation | Energy conservation | Supports endurance |
| Environmental navigation | Adaptability to surroundings | Guarantees successful journeys |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Month Is the Monarch Butterfly Migration?
The monarch butterfly migration typically starts in September for eastern populations, while western populations usually begin their journey in February or March.
You'll notice that their migration patterns are closely tied to seasonal changes, with millions of butterflies traveling south during autumn and returning in spring.
Each year, the timing can shift slightly due to environmental factors, but you can generally expect their migrations to follow these months consistently.
Where Can I See the Monarch Migration in the US?
Did you know that up to 15 million monarchs can gather in a single location during migration?
If you want to witness this spectacular event in the U.S., head to Cape May, New Jersey, in the fall. You'll find them actively migrating along the Atlantic coast.
California also offers great views as they leave their overwintering sites in early spring.
Keep an eye out for community science projects to track their journey!
How Does the Monarch Butterfly Migrate?
You'll find that monarch butterflies migrate using a combination of celestial cues and their internal body clocks. They rely on the sun and moon for navigation, showcasing remarkable instincts rather than learned routes.
As they travel, they exhibit a cone-shaped migration pattern, particularly noticeable in Texas. When they reach their overwintering sites, they seek water and nectar while resting, conserving energy for the long journey ahead.
It's a fascinating and intricate process!
What Is so Unusual About the Monarch Butterfly Migration?
Imagine a living compass, guiding butterflies across thousands of miles.
What's so unusual about the monarch butterfly migration is its multi-generational journey; the butterflies that leave in the fall aren't the same ones that return in spring.
You'll find they rely on innate instincts, celestial cues, and remarkable energy efficiency to navigate.
This extraordinary migration, a natural spectacle, highlights the resilience and interconnectedness of life, making it truly one-of-a-kind in the animal kingdom.
Conclusion
To summarize, the migration of monarch butterflies is a remarkable journey that showcases their resilience and adaptability. Did you know that these butterflies can travel up to 3,000 miles from Canada to Mexico? This incredible feat highlights the significance of conservation efforts and community science in protecting their habitats. By supporting these initiatives, you're not just watching these beautiful creatures; you're playing an essential role in their survival and ensuring future generations can witness their breathtaking migration.